Uploaded by
Audrey Lou Otico Catan
Math Curricula Comparison: England, Sweden, Philippines
advertisement
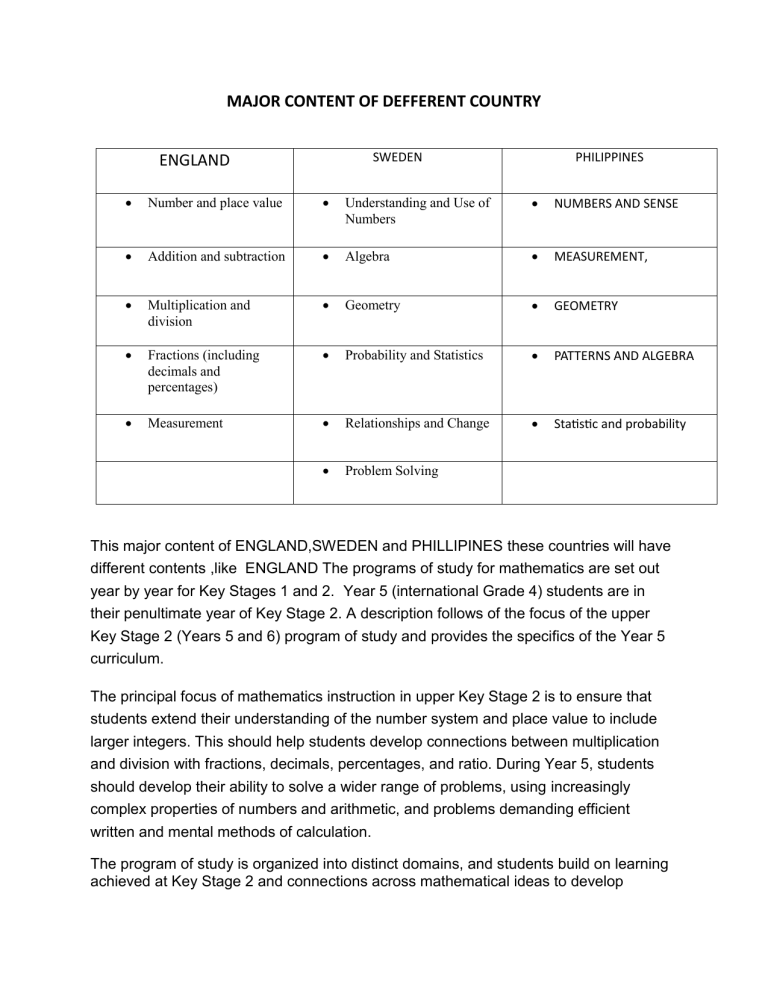
MAJOR CONTENT OF DEFFERENT COUNTRY SWEDEN ENGLAND PHILIPPINES Number and place value Understanding and Use of Numbers NUMBERS AND SENSE Addition and subtraction Algebra MEASUREMENT, Multiplication and division Geometry GEOMETRY Fractions (including decimals and percentages) Probability and Statistics PATTERNS AND ALGEBRA Measurement Relationships and Change Statistic and probability Problem Solving This major content of ENGLAND,SWEDEN and PHILLIPINES these countries will have different contents ,like ENGLAND The programs of study for mathematics are set out year by year for Key Stages 1 and 2. Year 5 (international Grade 4) students are in their penultimate year of Key Stage 2. A description follows of the focus of the upper Key Stage 2 (Years 5 and 6) program of study and provides the specifics of the Year 5 curriculum. The principal focus of mathematics instruction in upper Key Stage 2 is to ensure that students extend their understanding of the number system and place value to include larger integers. This should help students develop connections between multiplication and division with fractions, decimals, percentages, and ratio. During Year 5, students should develop their ability to solve a wider range of problems, using increasingly complex properties of numbers and arithmetic, and problems demanding efficient written and mental methods of calculation. The program of study is organized into distinct domains, and students build on learning achieved at Key Stage 2 and connections across mathematical ideas to develop fluency, mathematical reasoning, and competence in solving increasingly sophisticated problems with good written and mental arithmetic. The use of equipment such as calculators is recommended only as a supporting tool near the end of Key Stage 2. The content of SWEDEN The national mathematics curriculum for compulsory school begins with an overall statement of purpose describing the role of mathematics in society and human activity, and presenting arguments that defend the importance of learning and teaching mathematics. The syllabus presents content in six categories, which are the same for all three tiers: Understanding and Use of Numbers; Algebra; Geometry; Probability and Statistics; Relationships and Change; and Problem Solving. The syllabus emphasizes problem solving, identifying it as part of the overall aim that guides teachers in creating learning opportunities, and as a component of core content. The specific core content for each tier is presented below. The PHILIPPINES from K TO 3 the learner demonstrates understanding and appreciation of key concepts and skills involving numbers and number sense (whole numbers up to 10,000 and the four fundamental operations including money, ordinal numbers up to 100th, basic concepts of fractions); measurement (time, length, mass, capacity, area of square and rectangle); geometry (2-dimensional and 3-dimensional objects, lines, symmetry, and tessellation); patterns and algebra (continuous and repeating patterns and number sentences); statistics and probability (data collection and representation in tables, pictographs and bar graphs and outcomes)as applied - using appropriate technology - in critical thinking, problem solving, reasoning, communicating, making connections, representations, and decisions in real life. And the 4 to 6 the learner demonstrates understanding and appreciation of key concepts and skills involving numbers and number sense (whole numbers, number theory, fractions, decimals, ratio and proportion, percent, and integers);measurement (time, speed, perimeter, circumference and area of plane figures, volume and surface area of solid/space figures, temperature and meter reading); geometry (parallel and perpendicular lines, angles, triangles, quadrilaterals, polygons, circles, and solid figures); patterns and algebra (continuous and repeating patterns, number sentences, sequences, and simple equations); statistics and probability (bar graphs, line graphs and pie graphs, simple experiment, and experimental probability) as applied -using appropriate technology - in critical thinking, problem solving, reasoning, communicating, making connections, representations, and decisions in real life the curriculum guide of Philippines ,the purpose of teaching mathematics is to develop foundamental skills, critical thinking and problem-solving abelities . It aims to build a strong mathematical foundation for students, helping them understand basic concepts, numerical relationships ,and logical reasoning that will be essential for more advanced math learning in later grades Sweden: Focuses on conceptual understanding and reasoning, with less emphasis on memorization and procedures. Integrates real-world applications early on. England: Focuses on developing fluency with basic skills and building towards more complex concepts. Uses a mastery approach, ensuring students understand each concept before moving on. Philippines: Follows a spiral curriculum, revisiting concepts throughout the grades with increasing complexity. Places emphasis on computational skills and problemsolving using traditional methods. comparison of the math curriculum in Sweden, England, and the Philippines in elementary grades. All three countries emphasize developing basic numeracy skills in the early grades, including counting, addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. develop problem-solving skills and encourage students to apply their math knowledge to real-world situations.