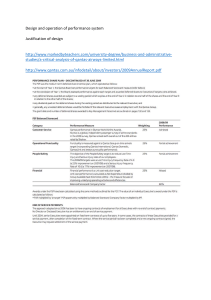
Introduction: In the ever-evolving landscape of finance, investment remains a cornerstone for individuals and institutions seeking to grow their wealth. While the concept of investment may seem straightforward, the intricacies of navigating the financial markets can be daunting for the uninitiated. This article aims to demystify the process of investment, providing insights into the various financial markets and strategies that investors employ to achieve their financial goals. Understanding Financial Markets: Financial markets serve as platforms where buyers and sellers come together to trade financial assets such as stocks, bonds, currencies, and commodities. These markets can be broadly categorized into primary and secondary markets. The primary market is where new securities are issued, while the secondary market facilitates the trading of existing securities among investors. Equity Market: One of the most well-known financial markets is the equity market, where shares of publicly traded companies are bought and sold. Investors in the equity market aim to profit from capital appreciation and dividends as the value of the company's stock increases over time. Bond Market: The bond market, on the other hand, deals with the buying and selling of debt securities issued by governments, municipalities, and corporations. Bonds offer fixed interest payments over a specified period, making them attractive to investors seeking income and capital preservation. Foreign Exchange Market: The foreign exchange (forex) market is the largest and most liquid financial market globally, where currencies are traded 24 hours a day. Participants in the forex market include central banks, financial institutions, corporations, and individual traders. Exchange rate fluctuations in the forex market present opportunities for investors to speculate on currency movements and hedge against foreign exchange risk. Commodity Market: Commodities such as gold, oil, wheat, and coffee are traded in the commodity market. Investors can gain exposure to commodities through futures contracts, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), or physical assets. Commodity prices are influenced by factors such as supply and demand dynamics, geopolitical events, and macroeconomic trends. Investment Strategies: Successful investing requires a well-thought-out strategy tailored to an individual's financial objectives, risk tolerance, and time horizon. Some common investment strategies include: Buy and Hold: This strategy involves purchasing securities with the intention of holding them for the long term, regardless of short-term market fluctuations. Buy-and-hold investors focus on the fundamental strength of the underlying assets and aim to benefit from compounding returns over time. Value Investing: Value investors seek to identify undervalued securities trading below their intrinsic value. By conducting thorough fundamental analysis, value investors aim to capitalize on market inefficiencies and profit when the market eventually recognizes the true worth of the asset. Growth Investing: Growth investors target companies with strong earnings growth potential, often characterized by high revenue growth rates and innovative products or services. Growth investors are willing to pay a premium for stocks of companies poised for rapid expansion, betting on future appreciation in share price. Conclusion: Investing in the financial markets can be both rewarding and challenging, requiring a solid understanding of market dynamics, investment vehicles, and risk management techniques. By diversifying their portfolios across different asset classes and employing sound investment strategies, investors can enhance their chances of achieving long-term financial success. However, it's essential to remember that investing carries inherent risks, and seeking professional advice is advisable before making any investment decisions. With proper knowledge and diligence, individuals can harness the power of the financial markets to build wealth and secure their financial future.