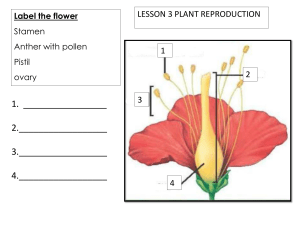
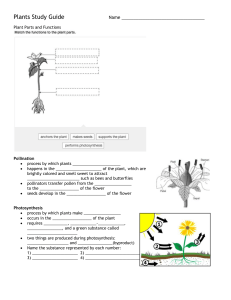
TYPES OF CROPS ACCORDING TO THEIR CATEGORIES I. FOOD CROPS primarily raise, culture, and harvest for human consumption. It has two subcategories, field crops and root crops. a. FIELD CROP grown on large scale for agricultural purposes wheat, rice, corn, sugarcane and other forage crops b. ROOT CROP are underground plant parts edible for human consumption cassava, potato, ginger, peanut, onion, carrot III. FEED CROP A plant that is primarily raised, culture and harvested for livestock consumption. oats IV. FIBER CROP A plant that is primarily raise, culture and harvest for its fibers which are used as raw material Abaca, silk, Pineapple IV. OIL CROP a plant that is primarily raise, culture and harvest as base for biodiesel production palm, coconut, soy bean V. ORNAMENTAL CROP for decorative purposes especially in gardens and landscape design projects. VI. INDUSTRIAL CROP cultured for their biological materials which are used in industrial processes into nonedible products. (Example: Tobacco) ACCORDING TO THEIR REPRODUCTION 1. SEXUAL plants that develop from a seed or a spore after undergoing union of male and female gametes POLLINATION the act of transferring pollen grains from the male anther of a flower to the female stigma. The goal of every living organism, including plants, is to create offspring for the next generation. One of the ways that plants can produce offspring is by making seeds. Parts of the Flower Parts of the Flower 1. Stamen- the male part which consists of: Anther- produces and holds up the pollen Filament- stalk that holds up the anther 2. Pistil - the female part which consists of the following: Stigma- catches pollen grains. Style- the neck of the pistil; the structure between the ovary and stigma Ovary- where the ovule resides Ovule- where the eggs are produces and seeds develop Parts of the Flower 3. Petals- highly colored part of the flower, may contain perfume and nectar glands. Corolla- the collection of petals in a flower. 4. Sepals- small green structures on the base that protect the flower bud Calyx- is a group of sepals 5. Pedicel- the stem of the flower Receptacle- the place where floral organs are attached and originate 2. ASEXUAL plants that reproduce by any vegetative means without the union of the sexual gametes. Grafting, buding, cutting ACCORDING TO MODE OF POLLINATION 1. NATURAL AND SELF POLLINATED CROP predominant mode of pollination in this plant is selfpollination. 2. NATURAL CROSS POLLINATED pollen transfer in these plants is from another of one flower in a separate plant. wind, water 3. BOTH SELF & CROSSPOLLINATION these plants are largely selfpollinated but in varying amounts. ACCORDING TO GROWTH HABITS 1. HERB succulent plants with selfsupporting stems basil, rosemary, oregano 2. VINES herbaceous climbing or twining plants without selfsupporting stem. 3. LIANAS woody climbing or twining plants which depend on other plants for vertical support to climb up to the tree. 4. SHRUB a small tree or tree like plants generally less than 5 meters in height but other authorities restricted to small, erect woody plants. 5. TREES plants having erect and continuous growth with a large develop of woody tissue, with a single distinct stem or trunk. 6. EVERGREEN plants that maintain their leaves throughout the year. 7. DECIDUOUS plants that naturally shed off or lose leaves annually for extended periods. Ficus virens ACCORDING TO THEIR LIFE SPAN 1. ANNUAL CROP a plant that completes its life cycle, from germination to production of seed, within one growing season, and then dies. Annual crops examples are rice, corn and others 2. BIENNIAL CROP a plant that takes two years to complete its biological lifecycle. Its examples are cabbage, parsley and others. 3. PERENNIAL CROP lives more than two years. with little or no woody growth from trees and shrubs, which are also technically perennials. Group Activity 1 Instruction: Using the table below identify the different crops in your locality according to their categories, classifications, and descriptions.