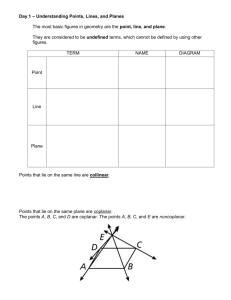
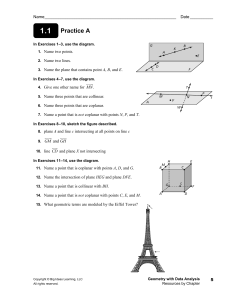
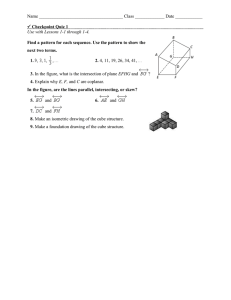
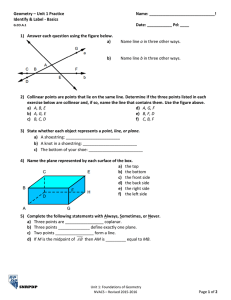
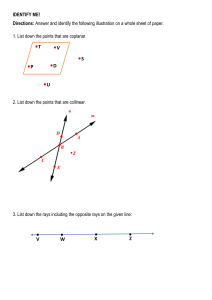
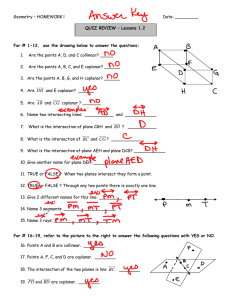
A Detailed Lesson Plan for Mathematics 7 I. Objectives At the end of the lesson, the students are expected to: a. describe the undefined terms; b. recognize the different kinds of points, lines, and planes and; c. name the identified point(s), line(s), and plane(s) in a given figure. II. Subject Matter a. Topic: Basic Concepts and Terms in Geometry b. Reference(s): Math Grade 7, Learners Material and Math for Life c. Instructional Materials: Projector, Laser, Laptop, Chalkboard, Visual Aids, and Motivational Chips III. Procedure Teacher’s Activity Learners’ Activity 1. Daily Routine 1.1 Greetings/Prayer “Class, please all stand up for our prayer. Mary Grace, lead the prayer.” “Good Morning class!” (The students will pray) “Good Morning Sir Delatina!” 1.2 Classroom Condition “Before you take your seats, kindly pick up the small pieces of papers and candy wrappers under your chairs.” (Now the teacher will check the attendance. Chairs that is not being occupied means the student(s) on the specified area(s) is/are absent.) 2. Recall “Class, can you recall our previous lesson?’ “Correct! How can you solve an absolute value equations and inequalities?’ “Very well-said!” “Last time sir, the discussion was all about Solving absolute value equations and inequalities.” “We can solve the absolute value of an equations and inequalities by following the steps and procedures to find a value on a given.” 3. Motivation (Group work) “Before we start, I will group you first into four groups. This area will be the group 1, this area will be the group 2, this area will be the group 3 and this area will be the group 4. Each group will receive an envelope that has 3 sets of jumbled letters inside. You are about to rearrange the jumbled letters inside the envelope that represent the things that we can see in our everyday living. Use the objects given as a clue to solve the jumbled letters. The group that could finish the activity first will receive a pack of chips as instant rewards. This activity will last 2 minutes only. Are we clear with that? “Good! Now you may start doing your activity” “Group 1 was the first group to finish the jumbled letters. Wilbert, can you tell to us the answers of your group? “Yes sir!” “The answer on the first set of jumbled letters is POINT” “The answer on the second set of jumbled letters is LINE” “The answer on the third set of jumbled letters is PLANE” 4. Lesson Proper “Your answers such as POINT, LINE, and PLANE will now lead us to our new topic for today, The Basic Concepts and Terms in Geometry” “Which among the following do you think is the best description a point?” a.) Any location in space represented by a dot and it has no dimension because it has no length, no width, nor thickness. b.) An idea that you try to make other people accept or understand. “Who wants to answer? Yes Nicole.” “Very Good Nicole!” “The correct answer is letter A” “We use capital letters to name a point.” ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ A B C D “Based on the definition, what do you think is the name of these points? Yes Regine.” “The name of the points on that figure is Point A, Point B, Point C, and Point D.” “Amazing! Can you think of example of an object that could represent a point inside our classroom? Yes Micaela” “Tip of ballpen” “Period in a sentence” Spectacular! “This figure is an example of a line. In naming a line, we use a lower case letter or any two points on the line. Therefore, the name of this line is line m or line RV. “On the next figure, what do you think are the possible names of the line? “The name of that line is line VI or line a.” “Kirstein what do you think?” “Exactly! Can you give me some objects that you think could represent a line?” “Yes Princess.” “Correct! What else, Dianne?” “Thread” “Electrical wires” “Marvelous! Let’s move on with plane.” “Which do you think is the best description of a plane?” a.) A plane is set of points in an endless flat surface. It is 2-dimensional, because it has length and width. b.) A plane is a tool for smoothing or shaping a wood surface. “What do you think is the correct answer, James?” “The correct answer is letter A.” “Correct! In naming a plane, we may use 3 coplanar points that lies on the same plane. In this figure, what do you think is the name of the plane?” “Yes Abigael?” “The name of that plane is plane WXY.” “Very Good! Next we have the other basic geometric terms on points and lines.” “The given illustrations are examples of collinear points.” “What do you think are collinear points? Yes Ashley?” “Absolutely! On the board, can you draw your own example of collinear points? Yes Shaira.” “Collinear points are points that lie on the same line” (A student will draw her example of collinear points.) “Good Work! The given illustrations are examples of coplanar points.” “What do you think is coplanar points? Yes Jezreel.” “Absolutely! Can you give me your own example of coplanar points? Please draw your example on the board, Martin.” “Very Good! Let’s proceed on coplanar lines.” “The figure shown is an example of coplanar lines” “Coplanar points are points that lie on the same plane.” (A student will draw his own example of coplanar points on the board.) “What do you think is a coplanar line?” Do you have any idea Reyciel? “Brilliant! “Can we consider our lines here as coplanar lines? What do you think Porsha?” “Coplanar lines are lines that lie on the same plane.” “No sir, because the lines are not on the same plane.” “Very Good! The next figure we have is an example of intersecting lines.” “What do you think is intersecting lines?” “Yes John Rey?” “Intersecting lines are lines that intersect at one point.” “Very well-said! Which among the following do you think could represent an intersecting lines?” a.) 11 b.) Cross c.) “B” “Yes Rodel, the correct answer is what?” “Right! The next figure is an example of parallel lines.” “What do you think are parallel lines? Yes Irish? Do you have any idea? “Letter B. Cross” “Parallel lines are lines that do not meet or intersect.” “Right! Can give me some examples of things that could represent parallel lines inside or outside the classroom? Yes Jerich? “The things that could represent parallel lines are the legs of a chair, window grills, and opposite sides of blackboard.” “Amazing! Next we have skew lines.” “Line AB and line CD are examples of skew lines. What do you think are skew lines? Arwen? “Very Good! On the board, can you draw another example of skew lines, Bryan?” “Skew lines are lines that do not lie on the same plane.” (A student will draw another example of skew lines.) “Great job!” 5. Application (Group work) Point: Corner of tiles Tip of hand clock Tip of pencil (The teacher will provide marker and worksheet on each group to answer) “Find as many objects as you can that could represent a point, intersecting lines, parallel lines, and plane in 5 minutes only. The group that will have the more correct objects will win and will receive a pack of motivational chips.” Line: Edge of tile Edge of blackboard Edge of the table Plane: Board Books Map Table Tile 6. Generalization “How can we name a point? Do you still remember Nicole? Draw an example of point on the board and give your idea about it.” (A student will draw her example of point on the board.) “We use capital letters to name a point.” “Correct! What is the difference between collinear points and coplanar points? Yes Jezreel. Draw an example of collinear points and coplanar points on the board and give your idea about it.” (A student will draw her example of collinear points and coplanar points on the board.) “The collinear points are points that lie on the same line while the coplanar points are points that lie on the same plane.” “Spectacular! What about a line? What is a line? Do you still remember Mary Grace? Draw an example of a line on the board and give your idea about it.” (A student will draw her example of a line on the board.) “A line is a set of points that goes on and on in both directions without end. It is also one dimensional because it has length.” “Right! What are coplanar lines Reyciel? Draw an example of coplanar lines on the board and give your idea about it.” (A student will draw her example of coplanar lines on the board.) “Coplanar lines are lines that lie on the same plane.” “Absolutely! What about intersecting lines Sophia? Draw an example of intersecting lines on the board and give your idea about it.” (A student will draw her example of intersecting lines on the board.) “Intersecting lines are lines that intersect at one point.” “Amazing! What are parallel lines? Yes Princess. Draw an example of parallel lines on the board and give your idea about it.” (A student will draw her example of parallel lines on the board.) “Parallel lines are lines that will not meet or intersect” “Marvelous! What about skew lines? Yes Irish. Draw an example of skew lines on the board and give your idea about it.” (A student will draw her example of skew lines on the board.) “Skew lines are lines that are not on the same plane.” “Good! What is a plane Martin? Draw an example of plane on the board and give your idea about it.” (A student will draw her example of plane on the board.) “A plane is a set of points in an endless flat surface. It is 2-dimensional, because it has length and width.” “Very Good! You did really understand our lesson well. Get your notebooks and do your seatwork.” IV. Evaluation Directions: Identify the following points and lines that are being described using the figure 1 shown. Write the letter of the best answer from the choices given. (10 items – 5 minutes) Figure 1 1. Point Q and point Y. a. collinear points b. coplanar points 2. Point T, point U, and point W. a. collinear points b. coplanar points 3. Line UW and line VX. a. parallel lines b. intersecting lines 4. Line TW and line JV. a. parallel lines b. intersecting lines 5. Line PI and line OC. a. coplanar lines b. intersecting line 6. Line IP and line RS. a. coplanar lines b. skew lines 7. Line NK and line RS. a. skew lines b. coplanar lines 8. Point J, point U, and point V. a. collinear points b. coplanar points 9. Line AG and line TU. a. coplanar lines b. parallel lines 10. Point M and point Z. a. collinear points b. coplanar points V. Assignment Given: The points A, B, C, D, E, F, G, and H are corners of a box shown below: Answer the following: 1. How many lines are possible which can be formed by these points shown above? (Hint: There are more than 20.) __________ 2. What are the lines that contain the point A? (Hint: There are more than 3 lines.) __________ 3. Identify the different planes which can be formed by these points shown above. (Hint: There are more than six) ___________ 4. What are the planes that contain line DC? __________ 5. What are the planes that intersect at line BF? __________ Prepared by: Vien E. Delatina Student Teacher, Mathematics 7 Checked by: Lysel P. Matiling Cooperating Teacher/Academic Coordinator Approved by: Levi P. Siazar OIC, Head Teacher VI