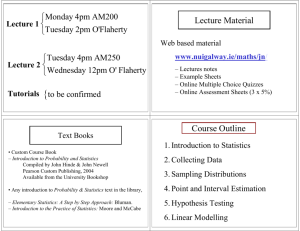
CQX7001 Research Methodology Prof. Dr. Noor Ismawati Jaafar Department of Decision Science Faculty of Business and Economics Universiti Malaya Ice Breaking Watch the movie trailer The Stanford Prison Experiment What can you briefly say about this movie trailer? 2 Learning Outcome • By the end of the session, you will be able to: • Understand the course requirements for CQX7001. • Identify the characteristics of a research and the types of research. • Understand the research process. 3 Activity 1 (5 minutes) • Go to www.menti.com and use the code provided 4 CQX 7001 Course Content Current course information from Spectrum Assessments Important date(s) Date 5 What is? 6 What is research? • Research is a “systematic investigation to find answers to a problem” (Burns, 1997, pg 2) • something that people undertake in order to find out things in a systematic way, thereby increasing their knowledge. • “Systematic Research” and “To find out things“ 8 Systematic • Suggests that research is based on logical relationships and not just beliefs. • Research will involve an explanation of the methods used to collect the data. • Will argue why the results obtained are meaningful. • Explain any limitations that are associated with them. 9 “To find out things” • Suggests there are a multiplicity of possible purposes for your research. • May include describing, explaining, understanding, criticising and analysing. • A clear purpose or set of ‘things’ that you want to find out, such as the answer to a question or number of questions. 10 Research • Research involves the collection of information. • More than just reading a few books or articles, talking to a few people or asking them questions. • Collecting data is part of the research process. 11 NOT RESEARCH • If it is not undertaken in a systematic way, on its own and in particular with a clear purpose, it will not be seen as research . • Data are collected, perhaps from a variety of different sources, and then assembled in a single document with the sources of these data listed. • No interpretation of the data collected. • While the assembly of data from a variety of sources may be part of the process of research, without interpretation it is not research. 12 Business Research Defined • Business research is the application of the scientific method in searching for the truth about business phenomena. • The process includes: • problem definition • searching for and collecting information • analyzing data • communicating the findings and their implications 13 How Evidence From Research Can Inform Practice • Decision makers use evidence to improve services or make processes more effective • Evidence-based practice is used to collect information to determine the appropriateness of practice taking into account: Evidence to deliver process/services effectively Critical judgement of service providers on suitability and appropriateness Consumer experience or preference Application of Research • Examine your own field. • Methodologists have developed research methods to understand your specific area. • There are many different procedures and techniques. • Reliability and validity depends on the soundness of the research methods adopted. Characteristics of research Data are collected systematically Data are interpreted systematically There is a clear purpose: To find things out 16 Types of Research 17 Basic & Applied Research Basic vs Applied Research Basic/Pure research is conducted Applied research is conducted without any specific goal. with a specific goal in mind. Aim The main aim is to advance knowledge. The main aim is to solve a specific and practical problem. Nature Basic research is exploratory in Applied research is descriptive in nature. nature. Theories and Principals Basic research identifies new ideas, theories, principals and new ways of thinking. Applied research is based on the theories, principals discovered through pure research. Findings Findings of basic research usually have a future use, not a current use. Findings of applied research always have a current use. 18 Research Process • research is a multi-stage process • The precise number of stages varies • include formulating and clarifying a topic, • reviewing the literature, • designing the research, • collecting data, • analysing data and • writing up. 19 Wish to do research Formulate and clarify your research topic Critically review the literature Formulate your research design Negotiate access and address ethical issues 20 Activity 2 (15 minutes) Go to www.menti.com and use the code provided 21 Stages of the Research Process 22 Planning the Research Design Research Design •A master plan that specifies the methods and procedures for collecting and analyzing the needed information. Basic design techniques : •Surveys •Interviews •Experiments •Secondary data •Observation Selection of the Basic Research Method •Survey •A research technique in which a sample is interviewed in some form or the behavior of respondents is observed and described. •Telephone •Mail •Internet •In person 24 Sampling Sampling •Involves any procedure that draws conclusions based on measurements of a portion of the population. Sampling decisions •Who to sample?—target population •What size should the sample be? •How to select the sampling units? •Random sample •Cluster-sample 26 Activity 3 (15 minutes) Go to www.menti.com and use the code provided 27 Summary • By the end of the session, you are able to: • Understand the course requirements for CQX7001. • Identify the characteristics of a research and the types of research. • Understand the research process. • Any question? 29 Learning Point Remember: Research is a process… 30 isma_jaafar@um.edu.my Thank you 31