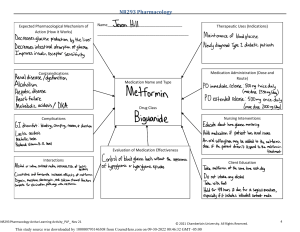
Date Ordere d Name of the Drug Classification and Indication Dose, Route, and Frequency Mechanism of Action Contraindication Side Effects Generic Name: Classification: Pharmacotherapeuti c: Selective inhibitor of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase type 3 Clinical: Antiplatelet and vasodilator agent Dosage: 100 mg Inhibits phosphodiesteras e type 3 (PDE3), leading to increased intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). This elevation of cAMP results in vasodilation, enhancing blood flow to the legs and reducing symptoms of intermittent claudication in peripheral arterial disease (PAD). Additionally, cilostazol exerts antiplatelet effects, inhibiting platelet aggregation, and demonstrates inhibitory effects on smooth muscle cell proliferation. These actions collectively Hypersensitivity. Vascular: Tachycardia, tachyarrythmia, hypotension Cilostazol Brand Name: Pletal Indication: Used for treatment of intermittent claudication. Prescribed to clients with PAD to increase walking distance and improve symptoms with reduced blood flow to the legs. Route: PO Frequency: OD Congestive heart failure. History of ventricular tachycardia. Fibrillation, tachyarrythmia, unstable angina pectoris, myocardial infarction. Recent haemorrhagic stroke. Active bleeding. Pregnancy and breastfeeding. Concomitant use of strong CYP3A4 inhibiors. Nursing Responsibility Cardiac: Angina pectoris, ventricular extrasystoles Gastrointestinal: Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, dyspepsia, flatulence, abdominal pain, abnormal feces Metabolism: Anorexia Respiratory, thoracic, mediastinal: Rhinitis, pharyngitis Skin: Ecchymosis, rash, pruritus Assess patient’s neurological status, vital signs, and signs of bleeding. Administer cilostazol according to physician’s order and medication chart. Implement therapeutic exercises and ambulation activities to augment the effects of drug therapy and promote increased walking distance. Educate patient and family on medication’s purpose, potential side effects, and contribute to its role in improving blood circulation and addressing symptoms associated with PAD. Generic Name: Edaravone Brand Name: Conjuvon Classification: Pharmacotherape utic: Free radical scavenger or antioxidant Clinical: Neuroprotective agent Indication: Dosage: 30 mg (1 amp) / 20 ml Route: IV Frequency: q12 Acts as a free radical scavenger, combating oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation. Its neuroprotective mechanism helps stroke. mitigate neuronal Hypersensitivity. Pregnancy and breastfeeding. Hepatic: Jaundice, bilirubinuria Severe renal impairment. Renal: Acute renal failure, proteinuria Liver dysfunction. Digestive: Belching importance of adherence. Instruct patient to report other bothersome side effects, including severe or prolonged headache or diarrhea. Document medication administration and patient’s response to medication. Assess patient’s neurological status, vital signs, and symptoms. Administer edaravone according to physician’s order and medication chart. damage, making it valuable in conditions like amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and acute ischemic Used for treatment of ALS and acute ischemic stroke. Skin: Rash, pruritus Vascular: Elevated blood pressure, flushing Other: Fever, anemopyretic cold, elevated triglyceride, decreased total serum protein. Generic Name: Atorvastati n Brand Name: Lipitor Classification: Hydroxymethylglut aryl CoA (HMGCoA) reductase inhibitor. Indication: Do not use in pts with active hepatic disease. Note: Individualize dosage based on Dyslipidemias PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 10–20 mg/day (40 mg in pts requiring greater than 45% reduction in LDL-C). Range: 10–80 mg/day. Atorvastatin works by inhibiting HMGCoA reductase, an enzyme involved in cholesterol synthesis. By reducing the production of cholesterol in the liver, it helps lower LDL cholesterol levels and may also have a modest impact Hypersensitivity. Active liver disease or unexplained persistent elevation of serum transaminases. Pregnancy and lactation. Children. Common: Atorvastatin is generally well tolerated. Side effects are usually mild and transient. Frequent (16%): Headache. Occasional (5%–2%): Myalgia, rash, pruritus, allergy. Rare Educate patient and family on medication’s purpose, potential side effects, and importance of adherence. Document medication administratio n and patient’s response to medication. Baseline assessment Obtain baseline cholesterol, triglycerides, LFT. Question for possibility of pregnancy before initiating therapy. Obtain dietary history. baseline LDL/cholesterol, goal of therapy, pt response. Maximum dose with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors: 20 mg/day. Heterozygous on raising HDL Hypercholeste cholesterol. rolemia PO: CHILDREN 10– 17 YRS: Initially, 10 mg/day. Maximum: 20 mg/day (less than 2%–1%): Flatulence, dyspepsia, depression. Intervention/e valuation Monitor for headache. Assess for rash, pruritus, malaise. Monitor cholesterol, triglyceride lab values for therapeutic response. Monitor LFTs, CPK. Patient/family teaching • Follow special diet (important part of treatment). • Periodic lab tests are essential part of therapy. • Do not take other medications without consulting physician. • Do not chew, crush, dissolve, or divide tablets. • Report dark urine, muscle fatigue, bone pain. • Avoid excessive alcohol intake, large quantities of grapefruit products. Generic Name: Metformin Brand Name: Metformin HCI Classification: Biguanide Antihypherglycemi c Indication: Treatment for NDDM (Type 2) 500mg tab Adult initially 500 mg bid; increase by 500mg daily in divided doses at weekly intervals, max: 3 g daily. If 2.5 g is required, give tid, 850-mg tab Adult initially 850 mg once daily or bid. May be increased to 2-3 g daily. Metformin, a commonly prescribed medication for type 2 diabetes, operates through a multifaceted mechanism. It primarily reduces liver glucose production, enhances insulin sensitivity in muscles, and activates AMPK for cellular energy balance. Metformin also Diabetic coma and ketoacidosis. Severe infection, stress, trauma. Renal or hepatic impairment. Heart failure, recent MI, dehydration, alcoholism or other conditions predisposing to lactic acidosis. Gastro Intestinal effects eg. Anorexia, nausea, and diarrhea. Brand Name: Telmisartan Generic Name: Micardis Classification: Angiostensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs) Indication: Used alone or in combination with other classes of The typical starting dose of telmisartan for adults in the treatment of hypertension is often 40 mg once daily. Depending on the patient's has effects on mitochondrial function and decreases intestinal glucose absorption. Notably, it avoids stimulating insulin release from the pancreas, minimizing the risk of hypoglycemia. Overall, its diverse actions make metformin a key player in managing type 2 diabetes by lowering blood glucose levels and improving metabolic control. Telmisartan acts by selectively and reversibly binding to angiotensin II AT1-receptors in vascular smooth muscle and the adrenal gland, Individuals with a history of hypersensitivity or allergy to telmisartan or any components of the medication. Dizziness, lightheadednes s, blurred vision, or back pain as your body adjusts to the medication. Other side effects of Regularly monitor the patient's blood pressure to assess the effectiveness of telmisartan in antihypertensives for the treatment of hypertension. Also used in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy in hypertensive patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, as well as the treatment of congestive heart failure (only in patients who cannot tolerate ACE inhibitors). response, the dosage may be increased to a maximum of 80 mg once daily. The medication is usually administered orally, with or without food. preventing the vasoconstrictor effects and the synthesis/releas e of aldosterone associated with angiotensin II. This leads to a reduction in systemic vascular resistance. Telmisartan does not inhibit angiotensinconverting enzyme, other hormone receptors, or ion channels. Additionally, studies suggest that telmisartan may act as a partial agonist of PPARγ, a target for antidiabetic drugs. This implies potential benefits in improving carbohydrate and lipid metabolism, as well as controlling Pregnant women, especially during the second and third trimesters, due to the potential risk of harm to the fetus. Micardis include stuffy nose, sinus pain, cough, stomach pain, diarrhea, headache, tired feeling, weakness, or skin rash. controlling hypertension. Educate the patient about the importance of consistently taking telmisartan as prescribed by their healthcare provider. Conduct ongoing assessments of renal function, especially in patients with pre-existing renal impairment or those at risk of renal dysfunction. Be vigilant for potential adverse effects, such as dizziness or lightheadedness Generic Name: Amlodipine Brand Name: Norvasc Classification: Hypertension PO: ADULTS: Calcium Channel Initially, 5 Blocker, mg/day as a Antianginal single dose. Agents, May titrate Dihydropyridine every 7–14 days. Maximum: 10 Indication: mg/day. Amlodipine may be SMALLused alone or in FRAME, combination with FRAGILE, other ELDERLY: 2.5 antihypertensive mg/day as a and antianginal single dose. agents for the May titrate q7– treatment of the 14 days. following Maximum: 10 conditions: mg/day. CHILDREN 6– • Hypertension 17 YRS: 2.5–5 mg/day. • Coronary artery disease CAD PO: ADULTS: 5–10 mg/day as insulin resistance, without the side effects associated with full PPARγ activators. Inhibits calcium movement across cardiac and vascular smooth muscle cell membranes. Therapeutic Effect: Dilates coronary arteries, peripheral arteries/arteriole s. Decreases total peripheral vascular resistance and B/P by vasodilation. , which can occur, especially at the beginning of treatment. Contraindication s: Hypersensitivity to amLODIPine. Cautions: Hepatic impairment, severe aortic stenosis, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy with outflow tract obstruction. Frequent (greater than 5%): Peripheral edema, headache, flushing. Occasional (5%–1%): Dizziness, palpitations, nausea, unusual fatigue or weakness (asthenia). Rare (less than 1%): Chest pain, bradycardia, orthostatic hypotension. Baseline assessment Assess baseline renal/hepatic function tests, B/P, apical pulse. Intervention/e valuation Assess B/P (if systolic B/P is less than 90 mm Hg, withhold medication, contact physician). Assess for peripheral edema behind medial malleolus (sacral area in bedridden pts). Assess skin for • Chronic stable angina • Vasospastic angina (Prinzmetal’s or Variant angina) • Angiographically documented coronary artery disease in patients without heart failure or an ejection fraction < 40% Carvedilol Piracetam a single dose. ELDERLY, PTS WITH HEPATIC INSUFFICIENC Y: 5 mg/day as a single dose. Dosage in Hepatic Impairment ADULTS, ELDERLY: (Hypertension) Initially, 2.5 mg/day. (Angina) Initially, 5 mg/day. Titrate slowly in pts with severe impairment. flushing. Question for headache, asthenia. Patient/family teaching • Do not abruptly discontinue medication. • Compliance with therapy regimen is essential to control hypertension. • Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until response to drug is established. • Do not ingest grapefruit products. Cinnarizine Clopidogrel Betahistine