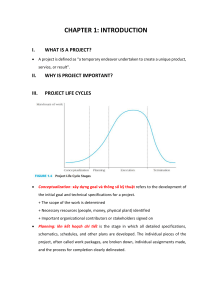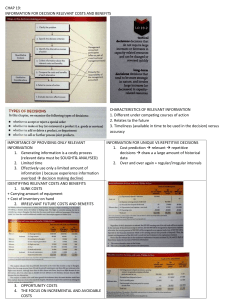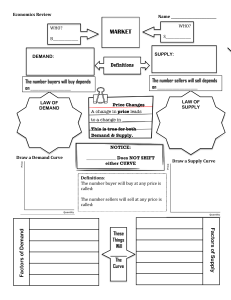
Assumptions: perfect competition (ko đc cộng price) 50 35 20 + price rise -> quantity demand fall price fall -> quantity demand rise price tăng -> mn đổ xô đi mua gold, stock, real estate P y=f(x) Qd = f(Px; Py; I; T; E; N;..) Px: the price of this good Py: the price of related good I: income of buyers E: Expectation of buyers T: taste of buyers N: number of buyers a P = Qd -b P = Qd -b /a -> inverse demand function Qd = aP+b (a<0) 50 = a*10+b 35 = a*20+b Then a =-1.5 (<0) and b = 65 Demand function is Qd = -1.5P + 65 P=-2/3Qd + 130/3 = change in quantity demanded only (not change in D) Caused by the change in Px -> movement along the D curve = change in D caused by Py; I, T, E, N Example: weather becomes hotter -> Qd increase at each price -> D increase -> D curve shift to the right P substitute rise -> D increase P subtitute decrease -> D decrease P pepsi rise -> Qd pepsi decrease -> Qd coke increase at each price -> D coke rise -> D coke shift to the right P complement increase -> D decrease P comliment decrease -> D increase Price printer increase -> Qd printer decrease -> Qd ink giảm at each P -> D ink giảm ->D ink shift to the left I tăng -> D tăng I giảm -> D giảm I tăng -> D giảm I giảm -> D tăng I Engel curve cho biết mối quan hệ thế nào giữa price và quantity demanded A. positive B. negative C. both D. none. -> D is correct Vì engel curve show mối qh giữa income và quantity demande Engel curve inferior good I normal good 0 Q N tăng -> D tăng N giảm -> D giảm 15 35 55 Qs = aP+b 15 = a*10+b 35 = a*20+b Then a=2 (>0) and b=5 Supply function is Qs = 2P-5 P i tăng -> Qs giảm at each price -> S giảm -> S curve shift to the left P Tax tăng. S2. S1 Subsidy tăng P <— 0 S2. S1 P1 —> Q 0 S1 P Q 0 Q1 Q