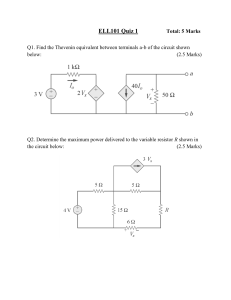
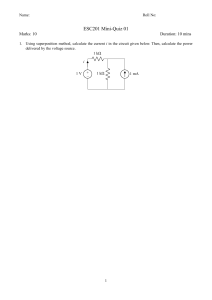
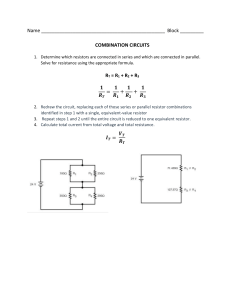
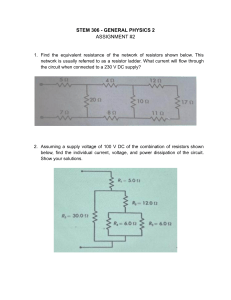
Questions Q1. (a) Diagram 1 shows a metal ball held at rest above the floor. The metal ball has a mass of 0.52 kg and is held at a height of 0.82 m above the floor. (i) State the formula linking gravitational potential energy (GPE), mass, g and height. (1) (ii) Calculate the decrease in the metal ball's GPE store when the ball falls to the floor from this height. (2) decrease in GPE store = ........................................................... J (iii) State the amount of energy in the metal ball's kinetic store just before it hits the floor. Ignore the effects of air resistance. (1) energy in kinetic store = ........................................................... J (iv) Calculate the speed of the metal ball just before it hits the floor. (4) speed = ........................................................... m/s (b) The metal ball is dropped from rest again from the same height above the floor, as shown in diagram 2. The metal ball now falls through a cylinder containing oil rather than the air. The speed of the ball just before it hits the floor when moving in oil is less than the speed of the ball just before it hits the floor when moving in air. Explain, using ideas about energy, the difference in speeds. (3) ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. (Total for question = 11 marks) Q2. A model electric motor is used to lift a load through a vertical height. (a) The load has a mass of 400 g and gains 3.2 J of energy in its gravitational store when lifted. (i) State the formula linking gravitational potential energy, mass, gravitational field strength (g) and height. (ii) Calculate the height the load is lifted. (1) (3) height = ........................................................... m (iii) State the amount of useful work done on the load by the motor when the load is lifted through this height. (1) work done = ........................................................... J (b) The load is lifted at a constant speed. Diagram 1 shows the lifting force acting on the load as it is lifted. Draw a labelled arrow on diagram 1 to show the other force acting on the load. Ignore the effects of air resistance. (2) (c) A joulemeter measures the amount of energy transferred electrically to the motor as the motor lifts the load. The joulemeter displays a reading of 11.0 J when the load has gained 3.2 J of energy in its gravitational store. (i) Calculate the efficiency of the motor. (3) efficiency = ........................................................... (ii) Justify why 7.8 J of energy must be dissipated into the thermal store of the surroundings as the load is lifted. (2) ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. (iii) Diagram 2 is an incomplete Sankey diagram. Complete the Sankey diagram to show the energy transferred by the motor. (3) (Total for question = 15 marks) Q3. This question is about a parachutist. (a) A parachutist leaves a helicopter that is hovering above the ground. The parachutist is initially at rest and falls vertically downwards. Calculate the speed of the parachutist after they have fallen through a distance of 1300 m. Ignore the effect of air resistance. (4) speed = ........................................ m/s (b) When the parachutist is much nearer to the ground, they open their parachute. The parachutist slows down. (i) Explain the change in speed of the parachutist. Use ideas about forces in your answer. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. (3) ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. (ii) It is observed that from when the parachute opens to just before the parachutist touches the ground, the GPE store and the KE store of the parachutist both decrease, yet energy is still conserved. Justify these observations. (3) ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. (Total for question = 10 marks) Q4. The driver of a racing car makes a pit stop during a race to change the tyres on the racing car. The area where the tyres are changed is called the pit lane. (a) Before entering the pit lane, the speed of the car must decrease for safety reasons. (i) The mass of the racing car is 830 kg. The maximum braking force is 41 000 N. Show that the maximum deceleration of the racing car is approximately 50 m / s2. (3) (ii) The racing car is travelling at an initial speed of 72 m / s. Calculate the minimum distance needed to decrease the speed of the racing car from 72 m / s to 26 m / s. (3) distance = ........................................................... m (b) The racing car slows down using its brakes. The brakes work using friction. The brakes become very hot when the racing car slows down. Using ideas about energy, explain why the brakes become hot. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. (3) ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. (c) The tyres of the racing car also get very hot during a race. A mechanic has to handle the hot tyres during the pit stop. They wear protective gloves which have several layers of insulating materials. Explain how the layers of insulating materials in the gloves reduce the risk of the mechanic burning their hands on the hot tyres. (2) ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. (Total for question = 11 marks) Q5. Diagram 1 shows a set of masses attached to a spring, which is suspended from a support. (a) After the masses are added, the length of the spring is 14.6 cm. The student measures the extension of the spring as 11.5 cm. (i) Calculate the original length of the spring. (1) original length = ........................................................... cm (ii) The student removes the masses and notices that the spring does not show elastic behaviour. Predict a value for the new length of the spring after the masses have been removed. (1) new length of spring = ........................................................... cm (b) The student puts the masses back on the spring. The student then pulls the masses down and releases them. The masses vibrate up and down in a vertical direction, as shown in diagram 2. The distance–time graph shows how the distance between the top of the masses and the support changes with time as the masses vibrate. (i) Explain how the gradient of the graph shows that the masses accelerate as they vibrate. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. (3) ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. (ii) Add crosses ( ) to the distance-time graph to show all the times when the masses are not moving. (2) (Total for question = 7 marks) Q6. A student does an experiment to determine the acceleration due to gravity, g. The diagram shows the apparatus used. This is the student's method. connect both light gates to a data logger drop a steel ball from rest at the top of the transparent tube record the speed of the ball at each light gate record the time taken for the ball to fall from light gate A to light gate B (a) The box shows the data recorded by the data logger. (i) 2 Show that the acceleration of the steel ball is approximately 9.6 m/s . (2) 2 acceleration = ........................................................... m / s (ii) Explain why the student's value for the acceleration of the steel ball is lower than the accepted value for the acceleration due to gravity, g. (2) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (iii) Calculate the distance between the light gates. (3) distance = ........................................................... m (b) The student changes the distance between the light gates by varying the position of light gate B. The student measures the time taken for the steel ball to fall from light gate A to light gate B when the light gates are different distances apart. The table shows the student's results. (i) Plot a graph of the student's results on the grid. (2) (ii) Draw the curve of best fit. (1) (iii) Explain how the graph shows that the steel ball is accelerating as it falls. (3) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (Total for question = 13 marks) Q7. The diagram shows a truck using a rope to pull a car along a level road. (a) The truck and car are travelling at a velocity of 14 m / s. The truck and car then accelerate at 1.6 m / s2 until they are travelling at a velocity of 22 m / s. (i) State the formula linking acceleration, change in velocity and time taken. (1) (ii) s. Calculate the time taken for the truck and car to accelerate from 14 m / s to 22 m / (3) time taken = ........................................................... s (iii) State the formula linking unbalanced force, mass and acceleration. (1) (iv) The car has a mass of 1200 kg. Calculate the unbalanced force acting on the car to produce an acceleration of 1.6 m / s2 . Give your answer to two significant figures. (3) unbalanced force = ........................................................... N (b) The rope breaks so the car and the truck are no longer connected. The engine of the car is not working. Explain what happens to the motion of the car after the rope breaks. (2) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (Total for question = 10 marks) Q8. A table tennis ball is a very light plastic ball filled with air. (a) A student drops a table tennis ball from rest. The ball falls 13 m to the ground. Show that the final speed of the ball, just before it reaches the ground, should be about 16 m/s. Assume that there is no air resistance. (3) (b) The student suggests that the ball will reach the ground with a speed that is less than 16 m/s because of air resistance. Use ideas about forces to justify the student's suggestion. (5) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (Total for question = 8 marks) Q9. The graph shows how the thinking distance and the braking distance vary with the speed of a car. (a) Which of these does not affect thinking distance? (1) A B C D (b) alcohol consumed by the driver condition of the road speed of the car tiredness of the driver Which of these would increase the braking distance of the car? (1) A B C D (c) faster reaction time of driver ice on the road more powerful brakes tyres with more grip Determine the stopping distance of the car when the speed of the car is 20 m / s. (3) stopping distance = ........................................................... m (d) (i) State the formula linking average speed, distance moved and time taken. (1) (ii) Determine the reaction time of the driver of the car. (3) reaction time = ........................................................... s (e) Calculate the mean braking acceleration of the car as it brakes to a stop from an initial speed of 30 m / s. (4) 2 acceleration = ........................................................... m / s (Total for question = 13 marks) Q10. When a meteor explodes, light waves and sound waves are produced at the same time. (a) (i) State the formula linking average speed, distance moved and time taken. (1) (ii) A person standing 1860 m away from the site of a meteor explosion hears the sound of the explosion 5.6 s later. Calculate the speed of sound in air. (2) speed of sound = ........................................................... m/s (iii) A scientist stands a long way from the meteor explosion. Explain why he hears the explosion at a different time to when he sees it. (2) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (b) Sound is a longitudinal wave. Describe what is meant by the term longitudinal wave. (2) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (c) In 2013, a meteor exploded above Russia. Just before the meteor exploded, it was travelling at a speed of 19.2 km/s. The mass of the meteor was estimated to be 1.25 × 107 kg. (i) State the formula linking kinetic energy, mass and speed. (1) (ii) Calculate the energy in the kinetic store of the meteor just before the meteor exploded. (2) energy in kinetic store = ........................................................... J (Total for question = 10 marks) Q11. A car is moving at a speed of 21 m/s. The driver of the car sees a hazard in the road and applies the brakes. (a) s. (i) Calculate the thinking distance if the driver of the car has a reaction time of 0.34 (3) thinking distance = ........................................................... m (ii) The braking distance of the car is 8.2 m. Calculate the stopping distance of the car. (2) stopping distance = ........................................................... m (b) (i) State the formula linking force, mass and acceleration. (1) (ii) The car has a mass of 780 kg and a braking force of 21 000 N. Calculate the acceleration of the car due to the braking force. (3) acceleration = ........................................................... m/s2 (Total for question = 9 marks) Q12. The diagram shows a velocity-time graph for a car from the time the driver sees an obstacle in the road until the car comes to rest. (a) (i) Calculate the acceleration of the car between 1.8 and 8.0 seconds. (3) acceleration = ........................................................... m/s2 (ii) Calculate the braking distance of the car. (3) braking distance = ........................................................... m (iii) Explain the effect, if any, of increased driver tiredness on the thinking distance and on the braking distance of the car. (4) thinking distance ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ braking distance ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (b) Which of these represents the distance-time graph for the car? (1) (Total for question = 11 marks) Q13. A car is moving along a road. (a) The car has an initial velocity of 26 m / s. 2 The car then accelerates at 1. 2 m / s until it reaches a velocity of 35 m / s. (i) State the formula linking acceleration, change in velocity and time taken. (1) (ii) Calculate the time taken for the car to accelerate to 35 m/s. (3) time = ........................................................... s (b) A radar speed gun is used to measure the speed of the moving car. The radar speed gun emits radio waves towards the moving car. The moving car reflects the radio waves back to a detector on the gun. The detected radio waves have a different frequency from the emitted radio waves. This change in frequency is used to measure the speed of the moving car. Explain this change in frequency when the car is moving towards the radar speed gun. (4) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (Total for question = 8 marks) Q14. A student does an investigation to show how the velocity of a toy car changes when the car rolls down a ramp onto a table and hits a wooden block. The graph shows how the velocity of the toy car changes with time. (a) Calculate the distance travelled by the car during the first 0.4 seconds. (4) distance = ........................................................... m (b) (i) Calculate the acceleration of the car between 0.40 s and 0.45 s. (3) 2 acceleration = ........................................................... m/s (ii) State the formula linking resultant force, mass and acceleration. (1) (iii) The car has a mass of 0.13 kg. Calculate the resultant force on the car as it slows down. (2) resultant force = ........................................................... N (c) A piece of soft material is fixed to the front of the toy car. Explain how this will affect the gradient of the velocity-time graph after the car hits the block. (3) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (Total for question = 13 marks) Q15. The diagram shows a truck travelling along a horizontal road. (a) (i) The driver sees an obstacle in the road and then applies the brakes. Which of these factors affects thinking distance? (1) A B C D (ii) condition of the tyres consumption of alcohol by the driver mass of the vehicle condition of the road Which of these factors affects both thinking distance and braking distance? (1) A B C D (b) (i) condition of the brakes condition of the road mass of the vehicle speed of the vehicle The truck experiences a braking force of 46 000 N. State the formula linking work done, force and distance moved. (1) (ii) The truck has 590 000 J of energy in its kinetic energy (KE) store before the driver applies the brakes. The braking force does work on the truck to reduce the KE store of the truck to 0 J. The braking distance is defined as the distance required for the KE store of the truck to reduce to 0 J when the brakes are applied. Calculate the braking distance of the truck. (3) distance = ........................................................... m (c) (i) The brakes increase in temperature when the truck is braking. State the name of the energy store that has increased for the brakes. (1) ............................................................................................. ................................................ (ii) State the method of energy transfer from the truck to the brakes. (1) ............................................................................................. ................................................ (Total for question = 8 marks) Q16. The diagram shows a circuit containing a light emitting diode (LED) and a resistor. (a) Add meters to the diagram to measure the voltage of the resistor and the current in the resistor. (3) (b) (i) State the formula linking voltage, resistance and current. (1) (ii) The current in the resistor is 7.3 mA. The voltage of the resistor is 0.92 V. Calculate the resistance of the resistor. (3) resistance = ........................................................... Ω (Total for question = 7 marks) Q17. The circuit diagram shows a resistor connected in series with a cell and a switch. There is an electric current in the circuit when the switch is closed. (a) Describe how another component could be added to the circuit to show that there is a current in resistor X when the switch is closed. (2) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (b) The electric current in the circuit is a flow of charged particles. Each charged particle has a charge of -1.6 × 10-19 C. (i) Give the name of the charged particle. (1) ............................................................................................. ................................................ (ii) When the switch is closed, the current in the cell is 160 mA. Calculate the number of charged particles that pass through the cell in 25 s. [charge transferred = current × time taken] (4) number of charged particles =............................................. (iii) Resistor X in the circuit is replaced by resistor Y. Resistor Y has a higher resistance than resistor X. Explain how the number of charged particles passing through the cell each second changes when resistor X is replaced by resistor Y. (3) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ Q18. The diagram shows a van der Graaff generator, which is designed to provide very high voltages. (a) (i) The unit of voltage is the volt. Which of these units is a volt? (1) A B C D (ii) coulomb per second joule per coulomb joule per second newton per coulomb State the formula linking energy transferred, voltage and charge. (1) (iii) Calculate the energy transferred to an electron when it passes through a voltage of 150 kV. [charge of electron = 1.6 × 10–19 C] (3) energy transferred = ........................................................... J (b) (i) –8 When the van der Graaff generator is fully charged, it stores 2.9 × 10 C of charge. State the formula linking charge, current and time. (1) (ii) The charge on the generator discharges through the air as a spark. The charge takes a time of 0.68 ms to leave the generator. Calculate the mean (average) current in the air. (3) mean current = ........................................................... A (Total for question = 9 marks) Q19. Diagram 1 shows a simple loudspeaker. The coil is connected to an alternating current (a.c.) supply. (a) Describe how the loudspeaker produces sound. (4) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (b) Diagram 2 shows two loudspeakers connected in series with a variable resistor. The variable resistor is set to 5.0 Ω. (i) The total voltage across the two loudspeakers is 0.75 V and the current in the circuit is 0.15 A. Show that the total power of the two loudspeakers is about 0.1 W. [power = current × voltage] (2) (ii) A student varies the resistance of the variable resistor. The table shows the power of the loudspeakers for different resistance values of the variable resistor. Plot the student's results on the grid. (3) (iii) Draw a curve of best fit. (2) (c) Diagram 3 shows the loudspeakers connected in series to a cell. Diagram 4 shows the loudspeakers connected in parallel to the same cell. Comment on how the total resistance of the loudspeakers in diagram 3 compares with the total resistance of the loudspeakers in diagram 4. (4) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (Total for question = 15 marks) Q20. The diagram shows an electric circuit containing component X and a lamp connected in series. (a) (i) Add another component to the diagram to measure the voltage of component X. (1) (ii) Give the name of component X. (1) ............................................................................................. ................................................ (b) The graph shows how the resistance of component X changes with light intensity. (i) Use the graph to determine the resistance of component X when the light intensity is 4.0 arbitrary units. (2) resistance = ........................................................... Ω (ii) The current in the circuit is 0.0018 A. Calculate the voltage across component X at a light intensity of 4.0 arbitrary units. (3) voltage = ........................................................... V (iii) Explain what happens to the brightness of the lamp when component X is covered with a dark sheet of paper. (2) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (Total for question = 9 marks) Q21. A teacher uses this circuit to investigate how the current in a circuit changes with the temperature of a room. (a) (i) Calculate the voltage across the thermistor. (2) voltage = ........................................................... V (ii) State the formula linking voltage, current and resistance. (1) (iii) Calculate the resistance of the thermistor. (3) resistance = ........................................................... Ω (b) (i) The graph shows how the resistance of the thermistor changes with temperature. Describe the relationship between the temperature and the resistance of the thermistor. (2) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (ii) Explain how the reading on the voltmeter changes when the temperature of the room decreases. (3) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (Total for question = 11 marks) Q22. The diagram shows a circuit that includes a battery, an ammeter, a voltmeter and three different resistors. (a) (i) Give the voltmeter reading. (1) voltage = ........................................................... V (ii) State the formula linking voltage, current and resistance. (1) (iii) Calculate the resistance of resistor X. (3) resistance = ........................................................... Ω (b) (i) Give the reason why the reading on the ammeter would be 16 mA. (1) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (ii) Calculate the resistance of resistor Y. (4) resistance = ........................................................... Ω (c) Resistor X and the voltmeter are removed from the circuit, leaving a break in this part of the circuit. Explain how the current in the battery changes when these components are removed. (2) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (Total for question = 12 marks) Q23. The circuit diagram shows a light dependent resistor (LDR) and a 73 Ω resistor connected in series with a 1.5 V cell. (a) Complete the diagram by adding an instrument to measure the voltage of the LDR. (2) (b) (i) State the formula linking voltage, current and resistance. (1) (ii) The current in the circuit is 7.8 mA. Calculate the voltage across the 73 ohm resistor. (2) voltage across resistor = ........................................................... V (iii) Calculate the voltage across the LDR. (2) voltage across LDR = ........................................................... V (c) (i) The graph shows how the resistance of the LDR changes with light intensity. Describe the relationship between the resistance of the LDR and light intensity. (2) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (ii) The resistance of the LDR decreases. State the effect on the current in the circuit. (1) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (iii) Explain why the voltage across the LDR decreases when the resistance of the LDR decreases. (2) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (Total for question = 12 marks) Q24. The circuit diagram shows a resistor, R, connected to a cell. (a) Draw additional components on the circuit diagram to measure the voltage of the resistor and the current in the resistor. (3) (b) (i) The voltage across the resistor is 9.00 V and the current in the resistor is 1.91 mA. State the formula linking power, current and voltage. (1) (ii) Calculate the power dissipated by the resistor. (2) power = ........................................................... W (c) The cell in the circuit is a source of direct current. State what is meant by the term direct current. (1) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (d) Explain how the current in the circuit changes when an identical resistor is connected in series with resistor R. (2) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (Total for question = 9 marks) Q25. A 12 V battery is connected to a component, X, and a fixed resistor, R, as shown (a) (i) State the name of component X. (1) ............................................................................................. ................................................ (ii) (b) Draw a voltmeter on the circuit diagram connected to show the voltage of component X. (2) The voltage across component X is 12 V. The resistor R has a value of 840 Ω. Show that the current in ammeter A1 is approximately 0.01 A. Use the equation voltage = current × resistance (2) (c) When the circuit is placed in daylight, the current in A2 is 0.011 A. (i) Calculate the value of the current through A3. (1) current = ........................................................... A (ii) room. Explain what happens to the current through A3 when the circuit is placed in a darkened (2) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (Total for question = 8 marks) Q26. A student investigates how the resistance of a lamp varies as the current is changed. She sets up the circuit shown. (a) Give a reason why component R is included in the circuit. (1) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (b) The student draws a graph of his results. (i) Describe how the current in the lamp changes as the voltage changes. Use data from the graph to support your answer. (3) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (ii) State the relationship between voltage, current and resistance. (1) ............................................................................................. ................................................ (iii) Calculate the resistance of the lamp when the voltage is 2.5 V. (3) resistance = ........................................................... Ω (c) State what happens to the resistance of a lamp when the current increases. (1) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (Total for question = 9 marks) Q27. Diagram 1 shows a light-emitting diode (LED) and a resistor in series with a cell and an ammeter. (a) The voltage across the LED is 0.63 V. Calculate the current in the circuit. Give your answer in milliamps. (4) current = ........................................................... mA (b) Diagram 2 shows a second LED and an extra resistor connected in parallel with the cell. The resistor and the LED are the same as the components used in diagram 1. The two resistors are identical and the two LEDs are identical. Explain how the ammeter reading will change. (4) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (Total for question = 8 marks) Q28. The circuit diagram shows a 9.0 V battery connected in series with a 250 Ω resistor and another resistor, X. (a) Draw a voltmeter on the circuit diagram to measure the voltage of resistor X. (2) (b) The current in the circuit is 0.012 A. Calculate the resistance of resistor X. (4) resistance = ........................................................... Ω (Total for question = 6 marks) Q29. The diagram shows an electric circuit. (a) When the thermistor is in hot water, its resistance is 490 Ω. Show that the resistance of the fixed resistor is about 400 Ω. (5) (b) Explain how the voltage across the fixed resistor changes when the hot water is replaced with cold water. (3) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (Total for question = 8 marks) Q30. The diagram shows part of a circuit used for an outdoor lighting system. (a) Draw a voltmeter on the diagram to measure the voltage of the 4500 Ω resistor. (2) (b) Give the name of component X. (1) ............................................................................................. ................................................ (c) (i) The voltage across component X is 3.0 V. Calculate the voltage across the 4500 Ω resistor. (1) voltage = ........................................................... V (ii) Calculate the current in the circuit. [voltage = current × resistance] (2) current = ........................................................... A (iii) Calculate the resistance of component X. Give your answer in kΩ. (3) resistance = ........................................................... kΩ (d) Explain where a lamp should be connected in this circuit, so that the voltage across it increases as the light received by component X decreases. (3) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (Total for question = 12 marks) Q31. This question is about waves. (a) (i) The diagram represents a wave. Determine the amplitude of the wave by measuring it with a ruler. (1) amplitude = ........................................................... cm (ii) Determine the wavelength of the wave by measuring it with a ruler. (1) wavelength = ........................................................... cm (b) (i) Microwaves are part of the electromagnetic spectrum. Name the part of the electromagnetic spectrum that has a lower frequency than microwaves. (1) ............................................................................................. ................................................ 8 (ii) Microwaves travel at a speed of 3.0 × 10 m / s in air. A microwave has a wavelength of 2.7 cm. Calculate the frequency of this microwave. [wave speed = frequency × wavelength] (3) frequency = ........................................................... Hz (c) A student uses a microwave source and a receiver to investigate microwaves. Photograph 1 shows how the student sets up their apparatus. The meter shows the strength of the microwaves detected by the receiver. The strength of the microwaves is measured in arbitrary units. The student varies the distance between the microwave source and the receiver, and records the meter readings. (i) Photograph 2 shows the analogue meter for one of the readings. Give the reading on the analogue meter. (1) reading = ........................................................... arbitrary units (ii) The graph shows the results of the student's investigation. The student concludes that the meter reading is inversely proportional to the distance between the microwave source and the receiver. To be inversely proportional meter reading × distance = constant Comment on the student's conclusion. You should use data from the graph in your answer. (4) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (Total for question = 11 marks) Q32. The photograph shows an x-ray image of a person's knee. The person has had part of their knee replaced. (a) X-rays are part of the electromagnetic spectrum. All electromagnetic waves are transverse waves and transfer energy. (i) State another property that all electromagnetic waves have in common. (1) ............................................................................................. ................................................ (ii) State a harmful effect of excessive exposure to x-rays. (1) ............................................................................................. ................................................ (iii) Describe the difference between transverse waves and longitudinal waves. You may draw a diagram to help your answer. (3) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (b) The diagram shows a part of the knee called the patella. The patella has been removed from a person's knee. The patella is a small, irregularly shaped bone that is denser than water. Describe how to find the mass and the volume of the patella bone. (4) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (c) A scientist finds the volume and mass of a patella. The mass of the patella is 17 g. 3 The volume of the patella is 13 cm . Calculate the density of the patella. Give your answer to 2 significant figures. (4) density = ........................................................... g / cm3 (Total for question = 13 marks) Q33. (a) Diagram 1 shows water waves just before they reflect off the side of a stationary boat. (i) Draw the normal at the point where the direction of travel of the waves meets the side of the boat. (1) (ii) Measure the angle of incidence of the water waves. (1) angle of incidence = .......................... degrees (iii) Complete the diagram to show the wavefronts after they reflect off the side of the boat. (3) (b) The boat starts to move, creating its own waves on the surface of the water. (i) Surface water waves are transverse. Describe the difference between transverse waves and longitudinal waves. (2) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (ii) Diagram 2 shows the boat moving towards an observer. Explain why the frequency of the water waves measured by the observer is larger than the frequency of the water waves created by the boat. (3) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (Total for question = 10 marks) Q34. Answer the question with a cross in the box you think is correct . If you change your mind about an answer, put a line through the box and then mark your new answer with a cross . The diagram shows the path of a ray of light. (a) (i) Measure the angle of incidence for the ray at point K. Which of these is the angle of incidence? (1) A B C D (ii) 43° 47° 51° 55° State the formula linking refractive index, angle of incidence and angle of refraction. (1) (iii) The block has a refractive index of 1.52 Use the formula to show that the angle of refraction is about 30° for the ray at point K. (3) (b) (i) The refractive index of the block is 1.52 Calculate the critical angle of the block. (3) (ii) State what happens to the ray at point L. (1) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (Total for question = 9 marks) Q35. Diagram 1 shows a ray of violet light entering a prism. (a) (i) Calculate the angle of refraction for the violet light. (1) angle of refraction = ........................................................... degrees (ii) State the formula linking refractive index, angle of incidence and angle of refraction. (1) (iii) Calculate the refractive index of the prism for violet light. Give your answer to 2 significant figures. (3) refractive index = ........................................................... Diagram 2 shows rays of red light and violet light entering the same prism. Red light has a longer wavelength than violet light. (b) Deduce a possible relationship between the wavelength and the refractive index for colours of the visible spectrum. (3) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (Total for question = 8 marks) Q36. The diagram shows the apparatus used to demonstrate the existence of electromagnetic radiation just beyond the visible spectrum. Electromagnetic radiation from the Sun passes through a slit and a prism. The electromagnetic radiation refracts through the prism onto the screen. Five thermometers are placed in front of the screen. (a) Complete the table to show the missing parts of the electromagnetic spectrum. (3) (b) Suggest why the lower part of each thermometer should be painted black. (2) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (c) The equipment is left for a short period of time. The thermometers now show higher temperatures than before. State the part of the electromagnetic spectrum in this demonstration that would give the largest temperature increase. (1) ............................................................................................. ................................................ (Total for question = 6 marks) Q37. This question is about electromagnetic waves. (a) Draw a straight line from each electromagnetic wave to its correct use. One has been done for you. (4) (b) State a hazard to humans of excessive exposure to infrared waves. (1) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (c) State a precaution that would reduce a person's risk of exposure to ultraviolet waves. (1) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (Total for question = 6 marks) Q38. This question is about refraction. (a) State what is meant by the term refraction. (1) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (b) The diagram shows a ray of light from a torch incident on the surface of a pool of water. The angle of refraction of the ray of light is 33° (i) Draw the path of the ray of light in the water. (ii) (iii) (2) State the formula linking refractive index, angle of incidence and angle of refraction. (1) Show that the refractive index of water is about 1.3 (2) (c) The torch is moved below the surface of the water. Light from the torch is incident on the water surface at an angle greater than the critical angle. (i) Explain the meaning of the term critical angle. You may draw a diagram to help your answer. (2) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (ii) State the formula linking critical angle and refractive index. (1) (iii) Calculate the critical angle of water. Assume the refractive index of water is 1.3 (3) critical angle = ........................................................... ° (iv) A ray of light leaves the torch as shown in the diagram. Complete the path of the ray of light. (2) (Total for question = 14 marks) Q39. X-rays and gamma rays are examples of ionising radiation. (a) Which of these is another example of ionising radiation? (1) A B C D (b) infrared microwave radio ultraviolet Give one use of x-rays and one use of gamma rays. (2) x-rays ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ gamma rays ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (c) (i) State the formula linking speed, frequency and wavelength of a wave. (1) (ii) Calculate the wavelength of a gamma ray with a frequency of 2.8 × 1019 Hz. [speed of gamma ray = 3.0 × 108 m/s] (3) wavelength = ........................................................... m (d) X-rays and gamma rays are electromagnetic waves. Which of these graphs is correct for waves travelling at a constant speed? (1) (Total for question = 8 marks) Q40. This is a question about light. (a) State what is meant by the term critical angle. You may include a diagram to help your answer. (2) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (b) The photograph shows a pair of binoculars. The diagram shows a cross-section through one half of a pair of binoculars. There are two glass prisms inside this half of the pair of binoculars. Complete the path of the light ray as it travels through this half of a pair of binoculars to the eye. [critical angle of glass = 42°] (3) (Total for question = 5 marks) Q41. Answer the question with a cross in the box you think is correct . If you change your mind about an answer, put a line through the box and then mark your new answer with a cross . This is a question about reflection. (a) Which diagram shows a light ray correctly reflected from a mirror? (1) (b) Name the equipment needed to measure the angle of incidence on a ray diagram. (1) ............................................................................................. ................................................ (c) Light from a laser on the Earth reflects off special mirrors on the Moon. The graph shows the data from a light sensor attached to the laser. The first peak shows when the light leaves the laser and the second peak shows when the light has returned from the Moon. (i) Determine the time taken for the light to travel from the Earth to the Moon and back again. (2) time taken = ........................................................... s (ii) The speed of light is 3.0 × 105 km/s. Calculate the total distance travelled by the light from the laser. [average speed = distance moved ÷ time taken] (2) total distance = ........................................................... km (iii) Calculate the distance from the Earth to the Moon.(1) distance = ........................................................... km (Total for question = 7 marks) Q42. The diagram shows the forces acting on a firework at take-off. (a) (i) Calculate the magnitude of the resultant force on the firework. (1) magnitude of resultant force= ........................................................... N (ii) State the formula linking resultant force, mass and acceleration. (1) (iii) The mass of the firework is 160 g. Calculate the acceleration of the firework. (3) acceleration = ........................................................... m/s2 (iv) Explain how the acceleration of the firework changes between take-off and running out of fuel. You can assume that the thrust force stays the same as the firework burns the fuel. (3) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (b) The firework makes a sound with constant frequency. As the firework moves upwards, people on the ground notice that the frequency of the sound they hear changes. This is called the Doppler effect. Explain how the Doppler effect causes the observed frequency of sound to change for the people on the ground. (4) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (Total for question = 12 marks) Q43. The diagram shows a ray of light travelling from air into glass. (a) Use a protractor to determine the angle of refraction. (1) angle of refraction = ........................................................... degrees (b) State the formula linking refractive index, angle of incidence and angle of refraction. (1) (c) Calculate the refractive index of this glass. (3) refractive index = ........................................................... (Total for question = 5 marks) Q44. A student does an investigation to determine the refractive index of a block made from flint glass. (a) She directs a ray of red light at the block, as shown in diagram 1. (i) Some of the light is reflected from the surface of the block at point A. On diagram 1, draw this reflected ray of light. (1) (ii) Use a protractor to determine the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction of the red light at point A on diagram 1. (2) angle of incidence = ........................................................... degrees angle of refraction = ........................................................... degrees (iii) State the formula linking refractive index, angle of incidence and angle of refraction. (1) (iv) Calculate the refractive index of the glass for red light. (2) refractive index = ........................................................... (v) Describe how the student could improve her investigation to obtain a more reliable value of the refractive index. (3) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (b) The student replaces the red light with a blue light. Diagram 2 shows a ray of blue light directed at point A, at the same angle of incidence as the previous ray of red light. The dashed lines on diagram 2 show the previous path of the ray of red light. The refractive index of flint glass for blue light is higher than the refractive index of flint glass for red light. Complete diagram 2 by drawing the path of blue light from point A until it passes into air. (3) (Total for question = 12 marks) Q45. (a) The diagram shows a fishing boat fitted with a high frequency sound wave emitter. The boat is above some fish. The high frequency sound waves travel from the emitter to the fish and then back to the emitter, where they are detected. (i) Name the wave behaviour that causes the sound waves to change direction when they reach the fish. (1) ............................................................................................. ................................................ (ii) The table gives some data about the sound waves used. Calculate the distance between the sound wave emitter and the fish. (4) distance = ........................................................... m (b) High frequency sound waves decrease in amplitude as they travel through soft tissue in the human body. The graph shows this decrease in amplitude for three different high frequency sound waves. (i) Estimate the distance travelled by a 2 MHz wave when its amplitude is 25% of its original value. (1) distance = ........................................................... cm (ii) Describe what the graph shows about the penetrating ability of high frequency sound waves as they travel through soft tissue. (3) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (Total for question = 9 marks) Q46. A helicopter is stationary above the ground. A bag of sand is dropped from the helicopter. (a) (i) The bag falls 6.3 m. The mass of the bag is 19 kg. Calculate the gravitational potential energy (GPE) change for the bag. [GPE change = mass × gravitational field strength × height change] (2) GPE change = ........................................................... J (ii) State the kinetic energy (KE) gained by the bag after falling 6.3 m. You can ignore the effects of air resistance. (1) KE gained = ........................................................... J (b) Closer to the ground, the effects of air resistance cannot be ignored. The bag travels at a constant speed when the air resistance equals the weight of the bag. The bag has a mass of 19 kg. Calculate the value of the air resistance when the bag travels at constant speed. (2) air resistance = .............................................................. N (c) The bag hits the ground and stops without bouncing. The Sankey diagram shows energy transfers for the bag from just before the bag hits the ground to when the bag stops. Use words from the box to complete the labels A, B and D. Label C has been done for you. Each word may be used once, more than once or not at all. (3) A: energy transferred mechanically from the bag's .............................................................. store B: energy transferred mechanically to the bag's .............................................................. store C: energy transferred mechanically to the ground's thermal store D: energy transferred .............................................................. to the surroundings (Total for question = 8 marks) Q47. A light bulb used in homes converts electrical energy into light energy. The input power of the light bulb is 52 W. The efficiency of the light bulb is 5.0%. Calculate the amount of light energy output by the lamp in 9.0 hours of use. light energy output = ........................................................... J (Total for question = 4 marks) Q48. The photographs show two different breeds of cat. Cat X has no fur and light-coloured skin. Cat Y has thick, black fur. Both cats have the same body temperature and transfer energy to their surroundings when they are outside on a cold day. Compare how cat X and cat Y transfer energy to their surroundings. Refer to conduction, convection and radiation in your answer. (6) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (Total for question = 6 marks) Q49. The chart shows the efficiencies of different methods of generating electricity. (a) The chart shows that the geothermal power station has an efficiency of 15%. Explain what is meant by an efficiency of 15%. (2) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (b) A small hydroelectric power station has a useful energy output of 6.0 kJ. Calculate the total energy input for this power station using information from the chart. (4) total energy input = ........................................................... kJ (c) (i) Name a fuel used in the reactor of a nuclear power station. (1) ............................................................................................. ................................................ (ii) These sentences describe the process of nuclear fission. Complete these sentences by writing a suitable word in each blank space. (5) A nucleus absorbs a ........................................................................................ ..... . The nucleus formed splits because it is ....................................................................................... ...... . The nucleus splits into two smaller nuclei called ................................................................................... .......... nuclei and two or three .................................................................................... ......... . The energy released is transferred into the ...................................................................................... ....... energy store of the fission products. (Total for question = 12 marks) Q50. The diagram shows a skier of weight 830 N skiing down a very steep slope. The skier starts from rest at point T. The force of gravity accelerates him down the slope. (a) When he reaches point B his kinetic energy is 5.5 × 104 J. State the gravitational potential energy of the skier at T. You should assume there is no friction on the slope. (1) gravitational potential energy = ........................................................... J (b) The skier stops at point P due to friction. The distance from B to P is 73 m. (i) State the relationship between work done, force and distance moved in the direction of the force. (1) ............................................................................................. ................................................ (ii) Calculate the mean frictional force as the skier moves from B to P. (3) mean force = ........................................................... N (Total for question = 5 marks) Q51. (a) The boxes give some situations and some energy stores. Draw one straight line from each situation to the energy store that decreases for that situation. The first one has been done for you. (4) (b) (i) Energy is transferred when a filament lamp is connected to a battery. Which method of energy transfer takes place between the battery and the lamp? (1) A B C D electrical heating mechanical radiation (ii) Which method of energy transfer takes place between the lamp and the surroundings? (1) A electrical B light radiation C mechanical D sound radiation (Total for question = 6 marks) Q52. Answer the question with a cross in the box you think is correct . If you change your mind about an answer, put a line through the box and then mark your new answer with a cross . A student investigates four cars P, Q, R and S. (a) How is energy transferred usefully from the engine of a car to its wheels? (1) A B C D (b) by heating by radiation electrically mechanically The engine of a car burns petrol, which transfers energy usefully from the chemical store of the petrol to the kinetic store of the car. The useful power output of car P's engine is 47 kW. (i) Calculate the useful energy output of car P's engine during a 15 minute period. (3) useful energy output = ........................................................... J (ii) State the formula linking efficiency, useful energy output and total energy output. (1) (iii) During the 15 minute period, 2.0 × 108 J of energy is transferred from the chemical store of the petrol. Calculate the efficiency of car P's engine. (2) efficiency = ........................................................... (c) The student extends her investigation by collecting data for cars P, Q, R and S. She records the useful power output of their engines, their masses and their maximum speeds. The table shows her data. Using information from the table, discuss the relationships between useful power output, mass and maximum speed. (4) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (Total for question = 11 marks) Q53. The photograph shows a toy car. When the toy car is pulled backwards, energy is stored in the elastic store as the rubber band is twisted. When the car is released, some of the energy from the elastic store is transferred to the kinetic store of the car. The remaining energy is transferred into the thermal store of the surroundings. (a) State what is meant by the principle of conservation of energy. (1) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (b) The car is pulled backwards so that there is 165 J of energy in its elastic store. When the car is released, this energy is transferred to the car's kinetic energy store with an efficiency of 15 %. (i) State the formula linking efficiency, useful energy output and total energy output. (1) (ii) Calculate the energy transferred into the thermal store of the surroundings. (4) energy transferred to thermal store = ........................................................... J (iii) Draw a labelled Sankey diagram for this energy transfer. (3) (c) The car is pulled backwards again. When released, 45 J of energy transfers into the car's kinetic store. The car travels a distance of 7.5 m during this energy transfer. (i) State the useful work done on the car. (1) work done = ........................................................... J (ii) Calculate the mean accelerating force acting on the car. (3) accelerating force = ........................................................... N (Total for question = 13 marks) Q54. A winch is used to pull a truck along a horizontal road. The winch is connected to the truck by a thick rope. (a) The winch does 41 kJ of useful work on the truck when the truck is pulled a horizontal distance of 15 m. (i) State the formula linking work done, force and distance moved in the direction of the force. (1) (ii) Calculate the force that the rope exerts on the truck. (3) force = ........................................................... N (b) The winch includes a small engine. The engine burns petrol to power the motor in the winch. The winch transfers energy mechanically to the truck. (i) The winch has an efficiency of 25% when pulling the truck. Draw a Sankey diagram for this energy transfer. (3) (ii) The winch can also be used to pull the truck uphill at a constant speed. The table gives some energy stores. Add one tick ( ) to each row to show what happens to the energy in each store as the truck is pulled uphill. (4) (Total for question = 11 marks) Q55. (a) Diagram 1 represents the atoms of a gas inside a container. (i) Explain how the atoms exert a pressure on the walls of the container. (3) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (ii) Explain why the pressure of the gas in the container decreases as its temperature decreases. The volume of the container does not change. (2) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (b) Diagram 2 shows a device called a magneto-optical trap (MOT). Physicists use the device to cool gases to extremely low temperatures. The MOT uses laser beams and magnetic fields to trap a small collection of atoms with extremely small kinetic energies. –27 Each trapped atom has a mass of 5.0 × 10 kg and a mean speed of 73 m / s. Calculate the temperature of the trapped atoms. [mean kinetic energy of an atom = 2.1 × 10–23 × temperature in kelvin] (4) temperature = ........................................................... K (Total for question = 9 marks) Q56. The diagram shows a building in a hot climate. The air temperature is 35 °C and the underground temperature is 12 °C. The external pipe is heated by the Sun. This causes cool air to enter the house through a tube in the ground. (a) How is energy transferred to the external pipe from the Sun? (1) A B C D (b) conduction convection evaporation radiation Explain why air moves upwards through the external pipe. (3) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (c) Warm air enters the tube at point X. Cool air leaves the tube at point Y. Explain how the air is cooled as it travels through the tube. (3) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (d) The external pipe is painted to increase the air flow through the building. Explain what colour of paint would give the greatest increase in air flow. (3) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (Total for question = 10 marks) Q57. (a) (i) State Hooke's Law. (2) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (ii) The graph shows how the extension of a rubber band varies with the force applied. Explain how the graph shows that the rubber band does not obey Hooke's Law. (2) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (b) Diagram 1 shows a model aeroplane powered by a rubber band. A person rotates the propeller of the model aeroplane, which twists the rubber band. He then releases the propeller and it spins. Energy transfer occurs during this process. The box lists words associated with energy. Use words from the box to complete the passage. (3) The person does ....................................................................................... ...... work to twist the rubber band. As the person twists the rubber band it extends, increasing the .................................................................................... energy store of the rubber band. When the rubber band is released it does mechanical work, increasing the ........................................................................................ ..... energy store of the propeller. (c) Diagram 2 shows the aeroplane flying horizontally to the right. The aeroplane flies at a constant speed. Diagram 2 shows two forces acting on the aeroplane. Draw labelled arrows on diagram 2 to show two more forces acting on the aeroplane. (4) (Total for question = 11 marks) Q58. The diagram shows a device called a hydraulic lift. The hydraulic lift consists of a tube of oil with a piston at each end. (a) Calculate the pressure difference between the bottom of piston X and the bottom of the oil. [density of oil = 820 kg/m3] (3) pressure difference = ........................................................... Pa (b) A 24 kg mass is placed on piston X. (i) Calculate the weight of the 24 kg mass. Give the unit. (3) weight =.......................................... unit.............................. (ii) Calculate the extra pressure on the oil due to the mass. (2) extra pressure = ........................................................... Pa (iii) The oil transfers the same extra pressure to piston Y. Calculate the force acting upwards on piston Y due to the extra pressure. (3) force = ........................................................... N (c) Piston Y starts at rest, rises slowly and then comes to rest. State how the following energy stores have changed from before the motion to after the motion is complete. (4) (Total for question = 15 marks) Q59. Diagram 1 shows a hydro-electric power station. (a) Water falls from the upper lake and passes position X in the tunnel. After falling to position X, 1.25 × 103 kg of water has 3.2 × 105 J of energy in its kinetic store. Calculate the speed of the water at position X. [kinetic energy = × mass × speed2] (3) speed = ........................................................... m/s 3 (b) Water with a mass of 1.25 × 10 kg falls through a height of 45 m from the upper lake to the turbine. (i) Calculate the decrease in the gravitational potential energy (GPE) store of the water between the upper lake and the turbine. (3) decrease in GPE = ........................................................... J (ii) State how much work has been done on the water by the Earth. (1) work done = ........................................................... J (iii) State the method of energy transfer required for this work to be done. (1) ............................................................................................. ................................................ (c) (i) State the formula linking total energy output, useful energy output and efficiency. (1) (ii) Diagram 2 shows a Sankey diagram for the generator in the hydro-electric power station. The generator is designed to transfer energy electrically to the transformer. Which of these is the correct expression for calculating the efficiency of the process shown in diagram 2? (1) (Total for question = 10 marks) Q60. Photograph 1 shows an outdoor swimming pool. (a) (i) The water in the swimming pool is heated by the Sun during the day. State how energy is transferred from the Sun to the water. (1) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (ii) State what happens to the average speed of the water molecules as the water is heated. (1) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (b) (i) The water in the swimming pool cools down at night. Suggest why the water cools down at night. (1) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (ii) Photograph 2 shows the swimming pool with a plastic cover over the water. Explain why the plastic cover reduces how much the water cools down at night. (4) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (Total for question = 7 marks) Q61. A dam is a structure designed to hold water in a reservoir. (a) The water in the reservoir has a depth of 35 m. (i) State the formula linking pressure difference, height, density and g. (1) (ii) Atmospheric pressure at the surface of the reservoir is 100 kPa. Calculate the total pressure at the bottom of the reservoir. 3 [for water, density = 1000 kg / m ] (3) pressure = ........................................................... kPa (b) An underwater camera is used in the water reservoir. The camera lens experiences a force of 430 N at a pressure of 260 kPa. (i) State the formula linking pressure, force and area. (1) (ii) Calculate the area of the camera lens. Give a suitable unit. (4) area = ............................... unit ............................ (c) Sea water has a density of 1030 kg / m3. Explain how the design of the dam would need to be changed to hold the same depth of sea water safely. (2) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (Total for question = 11 marks) Q62. The photograph shows a robotic vehicle called Opportunity. Opportunity landed on Mars in 2004. Several large balloons protected Opportunity during landing. (a) Explain how the gas molecules inside a balloon exert a pressure on the inside surface of the balloon. (3) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (b) The balloons were tested in a cold room on Earth so that the temperature of the gas was the same as on Mars. (i) Explain why the pressure of the gas decreases if the temperature of the gas decreases. (3) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (ii) State the formula linking pressure, force and area. (1) (iii) The pressure due to the gas inside the balloon is 1200 Pa and the balloon has an inside surface area of 11 m2. Calculate the force on the inside surface of the balloon due to the gas inside the balloon. (2) force = ........................................................... N (Total for question = 9 marks) Q63. Scientific balloons are tested in a laboratory before they are used. (a) In the first test the pressure of the air inside the balloon is 120 kPa. 3 The balloon is sealed and has a volume of 92 m . (i) The pressure of the air inside the balloon is reduced to 64 kPa by reducing the external air pressure. Calculate the new volume of the balloon. (2) 3 (ii) volume = ........................................................... m Give an assumption that is made in the calculation. (1) ............................................................................................. ................................................ (b) The pressure of the air in the balloon is returned to 120 kPa. The temperature of the air inside the balloon is 290 K. The balloon is tested again, changing the temperature of the air and keeping the volume of the balloon constant. (i) Explain why the pressure of the air in the balloon decreases when the temperature of the air decreases. (3) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (ii) Calculate the temperature of the air when the pressure of the air in the balloon is 64 kPa. Give your answer in kelvin. (3) temperature = ........................................................... K (Total for question = 9 marks) Q64. The diagram shows a container used to cool gases to very low temperatures. (a) (i) The gas inside the container is at a temperature of −251 °C. Calculate the temperature, in kelvin, of the gas. (1) temperature = ........................................................... K (ii)Explain why the gas in the container cannot be cooled below a temperature of −273 °C. (2) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (b) The gas in the container exerts a pressure of 7500 Pa on the inner surface of the container. The container has a square window of side length 5.4 cm. Calculate the force the gas exerts on the inner surface of the square window. (5) force = ........................................................... N (Total for question = 8 marks) Q65. A glass contains fizzy water. Bubbles of carbon dioxide form at the bottom of the glass and rise to the surface. (a) The graph shows the relationship between the volume of a bubble and the pressure of the gas in the bubble. (i) Describe the relationship shown by the graph. (2) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (ii) State the formula linking pressure difference, height, gravitational field strength and density. (1) (iii) The depth of the fizzy water in the glass is 22 cm. The density of the fizzy water is 1080 kg/m3. Calculate the pressure difference at the bottom of the glass due to the fizzy water. (2) pressure difference = ........................................................... Pa (iv) Calculate the pressure of the gas in the bubble when the bubble is at the bottom of the glass. [atmospheric pressure = 101 000 Pa] (1) pressure = ........................................................... Pa (v) When a bubble is at the top of the glass, the pressure of the gas in the bubble is equal to 101 000 Pa and the bubble has a volume of 0.084 cm3. Calculate the volume of the gas in the bubble when the bubble is at the bottom of the glass. Assume the temperature of the gas remains constant. (3) volume = ........................................................... cm3 (b) A force called upthrust acts vertically upwards on the bubble. When the bubble is released, it accelerates vertically upwards. Draw two labelled arrows on the diagram to show the forces on the bubble as it is released. (3) (Total for question = 12 marks) Q66. A scientist investigates different samples of rock. (a) The scientist wants to calculate the density of a rock sample. She needs to measure the mass and the volume of the rock. Describe how to obtain accurate measurements of the mass and the volume of the rock. You may draw a diagram to support your answer. (5) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (b) (i) The table shows the scientist's results for rocks made from different materials. State the formula linking density, mass and volume. (1) (ii) Rock X has a mass of 32 g and a volume of 12 cm3. Calculate the density of rock X. Give your answer to 2 significant figures. (3) density = ........................................................... g/cm3 (iii) Rock X is made from the same material as one of the samples in the table. Explain which material rock X is made from. (2) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (Total for question = 11 marks) Q67. The photograph shows a small glass ball used to investigate density and pressure. (a) The mass of the ball is 19 g. 3 The density of the ball is 2.3 g/cm . (i) State the formula linking density, mass and volume. (1) (ii) Calculate the volume of the ball. (2) volume = ........................................................... cm3 (b) The ball is dropped into deep water and sinks to a depth of 560 cm. (i) State the formula linking pressure difference, height, density and gravitational field strength. (1) (ii) Calculate the increase in pressure at this depth. [density of water = 1000 kg/m3] (2) increase in pressure = ........................................................... Pa (Total for question = 6 marks) Q68. The drawing shows a camel and a person in a desert. (a) Describe a method you could use to find the pressure a person exerts on the ground when standing on two feet. (4) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (b) The total area of contact of the camel's feet with the ground is 1300 cm2. The mass of the camel is 660 kg. Calculate the pressure this camel exerts on the ground. (3) pressure = ........................................................... N / cm2 (Total for question = 7 marks) Q69. A student investigates how much pressure she exerts on the ground when she is standing up. (a) (i) The weight of the student is 520 N. State the formula linking weight, mass and gravitational field strength (g). (1) (ii) Calculate the mass of the student. (2) mass = ........................................................... kg (b) The student measures the area of one of her feet when it is in contact with the ground. She draws around her foot on a piece of squared paper. (i) The squares on the paper have a side length of 2 cm. Estimate the area of the student's foot in contact with the ground. (4) area = ........................................................... cm2 (ii) State the formula linking pressure, force and area. (1) (iii) The weight of the student is 520 N. Calculate the pressure the student exerts on the ground when she is standing on both feet. Give the unit. (3) pressure = ............................................................ unit ............................................................ (Total for question = 11 marks) Q70. A student wants to determine the density of air using an irregularly-shaped balloon made of metal foil. 3 The balloon has a label stating that the volume of the balloon when full is 490 cm . This is part of the student's method. Step 1 measure the mass of the empty balloon Step 2 fill the balloon with air Step 3 measure the mass of the full balloon Step 4 subtract the mass of the empty balloon from the mass of the full balloon. (a) (i) Name the equipment the student could use to measure the mass of the balloon. (1) ............................................................................................. ................................................ (ii) Suggest how the student could improve the reliability of their data. (1) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (b) The table shows the student's results. Calculate the density of air to 2 significant figures. Give the unit. (4) density=.................................................. unit .................................................. (c) Describe how the volume of the balloon full of air could be measured using a large beaker and some water. You may use a diagram to help your answer. (3) ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ ............................................................................................. ................................................ (Total for question = 9 marks)