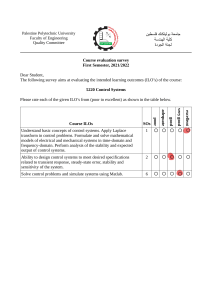
Programming in C language
Lecture 7:pointer in C
Omymah sarkez
Fall_2023
What are Pointers in C?
• Address in C
If you have a variable var in your program, &var will give you its address
in the memory.
• We have used address numerous times while using the scanf()
function.
scanf("%d", &var);
• The pointers storing the addresses of other variables
• [ char, int, function, array, or other pointers].
جامعة الزاوية كلية الهندسة _ قسم الحاسوب
How to Use Pointers?
• The use of pointers in C can be divided into three steps:
1.Pointer Declaration
2.Pointer Initialization
3.Pointer Dereferencing
جامعة الزاوية كلية الهندسة _ قسم الحاسوب
Pointer Declaration
In pointer declaration, we only declare the pointer but do not initialize it. To
declare a pointer, we use the ( * ) dereference operator before its name.
Example:
ptr
int *ptr;
int
• ptr is the name of the pointer.
• Int is the type of data it is pointing to.
• point to some random memory address
جامعة الزاوية كلية الهندسة _ قسم الحاسوب
Pointer Initialization
Pointer initialization is the process where we assign some initial value to the pointer
variable. We generally use the ( & ) address of operator to get the memory address of a
variable and then store it in the pointer variable.
Example
int var = 10;
int * ptr;
ptr = &var;
1
int *ptr = &var;
2
10
Int var
10
var
100
100
3
ptr
Int ptr
100
200
جامعة الزاوية كلية الهندسة _ قسم الحاسوب
Pointer Dereferencing
• Dereferencing a pointer is the process of accessing the value stored in
the memory address specified in the pointer. We use the same ( * )
dereferencing operator that we used in the pointer declaration
جامعة الزاوية كلية الهندسة _ قسم الحاسوب
#include <stdio.h>
void geeks()
{
int var = 10;
// declare pointer variable
int* ptr;
ptr = &var;
Example
var
10
0x7fff1038675c
ptr
0x7fff1038675c
printf("Value addres of var = %p \n", ptr);
printf("Value addres of var = %p \n", &var);
printf("Value at var = %d \n", var);
printf("Value at var = %d \n", *ptr);
printf("Value addres of ptr = %p \n", &ptr);}
int main()
{
geeks();
return 0;
}
Value addres of var = 0x7fff1038675c
Value addres of var = 0x7fff1038675c
Value at var = 10
Value at var = 10
Value addres of ptr = 0x7fff1038688B
جامعة الزاوية كلية الهندسة _ قسم الحاسوب
Types of Pointers in C
Pointers in C can be classified into many different types based on the parameter on
which we are defining their types.
• Integer Pointers :: point to the integer values
• Array Pointer :: pointer to its first element
char *ptr = &array_name;
• Function Pointers ::the pointer for this function int func (int, char) will be int (*ptr)(int, char);
• NULL Pointer :: that do not point to any memory location
Ptr = NULL
• Void Pointer :: they do not have any data type they can point to any type
جامعة الزاوية كلية الهندسة _ قسم الحاسوب
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int v[3] = { 10, 100, 200 };
Example
// Declare pointer variable
int* ptr;
// Assign the address of v[0] to ptr
ptr = v;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
// print value at address which is stored in ptr
printf("Value of *ptr = %d\n", *ptr);
// print value of ptr
printf("Value of ptr = %p\n\n", ptr);
// Increment pointer ptr by 1
ptr++;
}
return 0;
}
Value of *ptr = 10
Value of ptr = 0x7fff9a9e7920
Value of *ptr = 100
Value of ptr = 0x7fff9a9e7924
Value of *ptr = 200
Value of ptr = 0x7fff9a9e7928
جامعة الزاوية كلية الهندسة _ قسم الحاسوب
Relationship Between Arrays and Pointers
There is a difference of 4 bytes between two
consecutive elements of array x. It is because the size
of int is 4 bytes (on our compiler)
the address of &x[0] and x is the same. It's because the
variable name x points to the first element of the array.
From the above example, it is clear that &x[0] is equivalent to x. And, x[0] is
equivalent to *x.
Similarly,
•&x[1] is equivalent to x+1 and x[1] is equivalent to *(x+1).
•&x[2] is equivalent to x+2 and x[2] is equivalent to *(x+2).
•...
•Basically, &x[i] is equivalent to x+i and x[i] is equivalent to *(x+i).
جامعة الزاوية كلية الهندسة _ قسم الحاسوب
Pointers and Arrays
• in C, the name of an array, is actually a pointer to the first element of
the array.
• The memory address of the first element is the same as the name of
the array.
int myNumbers[4] = {25, 50, 75, 100};
int myNumbers[4] = {25, 50, 75, 100};
// Get the memory address of the myNumbers
array
printf("%p\n", myNumbers);
// Get the value of the first element in
myNumbers
printf("%d", *myNumbers);
// Get the memory address of the first array
element
printf("%p\n", &myNumbers[0]);
25
0x7ffe70f9d8f0
0x7ffe70f9d8f0
جامعة الزاوية كلية الهندسة _ قسم الحاسوب
1. To access the rest of the elements in myNumbers, you can
increment the pointer/array (+1, +2, etc) or loop
int myNumbers[4] = {25, 50, 75, 100};
// Get the value of the second element in
myNumbers
printf("%d\n", *(myNumbers + 1));
// Get the value of the third element in
myNumbers
printf("%d", *(myNumbers + 2));
50
75
int myNumbers[4] = {25, 50, 75, 100};
int *ptr = myNumbers;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
printf("%d\n", *(ptr + i));
}
25
50
75
100
جامعة الزاوية كلية الهندسة _ قسم الحاسوب
It is also possible to change the value of array elements with
pointers
int myNumbers[4] = {25, 50, 75, 100};
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
printf("%d\n", *(ptr + i));
}
// Change the value of the first element to 13
*myNumbers = 13;
// Change the value of the second element to 17
*(myNumbers +1) = 17;
25
50
75
100
----------------------13
17
75
100
for (i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++) {
printf("%d\n“ , *(ptr + i) ) ;
}
جامعة الزاوية كلية الهندسة _ قسم الحاسوب
END
جامعة الزاوية كلية الهندسة _ قسم الحاسوب