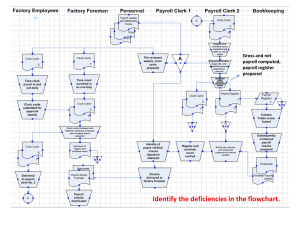
Accounting for Labor Chapter 3 LEARNING OBJECTIVES • Distinguish between the features of hourly rate and piece-rate plans. • Specify procedures for controlling labor costs. • Account for labor costs and payroll taxes. • Prepare accruals for payroll earnings and taxes. • Account for special problems in labor costing. Waqas Rehman (Lecturer) GIK Institute. School of Management Sciences. 2024 Issues • How can companies control labor costs in a highly competitive, global environment? • What incentive wage plans can be put in place to ensure that workers are compensated for providing value-added activity? • How should bonuses, holiday pay, and vacation pay be accounted for? Waqas Rehman (Lecturer) GIK Institute. School of Management Sciences. 2024 Factory payroll (Direct Labor vs Indirect labor) • Direct labor, also known as touch labor, represents payroll costs traced directly to an individual job. • Direct labor costs include the wages of machinists, assemblers, and other workers who physically convert raw materials to finished goods. • For example, a painter on the production line at the Toyota plant in Kentucky is a direct laborer. • The cost of direct labor is debited to Work in Process. Indirect labor consists of labor costs incurred for a variety of jobs related to the production process but not readily traceable to the individual jobs worked on during the period. Waqas Rehman (Lecturer) GIK Institute. School of Management Sciences. 2024 • Indirect labor costs include the salaries and wages of the factory superintendent, supervisors, janitors, clerks, and factory accountants who support all jobs worked on during the period. • For example, the plant manager of the Toyota manufacturing facility is an indirect laborer. Indirect labor costs are charged to Factory Overhead. For Service Industry • Example, auditors with a public accounting firm would be considered direct labor relative to the individual jobs that they worked on, whereas the salary of the managing partner would be indirect labor that should be allocated to all of the clients audited in determining the total cost of servicing clients. • Other examples of indirect labor in an accounting firm would include the human resources function, the technical support staff, and the secretarial function. Waqas Rehman (Lecturer) GIK Institute. School of Management Sciences. 2024 • The accounting system of a manufacturer must include the following procedures for recording payroll costs: 1. Recording the hours worked or quantity of output by employees in total and by job, process, or department. 2. Analyzing the hours worked by employees to determine how labor time is to be charged. 3. Charging payroll costs to jobs, processes, departments, and factory overhead accounts. 4. Preparing the payroll, which involves computing and recording employee gross earnings, withholdings and deductions, and net earnings. Waqas Rehman (Lecturer) GIK Institute. School of Management Sciences. 2024 Wage Plans • Incentive wage plan. • Hourly Rate Plan • a definite rate per hour for each employee. • computed by multiplying the number of hours worked in the payroll period by the established rate per hour. • widely used and is simple to apply. • Critics argue that it provides no incentive for the employee to maintain or achieve a high level of productivity. • Productivity is measured as the amount of output per hour of work. Waqas Rehman (Lecturer) GIK Institute. School of Management Sciences. 2024 • Piece-Rate Plan • A company that gives a high priority to the quantity produced by each worker should consider using an incentive wage plan, such as a piecerate plan, that bases earnings on the employee’s quantity of production. • The plan provides an incentive for employees to produce a high level of output, but • maximizing their earnings and also increasing the company’s revenue. • This plan may encourage employees to sacrifice quality in order to maximize their earnings, unless the plan is based on only the production of good units. Waqas Rehman (Lecturer) GIK Institute. School of Management Sciences. 2024 • Modified Wage Plans • Modified wage plans combine some features of the hourly rate and piece-rate plans. • Example: • a modified wage plan would be to set a base hourly wage that the company will pay if an employee does not attain an established quota of production. • If the established quota is exceeded, an additional payment per piece would be added to the wage base. • These variations occur because management wishes to minimize costs and maximize profits, while labor attempts to maximize employee earnings. Waqas Rehman (Lecturer) GIK Institute. School of Management Sciences. 2024 Waqas Rehman (Lecturer) GIK Institute. School of Management Sciences. 2024 Controlling Labor Cost • The timekeeping and payroll departments have the responsibility of maintaining labor records. • Automated timekeeping technology: magnetic cards to direct laborers who use them to ‘‘log on’’ and ‘‘log off’’ to specific job assignments. • computer sends this labor time information to the accounting department for preparation of the payroll and distribution of labor costs to the appropriate jobs. • The payroll function includes completing and maintaining the payroll records, the employees’ earnings records, and the payroll summaries. Waqas Rehman (Lecturer) GIK Institute. School of Management Sciences. 2024 Labor Time Records • shows the employee’s time spent on each job, as well as the time spent as indirect labor on machine repair. • Given the magnetic card-reading technology, the time record typically takes the form of a computer file. • a production supervisor should review the labor hours recorded on the time record for accuracy. • the time record is the source document for allocating the cost of labor to jobs or departments in the job cost ledger and factory overhead ledger. • The employer must compensate the employee for the time spent on assigned jobs. • When time is not fully utilized, the employer suffers a loss. Waqas Rehman (Lecturer) GIK Institute. School of Management Sciences. 2024 Payroll Function • primary responsibility is to compute the employees’ wages and salaries. • involves combining the daily wages, determining the total earnings, and computing deductions and withholdings for each employee. • Payroll is a function within a single accounting department, as opposed to being a separate department. • Also, many companies now outsource their payroll function to payroll preparation services. Waqas Rehman (Lecturer) GIK Institute. School of Management Sciences. 2024 Waqas Rehman (Lecturer) GIK Institute. School of Management Sciences. 2024 Waqas Rehman (Lecturer) GIK Institute. School of Management Sciences. 2024 Accounting for Labor Costs and Employers’ Payroll Taxes • For all regular hourly employees, the hours worked should be recorded on a labor time record. • The payroll department enters pay rates and gross earnings and forwards the reports to accounting. • Cost accountants examine the labor time records and charge the labor costs to the appropriate jobs or department and to factory overhead. • This analysis of labor costs is recorded on a labor cost summary • Salaried employees? Waqas Rehman (Lecturer) GIK Institute. School of Management Sciences. 2024 • The accounting department records the earnings on the labor cost summary and in factory overhead ledger accounts, because the salaried factory employees are supervisors and other factory managers who do not physically convert the raw materials to finished goods, and therefore their salaries are indirect labor. Work in Process . . .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27,950 Factory Overhead . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5,330 Payroll . . . . . . . . . . . . ... . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33,280 (Distributed payroll) Waqas Rehman (Lecturer) GIK Institute. School of Management Sciences. 2024 Waqas Rehman (Lecturer) GIK Institute. School of Management Sciences. 2024 • If an employee works beyond the regularly scheduled time but is paid at the regular hourly rate, the extra pay is called overtime pay. • If an additional rate is allowed for the extra hours worked, the additional rate earned is referred to as an overtime premium. • The premium pay rate is added to the employee’s regular rate for the additional hours worked. • The premium rate is frequently one-half the regular rate, resulting in a total hourly rate for overtime that is 150% of the regular rate. Waqas Rehman (Lecturer) GIK Institute. School of Management Sciences. 2024 Employers’ Payroll Taxes • Payroll taxes imposed on employers include social security tax and federal and state unemployment taxes. • Employers must periodically report and pay the taxes to the appropriate government agencies. • Employers who fail to file required reports or pay taxes due are subject to civil and, in some cases, criminal penalties. Waqas Rehman (Lecturer) GIK Institute. School of Management Sciences. 2024 • Federal Insurance Contributions Act (FICA) requires employers to pay social security taxes on wages and salaries equal to the amount withheld from employees’ earnings to FBR. • The employers and employees, therefore, share equally in the cost of the social security program. • FICA includes a tax to finance the Federal Old Age, Survivors, and Disability Insurance program (OASDI) and the Medicare program. • Federal Unemployment Tax Act (FUTA) requires employers to pay an established rate of tax on wages and salaries to provide for compensation to employees if they are laid off from their regular employment. Waqas Rehman (Lecturer) GIK Institute. School of Management Sciences. 2024 Accounting for Labor Costs The company maintains the following records: • Payroll record • Employee earnings records • General journal • General ledger • Job cost ledger • Factory overhead ledger the following general ledger accounts in accounting for labor costs: Cash, Work in Process, Wages Payable, FICA Tax Payable, Employees Income Tax Payable Federal Unemployment Tax Payable, State Unemployment Tax Payable, Health Insurance Premiums Payable, Payroll Factory Overhead, Sales Salaries, Administrative Salaries, Payroll Tax, Expense—Sales Salaries, Payroll Tax Expense— Administrative Salaries Waqas Rehman (Lecturer) GIK Institute. School of Management Sciences. 2024 Waqas Rehman (Lecturer) GIK Institute. School of Management Sciences. 2024 • a general journal entry records the payroll: • To record the payment of the net earnings to employees, the following entry must be made: Waqas Rehman (Lecturer) GIK Institute. School of Management Sciences. 2024 Waqas Rehman (Lecturer) GIK Institute. School of Management Sciences. 2024 • Special Labor Cost Problems • An employer may be required to account for a variety of labor-related costs that do not fall into the normal routine of accounting for payroll costs. • Special costs may include shift premiums, pensions, bonuses, and vacation and holiday pay. • Shift Premium • A work shift is defined as a regularly scheduled work period for a designated number of hours. • If a company divides each workday into two or three 8-hour shifts, the employees working on shifts other than the regular daytime shift may receive additional pay, called a shift premium. Waqas Rehman (Lecturer) GIK Institute. School of Management Sciences. 2024 Employee Pension Costs • Pension costs originate from an agreement between a company and its employee group, by which the company promises to provide income to employees after they retire. Defined benefit plan, • the amount of pension benefits paid to a retired employee is commonly based on the employee’s past level of earnings and length of service with the company. A defined contribution plan • specifies the maximum amount of contributions that can be made to the plan by employer and employee, but the amount of the pension benefits is tied to the performance of the company stock or other investments. Waqas Rehman (Lecturer) GIK Institute. School of Management Sciences. 2024 Bonuses • Employees may receive bonus pay for a variety of reasons, such as higher than usual company profits, exceeding departmental quotas for selling or production, or for any other achievement that the company feels merits additional pay. • Bonus plans may include some or all employees. The cost of bonuses is generally charged to the department in which the employee works. Vacation and Holiday Pay • is earned by the employee for daily service on the job over the course of the year. • the vacation cost is accrued throughout the year and assigned to the employee’s department. Waqas Rehman (Lecturer) GIK Institute. School of Management Sciences. 2024