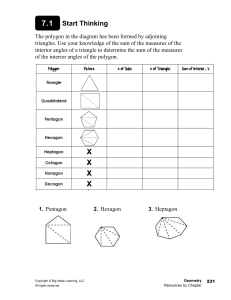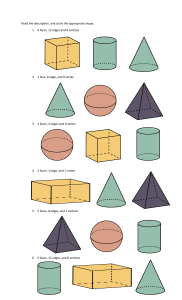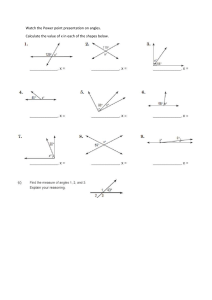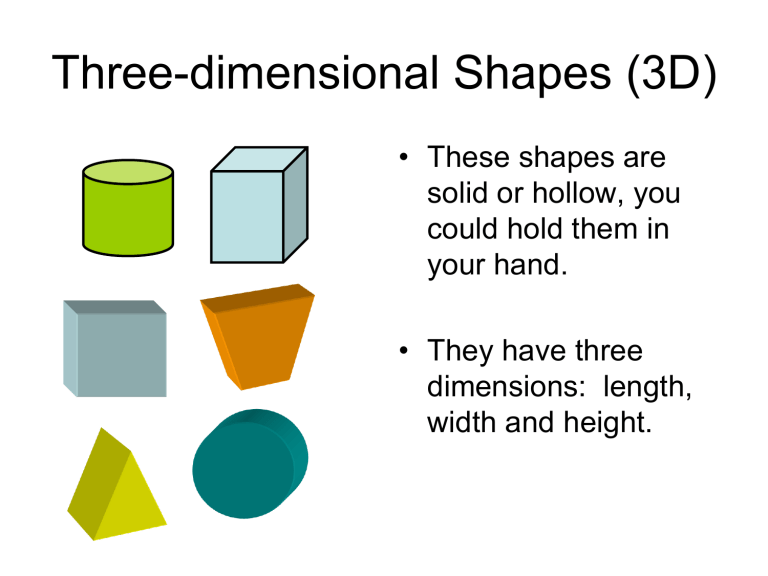
Three-dimensional Shapes (3D) • These shapes are solid or hollow, you could hold them in your hand. • They have three dimensions: length, width and height. Solid • A shape you can hold (3D). • A solid has length, width and height. • Examples: – – – – – Cube Cylinder Sphere Cone Prism Surface • The curved part of a 3D shape. • Cylinders and cones have surfaces. Face • Part of a 3D shape that is flat. • Example: A cube has 6 faces. Base • The bottom face of a 3D object. Base Edge • The line where two faces meet on a 3D object. • Example: A cube has 12 edges. Corner • The point where three or more edges touch. • This cube has 12 corners all together. Vertex (Vertices) • The point where three or more edges meet. • This cube has 12 vertices all together. Cube • A 3D shape (you can hold it). • It has 6 equal square faces. • Cubes in daily life: – A box – Blocks – Dice Cube • A three-dimensional shape which has: – 6 square faces all the same size – 12 edges – 8 corners Cube • A three-dimensional shape which has: – 6 square faces all the same size – 12 edges – 8 vertices Cube • A three-dimensional shape which has 6 square faces all the same size, 12 edges and 8 vertices. • Some faces parallel • Some edges parallel • Some faces perpendicular • Some edges perpendicular Sphere • A 3D shape (you can hold it) that can roll. • A Sphere has no corners or edges • Spheres in daily life: – A Ball – A Globe – A Marble Sphere • A perfectly round three-dimensional shape, like a ball. It has only one curved surface. • A sphere has – 0 faces – 0 edges – 0 corners Sphere • A perfectly round three-dimensional shape, like a ball. It has only one curved surface. • A sphere has – 0 faces – 0 edges – 0 vertices Cone • A 3D shape (you can hold it) that can roll. • A Cone has a circle at its base and a curved surface that comes to a point at its top (vertex). • Cones in daily life: – Ice Cream Cone – A Party Hat Cone • A three-dimensional shape made up of: – a circular base – a curved surface that comes to a point at the top (vertex). • A Cone has 0 edges and 0 corners. Cone • A three-dimensional shape made up of: – a circular base – a curved surface that comes to a point at the top (vertex). • A Cone has 0 edges and 0 vertices. Cylinder • A 3D shape (you can hold it) that can roll. • A Cylinder has 2 equal circles on its ends. • Cylinders in daily life: – A Soup Can – A Roll of Toilet Paper Cylinder • A three-dimensional shape with one curved surface and 2 equal circles on its ends. • A Cylinder has 2 faces, 1 surface, 0 edges and 0 corners. Cylinder • A three-dimensional shape with one curved surface and 2 equal circles on its ends. • A Cylinder has 2 faces, 1 surface, 0 edges and 0 vertices. Pyramid • A three-dimensional shape which has a polygon for its base and triangular faces which meet at one point (vertex). Rectangular Prism • A 3D shape (you can hold it). • It has 6 rectangular faces. • Cubes in daily life: – A Kleenex Box – A Refrigerator – A Cereal Box Rectangular Prism • A 3D shape that has: – 6 rectangular faces • 2 of those faces are equal – 12 edges – 8 corners Rectangular Prism • A 3D shape that has: – 6 rectangular faces • 2 of those faces are equal – 12 edges – 8 vertices Rectangular Prism • A 3D shape that has: – 6 rectangular faces • 2 of those faces are equal – 12 edges – 8 vertices • • • • Some faces are parallel Some edges are parallel Some faces are perpendicular Some edges are perpendicular Two-Dimensional Shapes (2D) • These shapes are flat and can only be drawn on paper. • They have two dimensions: length and width. • They are sometimes called plane shapes. Sides • The lines you can trace and count on the outside of a 2D shape. • Example: A triangle has 3 sides. A square has 4. Polygons • Two-dimensional shapes that have three or more sides made from straight lines. • Examples: – – – triangles squares rectangles Quadrilaterals • Any twodimensional shapes (polygon) with 4 straight sides and 4 angles • Ex. rhombus rectangle square kite trapezoid Quadrilaterals • Any twodimensional shapes (polygon) with 4 straight sides and 4 angles • The interior angles of a Quadrilateral add up to 360 degrees. • Ex. rhombus rectangle square kite trapezoid Parallelogram • A quadrilateral with parallel opposite sides of equal length. • Opposite angles are equal. Rectangle • A 2D shape with 4 corners and 2 pairs of opposite, equal, parallel sides. • Rectangles in daily life: – A Door – A Piece of Paper Rectangle • A 2D shape with 4 corners and 2 pairs of opposite, equal, parallel sides. • The sides meet at right angles. Rhombus • A 2D shape with four sides. Rhombus • A 2D, four-sided shape with opposite sides that are parallel. • All the sides are the same length. Rhombus • A 2D, four-sided shape with opposite sides that are parallel. • All the sides are the same length. • Diagonals of a Rhombus bisect each other at right angles. Trapezoid • A 2D shape (polygon) with four sides. • One pair of sides is parallel. Trapezoid • A 2D shape (polygon) with four sides. • One pair of sides is parallel. Circle • A 2D shape with no corners or edges. • Circles in daily life: – A Clock Semicircle • A 2D shape that is exactly half of a circle. • Semicircles in daily life: – Half of a pie – Half of a pizza Square • 2D shape with 4 equal sides and 4 corners • Squares in daily life: – A Window – Some Floor Tiles – Some Ceiling Tiles Square • 2D shape (polygon) with 4 equal sides and 4 right (90°) angles. • Opposite sides are parallel. Triangle • Two-dimensional shape with three straight sides and three corners. • Triangles in daily life: – The front of a tent Triangle • Two-dimensional shape (polygon) with three straight sides and three angles. • There are – – – – isosceles triangles, right triangles equilateral triangles scalene triangles Triangle • Two-dimensional shape (polygon) with three straight sides and three angles. • The interior angles of a triangle add up to 180 degrees. • There are – – – – isosceles triangles, right triangles equilateral triangles scalene triangles Patterns • A repeating design. Examples: AB AA B Growing Line • A long, thin mark that continues forever. • It has no endpoints. Line • An infinitely long, thin, twodimensional mark • It has no endpoints. Parallel • Lines that are the same distance apart from each other. • These type of lines stay the same distance apart for their whole length. They do not need to be straight or the same length. • They never intersect. Perpendicular • Lines that intersect at a perfect right angle (90º) to one another. • In solid shapes, edges could be at a right angle to one another. • Faces could also be at right angles to one another. Intersecting • Crossing over one another. • These lines are intersecting. Line Segment • A section of line bounded by two endpoints. • A line segment is not continuous. Point • A single position in space (dot). Distance A B • The length between two points or objects. Angles • A shape formed by two lines or rays that extend from a common point (vertex). • The amount of turning between two lines that meet at a common point (vertex). Vertex (angles) • The common point between two or more rays or line segments. Acute Angle • An angle that measures less than 90 degrees. Right Angle • An angle whose measure is exactly 90 degrees. Obtuse Angle • An angle whose measure is more than 90 degrees. Straight Angle • An angle whose measure is exactly 180 degrees. • A straight line. Interior Angles • Any angle inside a polygon. Congruent • Two figures are congruent if they have the same shape and size. • Two angles are congruent if they have the same measure. Vertical Angles • A pair of angles directly opposite each other formed by the intersection of straight lines. • Vertical angels are congruent (equal). Isosceles Triangle • A triangle with 2 equal sides and 2 equal angles Equilateral Triangle • A triangle with 3 equal sides and 3 equal angles. Right Triangle • A triangle with one right angle (90 degrees). Scalene Triangles • A triangle with 3 different side lengths and 3 different angle measures. Symmetry • An object is symmetrical when you can fold it in half and the two halves are congruent. • One half is a mirror image of the other. Symmetrical Not Symmetrical