Philippine Percentage Tax: Businesses & Transactions Guide
advertisement

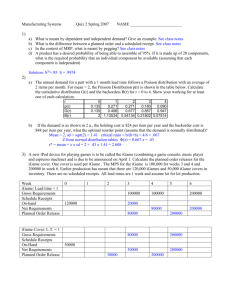
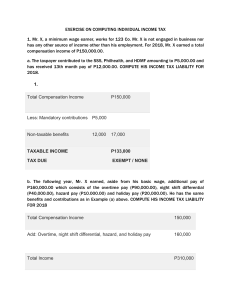
Businesses and Transactions Subject to Percentage Tax Percentage Tax Description Percentage Tax is a business tax imposed on persons, entities, or transactions specified under Sections 116 to 127 of the National Internal Revenue Code of 1997 (also known as Tax Code), as amended, and as required under special laws. It is imposed on the business entities not subject to value-added tax when the gross sales or receipts of the preceding taxable period are less than ₱3,000,000. Problem 1: Land Company, a taxpayer subject to percentage tax, had the following data for the second quarter of the year: Cash received from customers Receivables from customers Cash expenses incurred ₱800,000 450,000 520,000 How much are the gross receipts subject to percentage tax? Businesses subject to Percentage Tax 1.Business with gross annual sales of not ₱3,000,000 are subject to 3% percentage tax. more than 2. The following businesses are also subject to percentage tax: (a.) domestic carriers and keepers of garages; (b.) international air/shipping carriers doing business in the Philippines; (c.) franchise grantees; (d.) overseas communication from the Philippines; (e.) banks and non-banks financial intermediaries; (f.) other non-bank financial intermediaries; (g.) life insurance companies (h.) agents of foreign insurance companies; (i.) amusement places; and (j.) tax on winnings. Quarterly Percentage Tax Rates Table Quarterly Percentage Tax Rates Table Quarterly Percentage Tax Rates Table Quarterly Percentage Tax Rates Table Quarterly Percentage Tax Rates Table Quarterly Percentage Tax Rates Table Problem 2: Domestic carriers and keepers of garages Comfort Transport Company, a domestic common carrier, has a fleet of vehicles used to transport passengers and cargoes from Midsayap to Davao City. For February, the company had gross receipts of ₱500,000 from transporting passengers and ₱180,000 from transporting cargoes. What is the tax liability of the company? Solution: Value-Added Tax (₱180,000 x 12%) Common carrier tax (₱500,000 x 3%) Total business tax liability ₱21,600 ₱15,000 ₱36,600 Problem 3: International air/shipping carriers doing business in the Philippines Elegant Air Transport, an international air carrier, showed the following gross receipts during the second quarter of the taxable year: Point of Origin Singapore Philippines Philippines Point of Destination Australia China Iran Gross Receipts ₱900,000 1,200,000 700,000 Thirty percent (30%) of the shipments from the Philippines to Iran were later shipped from Iran to Turkey (transshipment). Required: Determine the percentage tax due. Solution: Gross receipts From Philippines to China ₱1,200,000 From Philippines to Iran (₱700,000 * 70%) 490,000 Total ₱1,690,000 Multiplied by 3% Common carrier tax ₱ 50,700 Problem 4: Franchise grantees Atlas Company, a business franchisee, reported the following gross receipts: Year 2022 ₱9,000,000 Year 2023 ₱11,000,000 Required: Determine the business tax liability of the taxpayer for years 2022 and 2023 assuming the business is a franchisee holder of: 1. Radio and/or television 2. Gas and water utilities Solution: Answer 1: Radio and/or television Year 2022: Percentage tax (₱9,000,000 x 3%) Year 2023: VAT (₱11,000,000 x 12%) ₱270,000 ₱1,320,000 Answer 2: Gas and water utilities Year 2022: Percentage tax (₱9,000,000 x 2%) Year 2023: Percentage tax (₱11,000,000 x 2%) ₱180,000 ₱220,000 Problem 5: Overseas communication from the Philippines During the current taxable quarter, Quick Telecommunication Company presented the following data on its gross receipts: Call Origin Call Destination Amount collected Philippines Philippines ₱6,000,000 Philippines Abroad ₱5,000,000 Determine the business tax liability of the company. Solution: Domestic calls (₱6,000,000 x 12%) Overseas calls (₱5,000,000 x 10%) Total business tax ₱720,000 ₱500,000 ₱1,220,000 Problem 6: Banks and non-banks financial intermediaries Orion Bank had the following interest receipts during the month: Source of Income Total Amount Interest income from loans maturing within 2 years ₱2,500,000 Interest income from loans maturing more than 2 years but within 5 years ₱1,000,000 Interest income on loans maturing more than 5 years ₱1,200,000 Processing fees ₱300,000 Rent income from foreclosed properties ₱200,000 Dividends income ₱50,000 Solution: The gross receipt tax of the bank shall be computed as follows: Interest on short term loans: Up to 2 year loans More than 2-5 year loans Total Tax Rates %Tax ₱2,500,000 1,000,000 ₱3,500,000 5% ₱175,000 Interest on long-term loans: More than 5 year maturity ₱1,200,000 1% 12,000 0% 0 7% 35,000 ₱222,000 Dividends ₱ 50,000 Other items of gross income: Processing fees ₱ 300,000 Rent Income 200,000 Total ₱ 500,000 Gross receipt tax Problem 7: Life insurance companies Great Insurance Company, a life and non-life insurance company, had the following gross receipts for June of the current taxable year: Fire and accident insurance: Cash payment received ₱300,000 Payments received through credit cards 250,000 Life insurance: Cash received Post-dated check received as payment of premium Determine the business tax liability. 400,000 200,000 Solution: Non-life insurance - VAT (₱550,000 x 12%) Life insurance - Percentage tax (₱600,000 x 2%) Total business taxes ₱66,000 12,000 ₱78,000 Problem 8: Agents of Foreign Insurance Mang Pandoy insured his buildings with a foreign insurer. He paid ₱150,000 premiums during the month. Determine the premium tax. Problem 9: Amusement places Jake is an operator of a disco (cabaret) and bowling alleys. During a particular quarter, it reported the following: Gate receipts Sales of foods and beverages Cabaret ₱200,000 800,000 Determine the total amusement tax. Bowling alleys ₱200,000 150,000 Solution: Gate receipts Sales of foods and beverages Total receipts from cabaret business Multiply: Amusement tax rates Amusement tax ₱200,000 800,000 ₱1,000,000 18% ₱ 180,000 Problem 10: Tax on winnings On March 12 of the current taxable period, Mr. V. Cruz spent his day at the horse track. He bought a ticket of ₱500 and placed his bet on the race horse “Shining Star” owned by Mr. S. Tomas. The race horse won and the price money for the ticket was ₱25,000 and that of the winning horse was ₱300,000. Required: Compute the business tax liability of: 1. Mr. V. Cruz; and 2. Mr. S. Tomas Solution: Answer 1: Tax liability of Mr. V. Cruz will be: Prize money won ₱25,000 Less: Cost of the ticket 500 Net ₱24,500 Multiplied by percentage tax rate 10% Amusement tax to be withheld by the owner of the race track ₱ 2,450 Answer 2: Tax liability of Mr. S. Tomas is completed as: Prize money won ₱300,000 Multiplied by percentage tax rate 10% Amusement tax to be withheld by the owner of the race track ₱ 30,000 EXEMPTION FROM PERCENTAGE TAX The percentage tax does not cover: 1. VAT taxpayers 2. Self-employed and or professionals who opted to the 8% income tax 3. Cooperatives Thank You!