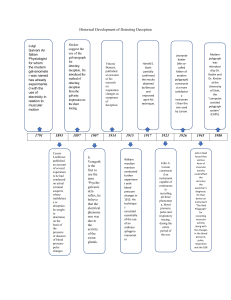
POLYGRAPHY (LIE DETECTION) NOTES By Juliana Celine Tolentino EARLY METHODS OF DETECTING DECEPTION POLYGRAPHY ● ● ● ● refers to the scientific method of detecting deception with the use of the polygraph. administered by a trained polygraphist, lie detector specialist, forensic psychophysiologist, polygraph examiner. The polygraph is commonly called a lie detector; polygraph machine, deceptograph, and truth verifier. most used method in the law enforcement. POLYGRAPH ● ● ● an instrument or device capable of recording changes in blood pressure, pulse, respiration, and skin resistance in the physiological phenomena that may be used as bases for the application of a reliable technique of diagnosing truth of deception. derived from the two Greek words poly, which means “many or having several” and graph, which means “writings. polygraph means many writings. WHY DO PEOPLE SEEK THE TRUTH? ● knowledge of truth is the fundamental requirement in administering justice ● Dr. Hans Gross defined search for truth as “the basis and goal of all criminal investigations.” In System der Kriminalistiks, it was emphasized that a large part of the criminalist's work involves battle against lies. criminalist has to discover the truth and must fight the opposite, which is lies and deceit TRIAL BY ORDEAL - closely related to the Medieval Latin “dei indicum” meaning "miraculous decisions" for ancient cases were decided through several tests, usually on physical strength. ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● PHRENOLOGY - a study that suggests the human brain is the central GRAPHOLOGY - study of handwritings PALEOGRAPHY - study of ancient writings. Some primitive lie detection methods were customs based on physiological principles. BASIC LIE DETECTION METHODS: ● Methods of Detecting Deception ● ● In attempting to discover lies and deceit, primitive people developed methods that are founded with magic and mysticism. early people believed that their gods send them messages through fire and water, they used these things as a means to know the truth This procedure is known as the “TRIAL BY ORDEAL” Red Hot Iron Ordeal Ordeal by Balance Ordeal by Boiling Water Ordeal by Rice Chewing Trial by Combat Ordeal of the Red Water Ordeal by Eating Corsnead Ordeal by Drinking Decoction Ordeal by the Eucharist Ordeal of the Bier Ordeal by Heat and Fire Ordeal by Boiling Oil or Water Ordeal by Using Red Hot Needle Ordeal of the Tiger Ordeal by Combat Ordeal of the Cross Ordeal by Waxen Shirt Ordeal by Donkey’s Tail ● ● Cross-checking the information: in-lined with testimonies, physical evidence; or any other existing data. Psychological method – evaluation: emotional, behavioral, and cognitive reactions of a person. Interrogation and testing the credibility - suspect’s statement using the polygraph. Methods with the use of scientific devices: ● ● ● Word Association Technique Psychological Stress Evaluation Polygraph Method or Polygraph Methods with the use of substances that inhibits the inhibitor: ● ● ● Truth Serum administration Narcoanalysis or Narcosynthesis Intoxication with Alcohol Other methods: ● ● ● Hypnosis Scientific Observation Scientific Interrogation New sophisticated techniques: ● ● ● Computerized Voice Stress Analysis Brain Scanning (Brain Fingerprinting) Iris Analysis 💡 As scientific lie detection methods are usually applied to resolve legal matters, the field of lie detection is now included a one area of forensic science. 💡 Forensic lie detection is better known in the academe as FORENSIC PSYCHOPHYSIOLOGY. Dr. William J. Yankee states that Polygraph examination is one of the most complex psychophysiological examinations ever developed. In other countries, there are preferred descriptions of lie detection through polygraph examination such as: Psychophysiological Veracity Examination, Psychophysiological Detection of Deception, Psychophysiological Credibility Assessment. CARDIO-SPHYMOGRAPH PNEUMOGRAPH GALVANOGRAPH Cesare Lombroso (1895) hydrosphygmograph: sought to determine truthfulness or deception on the basis or absence of blood pressure— pulse changes when suspects were questioned about the offense. He is the first to utilize an instrument to detect lies. Vittorio Benussi (1914) - published an account of his research on respiration changes as symptoms of deception. In test cases, he measured recorded respiratory tracings. He detected deception with a pneumograph that graphically measures the inhalation and exhalation and demonstrated the changes in respiration-expiration ratio during fraud. (Before telling the truth, the ratio is greater. Greater after lying. Luigi Galvani (1791) - accorded the distinction for developing the galvanic skin reflex or the galvanometer which records electrical bodily resistance in terms of ohms, the lowest current ever recorded. Angelo Mosso (1895) - influenced by Lombroso. Mosso pursued his studies of emotion and fear and its influence on the heart and respiration using an instrument for measuring blood pressure and pulse change — plethysmograph by Francis Franke. This reveals periodic undulations in blood pressure caused by respiration cycle Harold E. Burtt (1918) conformingly utilized the techniques of Benussi. He considers that measuring the recorded respiratory tracings to be less diagnostic value than blood pressure techniques. Burtt determines that respiratory changes were indications of deception, and found out that changes in systolic blood pressure were of greater value in determining deception than in respiratory changes. Sticker (1879) - discovered the fantastic possibility of Electro dermal response in creating emotions. He claims that a person has no control as to their response. He is the inventor of the first lie detector using Electro dermal answers. William Moulton Marston (1915) sphygmomanometer: through this instrument, Marston obtained periodic, discontinuous blood pressure reading during the course of a test. He also recorded the respiration and noted the time the subjects’ verbal responses, as well as, he experimented with the galvanometer to record skin resistance changes and gripping devices to record tension. Marston used the Word Association test, and is considered to be the self-proclaimed” Father of Polygraphy. John A. Larson (1921) - constructed an instrument capable of continuously recording all the three phenomena - blood pressure, pulse, and respiration. This instrument doesn’t only have recording pen for cardiosphymograph, pneumograph, galvanograph but has muscular movement pen for arms and thighs. Father of Polygraphy. S. Veraguth (1907) - coined the term “psychogalvanic skin reflex”, he believes that the electrical phenomenon is due to the activity of sweat glands. Leonard A. Keeler (1926) - he made an additional changes in Larson’s instrument. the Galvanic Skin Reflex or electrodermal response. He introduced the card test and the peak of tension test. Father of Modern Polygraphy. Richard O. Archer or Arther OTHER PIONEERS POLYGRAPHY in the DEVELOPMENT - OF regular basis, the chest and abdominal breathing patterns - ANTON MESMER (1778) - hypnotism as a method of detection. FRANCIS GALTON (1879) - Word Association Test; the patient is presented with group of words sufficiently separated in time to allow the patient to utter his first thought generated by each word. Dr. Carl Guztav Jung also worked out for this. - ● ● psychogalvanic skin reflex proposed the electro-dermal response Richard I. Golden (1969) - experiments using existing control question techniques but requiring the subject to answer the question twice Control Question Test (CQT) and Guilty Knowledge Test (GKT) - ● ● psychological stress evaluator worked with Charles Mcquiston (1972) Ronald E. Decker ● ● head of the Army Polygraph School introduced the modification of the Reid Polygraph Technique and GQT James Allan Matte - “POLYGRAPHY QUADRI-ZONE COMPARISON TECHNIQUE” Sir James Mackenzie (1906) - First described the instrument in an article entitled “the Ink Polygraph” which appeared in 1908 in the British Medical Journal Two types of questions: control questions and relevant questions - electronic psychrometer using electrodermal responses Allen Bell (1972) Presented a paper at the Annual Seminar of American Polygraph Association at Houston, Texas regarding his Paul Wilhelm and Donald Burns (1951) ● Introduced the Arther II polygraph instrument which contains a stimulus marker electro-cement response Christian Ruckmick (1936) 1966, founded the Journal of Polygraph Science, the oldest of the polygraph publications FERE (1888) ● Is the first polygraphist to record simultaneously, on a Measures the suspect’s detailed knowledge of a crime that he or she does not want to share ● 81% - 91% reliability of polygraph by National Academies of Science. Dr. Edward Mandel House - A US psychiatrist and diplomat who introduced the truth serum American Polygraph Association - 1966, was established with 2,500 members - Continues to be the leading polygraph professional association, establishing standards of ethical practices, techniques, instrumentation, research, and advanced training and continuing educational programs Training and Certification - Is involved in setting standards for training and certification of polygraph examiners Research and Development - TERMINOLOGIES IN POLYGRAPHY Encourages and supports research in the field of polygraphy - LIE DETECTION Involves the exploration of new techniques, - Otherwise known as “deception detection” methodologies, and technologies to enhance - Uses questioning techniques along with technologies the effectiveness and reliability of polygraph able to record physiological functions to ascertain truth examinations and falsehood. - Commonly used by law enforcement Professional Networking - A platform for polygraph professionals to connect, share knowledge, and exchange PSYCHOPHYSIOLOGY - experiences - Greek word; psykhe (breath, life, soul), physis (nature, origin, “study of”) Helps in fostering a community of experts in - the field A branch of psychology concerned with physiological and psychological processes. - Study of the relations between physiological manipulations and resultant physiological responses Ethical Standards - measured in the individual. Upholding ethical standards in the practice of polygraphy - POLYGRAPH EXAMINATION Includes promoting transparency, accuracy, and - fairness in the use of polygraph examinations All activities taking place between a polygraph examiner and an examinee - Valid polygraph examination = respiration, electro-dermal activity, and cardiovascular activity must Public Education - be monitored. Is involved in educating the public about the - capabilities and limitations of polygraph Also termed as “Forensic Psychophysiological Detection of Deception” examinations - May include providing information in the scientific basis of polygraphy and its application in various settings The University of Utah Research - The US Justice Department funded experiments conducted by 3 doctors of psychology from 1975-1976 at the University of Utah showed the polygraph to be 90% accurate - Only 10% of the results were declared inconclusive - The confirmed average validity was shown to be 96% accurate in more recent research POLYGRAPH TEST - Techniques applied or used by the polygraph examiner. QUESTIONING TECHNIQUES ● Relevant-irrelevant tests - guilty reacts only to relevant questions, and innocent shows no reactions. LEONARDE A. KEELER ● Reviewed control questions - to stimulate the innocent subject to identify the general nervous tension and guilt complex reactor and to improve the contract between innocent and guilty subjects. ● Guilt Complex Test - administered to the overly sensitive subjects. JOHN E. REID ● Backster Zone Comparison Test - the basis of his zone of comparison technique that provides constant monitoring of the subject’s reactivity and designed to disclose outside issue. CLEVE BACKSTER And many other tests. POLYGRAPH From the word “poly” which means “many”, “graphos” meaning “writings” = many writings. Science of the test by which several physiological Paired Testing - done when two persons are responses and changes are measured at the same time to contradicting each other; questioned separately and at detect signs of deception, this process is called, the same time. FORENSIC PSYCHOPHYSIOLOGY - 4. 5. An instrument for recording changes in blood pressure, Post-conviction sex-offender testing - those sexual offenders under parole or probation. pulse rate, respiration, skin resistance. This does not detect lies; only deceptive behaviors. - Other terms related…. Administered by a trained polygraphist, lie detector specialist, forensic psychophysiologist - Commonly called “lie detector”, polygraph machine, deceptograph, and truth verifier. General Types of Polygraph 1. Conventional Polygraph Instrument - old and traditional 2. Computerized Polygraph Instrument - sophisticated LYING - Uttering or conveying falsehood DECEPTION - Act of deceiving; misleading STIMULUS - Excites the perceptors LIE - Uttering intentionally statements DETECTION - Act of discovering presence of something hidden FEAR - Emotional response to danger CHART OR POLYGRAMS - Composite records of the pneumograph, galvanograph, and cardiograph tracings state of art computer-aided polygraph instrument Uses of Polygraph 1. Pre-Employment Screening - In the USA, this is only applicable to those working in gov’t agencies such as the FBI, CIA and the likes. - Employee Polygraph Protection Act of 1988 (EPPA) 2. Periodic Audit - determine honesty and integrity of present employee in the company. 3. Case Investigation - conducted when there is an incident or issue under question. THE SCIENCE OF HUMAN BODY SYSTEM Body Activities Recored by the Polygraph 1. Respiratory Activity 2. Electro-dermal or Sweat Gland Activity 3. Cardiovascular Activity false PHYSIOLOGICAL EFFECTOR MECHANISM/ - AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM and pump it to the arteries. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM: brain and spinal cord ○ Somatic Nervous System: guides Cardiac Cycle your voluntary movements. ○ Autonomic Nervous System: involuntary physiological functions. HYPOTHALAMUS ● Systole - contraction of the auricles Diastole - relaxation from contraption by a brief period of inactivity. main effector mechanism which the polygraph is concerned with. ● responsible for regulating mechanisms that correct the slightest deviation of the blood, body temperature, levels THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM - chemical substances that maintain the activity of all cell membranes are finely adjusted. the hypothalamus causes our involuntary reflexes, those that we cannot control consciously such as our heartbeat, pulse rate, increase and decrease in blood Major Parts of the Respiratory System Respiratory Tract - nose, mouth, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs - In polygraph testing, the receptor is the ear of the subject, which receives the threatening question or stimulus from the polygraphist. The stimulus is transmitted from the ears via sensory neurons into the THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM: SKIN - Skin is the largest organ in the body. - Epidermis; 4 layers of stratified epithelium, Corium; connective tissue containing lymphatic nerves and nerve brain, then the hypothalamus will analyze, evaluate, and endings, blood vessels, sebaceous, and sweat glands and resolve the particular question. ● elastic fibers. activates the sympathetic subdivision of the ANS which causes the fight-or-flight response; adrenal glands to release hormones such as epinephrine and norepinephrine. ○ norepinephrine as a neurotransmitter increases alertness, arousal, and attention; this affects your sleep-wake cycle, mood, and memory. Basic Function - Protection against injuries and parasitic infections - Regulation of body temperature - Aid in the elimination of bodily waste product. - Contributes to the PE through measuring electrodermal activity– sweating. stress triggers the release of norepinephrine. ■ ○ Flight or fight response epinephrine plays a role in metabolism, attention, focus, panic, and excitement. ● Bony cage: thoracic vertebrae, the ribs, and the breast bone, or the sternum pressure, and expansion of the arteries. ● Taking of air into the lungs, expelling carbon dioxide from the body. of potassium, sodium, calcium magnesium and all the ● Ventricles - received blood from the auricles GALVANIC SKIN RESPONSE/TEST - Records changes in subject’s increase or decrease resistance to a constant electrical current. the second division of the ANS is the parasympathetic nervous system. Its function is antagonistic to the SNS, and its role is to maintain the homeostasis of the body necessary for normal functioning. THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM: BLOOD, VEINS - Responsible for the movement of blood in the veins - Four Chambers of the Heart: Auricles and Ventricles. - Auricles - receives the blood being returned to the heart. SCIENTIFIC METHOD OF DECEPTION - A method of gathering and knowing from the subject about the crime dispute; question of issue employing the use of machine, drugs, or substances. A. BRAIN WAVES - - Neurophysiology - One - type of to get information from the subject. Brain-wave; Event-related - sodium amytal; pentothal; seconal and other barbiturates; ERPs: recorded by sensors placed on the scalp. methedrine; methylphenidate; droperidol; scopolamine; This has the ability to reveal the timing and trichlorethylene (anesthetic drugs), etc. - brain. It can also reveal whether an individual has guilty knowledge of the crime. - Drugs act as a depressant on the nervous system. - Under the influence of the serum, statements obtained - Developed by Carl Jung software that can track the brain’s use of blood over - Individuals harbored “complexes” associated with certain time. It is assumed that more blood is used in particular words, and that interfered with the person’s ability to regions of the brain when they are active than when they respond to stimuli - The regional imaging technique “works” is that it can statistically separate control items from guilty items. EYE TRACKING - F. REACTION TIME An fMRI device is a powerful magnet and sophisticated are inactive. C. from the subject are not admissible as evidence. A leading candidate for technology for lie detection is Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI). - Suggests that pattern of a person’s eye movements over before. - Movement of the eyes are monitored by illuminating - narration, and amount of time covered in the passages. Often used by police in initial investigation: to eliminate suspects, or direct the course of an ongoing investigation Suggests that short duration facial expressions can reveal concealed emotions. H. VOICE STRESS ANALYSIS/ VOICE RISK ANALYSIS Micro-expressions; corresponds with emotions that an (VSA)/ PSYCHOLOGICAL STRESS EVALUATOR individual is attempting to mask. - Developed by Allen Bell Jr. & Charles McQuiston Facial electromyography (fEMG) refers to an - Uses computers to compare pitch, frequency, intensity, electromyography technique that measures muscle activity by detecting and amplifying the tiny electrical - Relies upon the analysis of written text for pattern of word choices, pronouns and verb tenses, sequence of FACIAL ANALYSIS - Approach to lie detection that does not use device/technology. - Rule: the act of deception causes responses to be delayed. G. STATEMENT CONTENT ANALYSIS them with an “eye-safe” infrared light. D. The act of lying involves more cognitive processes that slows the response time. - an image can reveal whether he/she has seen the image - Information gathered from the subject is not reliable to be true. B. BRAIN IMAGERY - Drugs being used: hyoscine hydro-bromide (common); Potentials (ERPs) general location of the electrical activity in the - This method uses narcotic or anesthetic drugs in order and micro tremors. - When a person lies, an involuntary interference of the impulses that are generated by muscle fibers when they nerves causes the vocal cords to produce a distorted contract. sound wave (frequency level), different from the same Activity like corrugator muscle (lowers eyebrow and person when telling the truth involved in producing frowns), are found inversely with emotional valence of stimuli and reports mood state. - I. THERMAL IMAGING Zygomatic major muscle (controls smiling), is associated - Method that uses body heat to detect deception with positive emotional stimuli and positive mood state. - Special thermal cameras capture subtle changes in temperature of a person's face, around the eyes, that are E. NARCO-INTERROGATION/NARCO-ANALYSIS/ ADMINISTRATION OF TRUTH SERUM associated with physiological arousal. - When these areas become warmer, they signal a reaction to the picture, word, or question that was presented. - One advantage is non-contact, it does not entail the - placing of sensors on the body unlike polygraph. - and on observing the responses and reactions of the Expensiveness is one disadvantage. subject on every question - J. GESTURE ANALYSIS - Examiner focuses on the formulation of the questions The instrument is responsible for detecting and recording changes in physiological responses of the Movement of hands, arms, legs, and head can subject, focusing on cardiovascular activity, skin communicate underlying emotions and attitudes resistance and respiration. - Shows a weak but positive effect in detecting deception - Suggests that gestures may help augment other TRUTH VS. LIE information but should not be used alone for deception detection TRUTH - K. USE OF ALCOHOLIC BEVERAGES - the recollection of a person Found effective by some investigators in obtaining facts from people who are reluctant to give information - Deliberate, complete, and objective communication of LIE Believes in vino veritas- “in wine there is truth” - Omission of information stated with an intent to deceive and mislead someone L. WORD ASSOCIATION TEST/ STIMULUS - PREVARICATION ASSOCIATION TEST - First devised by Francis Galton in 1870 - A group of words, objects or photographs are presented and the principle of time pressure is used. - There are to main criteria for detecting indications of deception: Incriminating Answer words 1. Derail - changing the subejct to avoid truth. 2. Confuse - quibble; use of ambiguity in order to deceive and Delayed Answer. - VARIATIONS OF LIE or mislead. 3. Misinform - perpetrate a false story. Interrogator will study the time interval and reaction of the subject. - Not reliable as a deception detection method because of: - A person like a recidivist and really guilty may TYPES OF LIE 1. defeat the test by lying. - The test requires the use of intelligence in concerned that it is a lie 2. answering questions - A nervous person who is innocent may have a BALD-FACED LIE/BOLD FACE LIE - obvious to all LIE OF OMISSION - missing out on important facts; failures to correct pre-existing misconceptions 3. long time interval in answering questions LIE-TO-CHILDREN - a platitude that may use euphemism; told to make the subject acceptable to children M. USE OF HYPNOTISM - 4. One of the most unreliable means because the subject is implications; often used to maintain harmony of under control of hypnotist friendship or in the office. Subject in this test are deprived of free will to think and 5. NOBLE LIE - a lie that gives benefits to others. speak freely, making all information inadmissible as 6. DIRECT DENIAL - creates an emotional sense of evidence in court. - WHITE / BENIGN LIE - to avoid harmful Hypnosis is the alteration of consciousness and disturbance 7. concentration in which the subject manifests a heightened suggestibility while awareness is maintained. LIE OF FABRICATION - most difficult type of lie that a subject could use in an interview. 8. LIE OF MINIMIZATION - telling the truth but not the whole truth. N. POLYGRAPHY 9. EMERGENCY LIE - strategic lie when telling the truth may be cause harm to the third party. 10. RED LIE - common to communist countries; meant to destroy other ideologies SEVEN COMMON SIGNS OF LYING 1. 11. BLUFFING - not usually seen as immoral; pretending to look you in the eye, during a certain part of the have capability or intention one does not. 12. DISSEMBLING LIE - NO EYE CONTACT. If someone is lying, they will not conversation. euphemism for lying; 2. downplaying one’s abilities, achievements or knowledge person’s tone, or a lot of stammering (umm, ah), or to appear modest; purpose is to harbor recognition or validation CHANGE IN VOICE. A change in the pitch of a throat clearing could indicate a lie. 3. UNUSUAL BODY LANGUAGE. If a person taps their 13. LIE OF EXAGGERATION - occurs when the most foot a lot, fidgets with their hands, raises shoulders, turns fundamental aspect of statement is true, but the degree away from you or brings their hand to their faces to which it is true is not correct; stretching the truth. (touching chin or nose) – if they act nervous or 14. JOCOSE LIE - meant in jest; usually understood as such by all present parties; Sarcasm. 15. PROMOTION/PUFFERY uncomfortable – could mean lying. 4. LIE - advertisements; that contradict each other, are inconsistent or don’t statements that are not credible. 16. BELIEF SYSTEMS sound quite right are usually part of a lie. 5. 17. LIE OF COMPLIMENT/ FALSE ASSURANCE - accusing you of lying. 6. KINDS OF LIAR 2. CHANGES SUBJECT EASILY. Chances are high that they’ll go right along with it when you change the PANIC LIAR - avoiding consequences of confession; afraid of embarrassment. OVERLY DEFENSIVE. They will become extremely defensive, refusing to answer any questions and even intended to please others 1. SOMETHING SOUNDS FISHY. Making statements subject. 7. OCCUPATIONAL LIAR - someone who has lied for HUMOR OR SARCASM. Guilty person often try to change the subject using humor or sarcasm. years; practical liar; lies when it has higher pay-off 3. TOURNAMENTAL LIAR - loves to lie; excited by the challenges of not being detected; views interview as another contest and wants to win; convicted but will not THEORY OF LIE DETECTION give satisfaction of hearing him/ her confess. 4. ETHNOLOGICAL LIAR - person taught not to be a ● squealer; loves to be interrogated; taken creed 5. There is no such thing as an instrument that will detect lies. PSYCHOPATIC LIAR - may cause death to others; no ● Lie Detector is somewhat misleading. conscience nor feeling of remorse. ● No collection of non-living objects, including the very finest and complicated modern computers can detect lies on the part of any human being. ● PSYCHOLOGY OF LYING - The body adapts itself as efficiently as possible to its environment. If the environment changes, the body will A person fears detection and possible exclusion by the rapidly adjust itself to these changes. offended community. - Risking one’s entire life; individual may display both With this understanding, it will be easy to follow the theory of lie internal and external reactions. These changes occur detection. beyond their ability to control or suppress, putting them - in a vulnerable position. - Self-defense mechanism When a person is being examined on the lie detector, all physiological activities are recorded simultaneously. - Examiner asks the subject a number of questions. - If any of the questions are considered by the subject to be threatening to his person, the subject’s body will automatically readjust to a change in environment. THEORY OF POLYGRAPH A. PSYCHOLOGICAL THEORY OF A LIE: emotional changes occur in a person causing physiological changes that can be recognized and diagnosed. B. PSYCHOLOGICAL SET OF A LIE: a person’s fears, anxieties and apprehensions are focused (directed) to the areas that hold (Poses) the greatest threat to his well-being or self. C. PSYCHOLOGY OF TEST QUESTIONS: the test is structured so as to pose a threat to the security of both the innocent and guilty subject and force him/her to focus (direct) his/her attention to that specific area of the test. FEAR is the greatest psychological factor - fear of being detected as an untruth.