Atomic Structure Worksheet: Bohr Model, Ionization, Electrons
advertisement

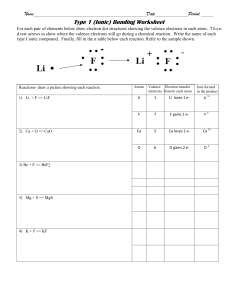
1)Describe the Bohr model of the atom?
Bohr model, atoms have a type of structure that consists of a central nucleus surrounded by
orbiting negative charge are called electrons. The nucleus consists of positively charged
particles called protons and uncharged particles called neutrons.
2)Discuss electron shells and orbits and their energy levels?
Each discrete distance (orbit) from the nucleus corresponds to a certain energy level. The
orbits are grouped into energy levels known as shells. The atom has a fixed number of shells.
Each shell has a fixed maximum number of electrons. The shells (energy levels) are
designated 1, 2, 3, and so on, with 1 being closest to the nucleus. The Energy between two
shells > The Energy between two orbits.
3)What is the difference between valence and conduction
electrons?
valence electrons are electrons with the highest energy exist in the outer shell of an atom and
are relatively loosely bound to the atom.
Conduction electrons are electrons that are free to move throughout the material and are
responsible for electrical conductivity.
4)Discuss the difference between positive and negative
ionization?
Positive ionization is the process of losing a valence electron and the resulting positively
charged atom.
Negative ionization is the reverse process that can occur in atoms when a free electron is
captured. The atom that has gotten the extra electron is called a negative ion.
5)Discuss the difference between the conductor, insulator, and
semiconductor materials? Show the energy band gap diagrams
for three materials?
Insulator is a material that:
* Does not conduct electrical current and
* has very high resistivity.
* Valence electrons are strong bound to the atom.
* Energy band gap is very large.
Conductor is a material that:
* Easily conducts electrical current.
* Has very low resistivity.
* Valence electrons are weak bound to the atom.
* Energy band gap is very small.
Semiconductor is a material that:
* Is between conductors and insulators in its ability to conduct electrical current.
* Has medium resistivity.
* Valence electrons are medium bound to the atom.
* Energy band gap is medium.
6)Define: Energy gap - atomic number – Doping – Ionization – PN
junction?
Energy gap is the difference in energy between the valence band and the conduction band.
This is the amount of energy that a valence electron must have to jump from the valence band
to the conduction band.
Atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus, which is the same as the number of
electrons in balanced (neutral) atom.
Doping Since semiconductors are poor conductors, their conductivity can be increased by the
controlled addition of impurities to the pure semiconductor’s material. This process is called
doping.
There are two main types of doping:
1/ N-Type Semiconductors {increases the number of current carriers (electrons)}.
2/ P-Type Semiconductors {increases the number of current carriers (holes)}.
Ionization When an atom absorbs energy from a heat source or from light, The valence
electrons can escape from the outer shell.
the process of losing a valence electron and the resulting positively charged atom.
the reverse process that can occur in atoms when a free electron is captured. The atom that
has gotten the extra electron is called a negative ion.
PN junction When you take a block of silicon and dope part of it with a trivalent impurity and
the other part with a pentavalent impurity, a boundary called the p-n junction is formed
between the resulting p-type and n-type portions. The p-n junction is the basis for diodes,
transistors, solar cells, and other devices. The free electrons near the junction in the n region
begin to diffuse across the junction into the p region where they combine with holes near the
junction.
7)Compare between Semiconductor and Conductor Atoms?
Silicon is a semiconductor and copper is a conductor.
The valence electron in the copper atom has an attractive force of +1 compared to a valence
electron in the silicon atom which has an attractive force of + 4.
There is more force trying to hold a valence electron to the atom in silicon than in copper.
The copper’s valence electron is in the fourth shell, which is a greater distance from its
nucleus than the silicon’s valence electron in the third shell. The electrons farthest from the
nucleus have the most energy.
The valence electron in copper has more energy than the valence electron in silicon. This
means that it is easier for valence electrons in copper to acquire enough energy to escape
from the atoms and become free electrons than it is in silicon.
8)Compare between Silicon and Germanium Atoms? (OR) Why
the silicon is the most widely used than Germanium?
The valence electrons in germanium are in the fourth shell while those in silicon are in the
third shell. This means that the germanium valence electrons are at higher energy levels than
those in silicon and require a smaller amount of additional energy to escape from the atom.
This property makes germanium more unstable at high temperatures, therefore the silicon is a
more widely used semiconductor material than germanium.
9)How are covalent bonds formed?
A silicon (Si) atom with its four valence electrons shares an electron with each of its four
neighbors. This effectively creates eight shared valence electrons for each atom and produces
a state of chemical stability. This sharing of valence electrons produces the covalent bonds
that hold the atoms together.
10)What is the difference between electron-hole pair generation
and Recombination?
Electron-Hole Pair Generation is the process that if any electron raised to the conduction band
by external energy, there is one hole left in the valence band.
Electron-Hole Pair Recombination is the reverse process that occurs when a conduction-band
electron loses energy and falls back into a hole in the valence band.
11)What is means the Carrier Concentration in Intrinsic
Semiconductor?
The electrons are called the majority carriers in N-Type material. Holes in an N-Type material
are called minority carriers.
The holes are the majority carriers in P-Type material. electrons in P-Type material are the
minority carriers.
12)What is the difference between electron and hole current?
Electron Current is the movement of free electrons in the Conduction Band of the
semiconductor.
Hole Current is the movement of holes in the Valence Band of the semiconductor.
13)How can increase the conductivity of the semiconductor
material?
by adding impurities to the intrinsic material.
14)What is the difference between intrinsic and extrinsic
semiconductors?
Intrinsic Semiconductors
An intrinsic semiconductor is a material in its pure form.
Extrinsic Semiconductors
Extrinsic semiconductors, also known as doped semiconductors, result from adding a small
amount of chemical impurity to an intrinsic semiconductor.
15)How is an n-type and p-type semiconductor formed?
N-type and P-type semiconductors are both created through a doping process. (adding impurities)
N-type:
To increase the number of conduction-band electrons in intrinsic silicon, pentavalent
impurity atoms are added. These are atoms with five valence electrons.
The resulting contains majority electrons and minority holes.
P-type:
To increase the number of holes in intrinsic silicon, trivalent impurity atoms are added. These
are atoms with three valence electrons.
The resulting contains majority holes and minority electrons.