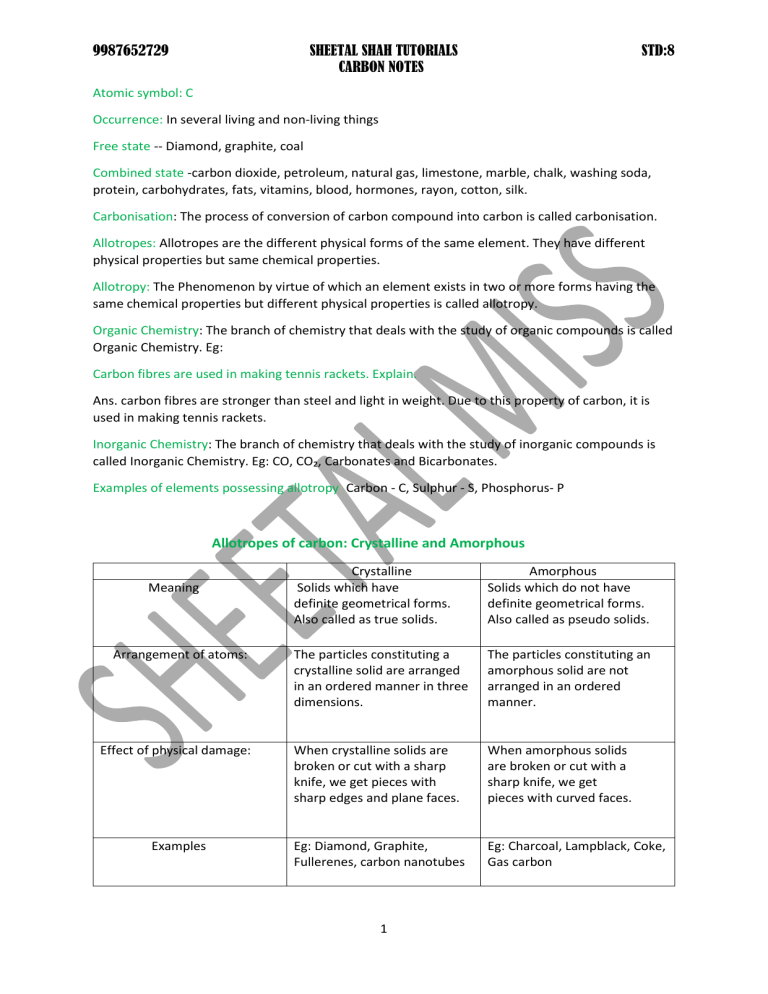
9987652729 SHEETAL SHAH TUTORIALS CARBON NOTES STD:8 Atomic symbol: C Occurrence: In several living and non-living things Free state -- Diamond, graphite, coal Combined state -carbon dioxide, petroleum, natural gas, limestone, marble, chalk, washing soda, protein, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, blood, hormones, rayon, cotton, silk. Carbonisation: The process of conversion of carbon compound into carbon is called carbonisation. Allotropes: Allotropes are the different physical forms of the same element. They have different physical properties but same chemical properties. Allotropy: The Phenomenon by virtue of which an element exists in two or more forms having the same chemical properties but different physical properties is called allotropy. Organic Chemistry: The branch of chemistry that deals with the study of organic compounds is called Organic Chemistry. Eg: Carbon fibres are used in making tennis rackets. Explain. Ans. carbon fibres are stronger than steel and light in weight. Due to this property of carbon, it is used in making tennis rackets. Inorganic Chemistry: The branch of chemistry that deals with the study of inorganic compounds is called Inorganic Chemistry. Eg: CO, CO₂, Carbonates and Bicarbonates. Examples of elements possessing allotropy: Carbon - C, Sulphur - S, Phosphorus- P Allotropes of carbon: Crystalline and Amorphous Crystalline Solids which have definite geometrical forms. Also called as true solids. Amorphous Solids which do not have definite geometrical forms. Also called as pseudo solids. The particles constituting a crystalline solid are arranged in an ordered manner in three dimensions. The particles constituting an amorphous solid are not arranged in an ordered manner. Effect of physical damage: When crystalline solids are broken or cut with a sharp knife, we get pieces with sharp edges and plane faces. When amorphous solids are broken or cut with a sharp knife, we get pieces with curved faces. Examples Eg: Diamond, Graphite, Fullerenes, carbon nanotubes Eg: Charcoal, Lampblack, Coke, Gas carbon Meaning Arrangement of atoms: 1 9987652729 SHEETAL SHAH TUTORIALS CARBON NOTES STD:8 PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF DIAMOND: Purest form of carbon. It is the hardest known natural substance. It is hard due to the presence of three dimensional rigid structure and strong bonds. Black diamonds are the hardest. It is transparent and colourless. Some are coloured due to the presence of impurities. Hardest substance known to us (can be cut only by another diamond) Rare occurrence (formed at high temperature and pressure that exists 150km below the earth’s crust) Insoluble in any solvent Density =3.51 g/cm³ Bad conductor of heat and electricity. Melting point 3550°C Cut diamond can bend back a great percentage of light falling on it. Diamond Sparkles Reason: Diamond has high refractive index- 2.5.it undergoes multiple reflections when light enters a Diamond and hence it sparkles. Found in Russia, USA, South Africa and Namibia. In India it is found at Panna in Madhya Pradesh and Wajrakarur in Andhra Pradesh. Kohinoor, Pitt diamond and Cullinan are natural diamonds. Some diamonds have distinct colours such as red, pink, blue, brown, green and tinged yellow. These colours are due to the presence of impurities such as traces of metal oxide and salts. These coloured diamonds are called gems, Black diamonds contain copper oxide as impurity. Although, they are not gems, they have important industrial applications. Diamonds are made artificially from graphite. Graphite is subjected to a very high temperature (about 3000°C) and pressure in the absence of air to from synthetic diamonds. STRUCTURE OF DIAMOND: Diamond has a giant molecular structure. There are four valence electrons in a carbon atom. Each carbon atom in the diamond crystal is linked to four other neighbouring carbon atoms by strong bonds and forms a rigid three dimensional tetrahedral structure. The four surrounding carbon atoms are at the four vertices (four corners) of a regular tetrahedron. This basic unit of a diamond crystal repeats itself and extends in all directions. It results in the formation of three dimensional rigid octahedral shape. 2 9987652729 SHEETAL SHAH TUTORIALS CARBON NOTES STD:8 USES OF DIAMOND 1) Making Jewellery: Diamond crystals, after polishing attains extraordinarily brilliant shine. It also has high refractive index. 2) Black diamonds are used for cutting glass and drilling rocks or for cutting tungsten wires which are used as filament in electric lamps. Diamond is the hardest natural substance and has very sharp edges with which cutting thin filament is possible. 3. Surgical tools: Sharp-edged diamond are used by eye surgeons as a surgical tool to remove cataract from eyes 4. Protective windows: Diamonds prevent the entry of harmful radiation. Hence they are used for making protective windows of space satellites 5. Thermometers: Diamonds are highly sensitive to heat rays. So they are used for making highly accurate thermometers. How to identify real diamond from artificial ones? Ans: Natural diamonds are transparent to X-rays whereas artificial diamonds are opaque to X-rays. PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF GRAPHITE Most stable allotrope of carbon Common in occurrence insoluble in any solvent Soft and slippery due to its sheet like structure. Greyish - black and lustrous crystalline solid. It leaves a black mark on paper. Density is 2.39g/cm³ Good conductor of heat and electricity Melting point is 3700°C Burns in air at 700 C ͦ to form carbon dioxide C + O₂→ CO₂ Found in Russia, India, Srilanka, Siberia. Jammu Kashmir, Rajasthan West Bengal Odisha and Bihar. 3 9987652729 SHEETAL SHAH TUTORIALS CARBON NOTES STD:8 Structure of graphite or The surface of graphite is soft and slippery. Explain. In graphite, each carbon atom is attached to 3 other carbon atom by strong bond to form flat hexagonal rings. Each layer is bonded to adjacent layers by weak forces. This allows each layer to slide over the other easily. USES OF GRAPHITE 1) Used as an electrode: graphite is a good conductor due to free electrons in it. 2) Used for making crucibles for casting metal/ in laboratories: Good conductor of heat and has a high melting point (3700 ͦC) 3) Used as the pencil lead: graphite it is soft, flaky and greyish -black. It is mixed with clay to make little hard. It gets transferred on paper due to friction between tip of pencil and paper surface. 4) Used in nuclear reactors as a moderator: Graphite is used to slow down or control the speed of neutrons in nuclear reactors. 5) Used as a lubricant in machines to reduce friction between machine parts: Powdered graphite is mixed with petroleum jelly to make grease which is used as lubricant. 6) Used for making pigments, polishes and paints to iron article: Mixture of graphite and linseed oil is greyish-black and lustrous and forms a protective layer. Comparison of the Properties of Diamond and Graphite (learn from text book) PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF FULLERENES It Is found in nature in small quantities. It is found in soot, interstellar dust (space between the stars), and geological formations on the Earth. It is soluble in many solvents. A large number of carbon atoms are held together in a cage-like structure in fullerenes. A fullerene containing sixty carbon atoms (C) is called Buckminster fullerene. It is named after an American architect Richard Buckminster Fuller who designed the domes similar to those of fullerene molecules. 4 9987652729 SHEETAL SHAH TUTORIALS CARBON NOTES STD:8 Properties of Fullerenes: 1. Fullerenes are of different colours. The colour depend upon the number of carbon atoms present in them. 2. Fullerenes are more reactive than diamond and graphite. Their cage-like structure breaks on heating upto 1000 °C. 3. They are soluble in organic solvents. 4. Their specific gravity is 1.8g/cm³ to 2.11g/cm³ 5. They do not conduct electricity and act as insulators. However, some of them act as superconductors at high temperature. Uses of Fullerenes: 1. They are used as dry lubricants and in cosmetics. 2. Some compounds of fullerenes are used as superconductors. 3. It plays a great role in nanotechnology. When the constituent particles of a substance are not arranged in a regular geometrical pattern and do not form a particular shape, the substance is called amorphous. The amorphous forms of carbon are coal, coke, charcoal, lamp black and gas carbon. Different forms of coal: 1. Peat: Peat is light brown in colour. It is formed in the first stage of formation of coal. It has 50-60% carbon content. 2. Lignite: Lignite is brown in colour. It is the second stage of formation of coal. It has more than 60% carbon. It is harder and has better burning efficiency than peat. 3.Bituminous: Bituminous is the third stage in the formation of coal. The carbon content is about 70%-90%. It is the most common type of coal used by the power plants and it is also used as household fuel. It produces both volatile and non-volatile substances on burning. 4. Anthracite: It is hard, dense and black. It contains more than 90% of carbon. It is the purest variety of coal. It takes time to catch fire. But, once it catches fire, it burns for a long time. 5 9987652729 SHEETAL SHAH TUTORIALS CARBON NOTES STD:8 USES OF COAL: 1. coal was used to produce steam to run the steam engine. 2. It is used in thermal power plants to produce electricity. 3. It is used in many houses in villages as a fuel to cook food in chulhas. 4. It is used in industries to produce organic compounds like benzene, naphthalene and aniline. 5. It is used to prepare coke, coal gas and coal tar. 6. It is used to manufacture drugs, synthetic textiles and perfumes. Define destructive distillation. Q: What is destructive distillation? Ans: The process of heating an organic substance strongly in the absence of air to break bigger molecule into smaller ones to get various useful products is called destructive distillation. Product of destructive distillation of wood: (1) Wood Charcoal (i) Wood tar (iii) Pyroligneous acid (iv) wood gas: (Combustible gases: carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, methane and hydrogen.) Refer to activity 3 on pg no. 128 Different products obtained by destructive distillation of coal are as follows: Refer to activity 3 on pg no. 127 1. Coke: It is a black and porous solid substance. It is almost pure form of carbon. It contains 98% carbon. Coke is obtained as a residue during destructive distillation of coal. It burns without smoke. However, it is not commonly used as household fuel because it is expensive. Uses of coke: There are two types of coke - hard and soft. Hard coke is light and lustrous. It is used in industrial furnaces. Soft coke is black and porous. It is used in household furnaces. (i) It is an essential raw material for the iron and steel industry. It is required to heat the furnace. (ii) It is also used as a reducing agent for the extraction of many metals from their ores. (ii) It is used to prepare metallic carbides, i.e calcium carbide. (iv) it is used in the manufacture of artificial graphite, water gas (CO + H₂) and producer gas (CO + N₂) 6 9987652729 SHEETAL SHAH TUTORIALS CARBON NOTES STD:8 2. Coal Tar: It is a black and thick liquid. It has an unpleasant smell. It is a mixture of different carbon compounds. Many chemical substances are obtained by the fractional distillation of coal tar. The chemical substances obtained by the fractional distillation of coal tar are used for manufacturing dyes, explosives, paints, varnishes, plastics, synthetic fibres and drugs. 3. Coal gas: Coal gas burns to produce heat. Thus, it is an excellent fuel. It is used as a fuel in industries situated near the coal producing plants. 4. Ammoniacal liquor: It is used to prepare fertilisers. CHARCOAL: There are three main types of charcoal depending upon the source of carbon compound: (1) Wood charcoal - Wood charcoal is black, porous and brittle solid. It is prepared by the destructive distillation of wood. Wood is converted into charcoal leaving behind volatile impurities like wood tar and wood gas. Physical properties of wood charcoal: 1. It is a soft, black and porous solid. 2. It is brittle and tasteless substance. 3 It is a poor conductor of heat and electricity. 4 It is porous and has a large surface area. This makes it a good adsorbent of gases and liquids. 5 t is porous. Thus, it holds air in the pores and floats on water. Activated wood charcoal. It is prepared by heating wood charcoal at 900 °C. This surface area of the charcoal increases greatly.1 kg of activated charcoal in powder form has a surface area of 1 km² .Hence, activated charcoal is much more active than wood charcoal. It is used as a catalyst to facilitate certain chemical reactions. 7 9987652729 SHEETAL SHAH TUTORIALS CARBON NOTES STD:8 USES OF WOOD CHARCOAL. 1. Fuel: Wood charcoal is used as a fuel. It is better fuel than wood for the following reasons: i) It produces more heat on burning as compared to burning of equal mass of wood. ii) It produces less smoke than wood and hence reduces air pollution. 2. Reducing agent: it is used in the extraction of metals from their metallic ores. 3 Gunpowder: It is used in making gunpowder (an explosive). Gunpowder is used in guns and rifles. 4 High adsorbing power: Wood charcoal is good adsorbent of gases and liquids. (i) it is used for making gas masks as it adsorbs harmful poisonous gases. (ii) It is used in tablets to cure indigestion and gastric problems. The tablets adsorb the gases produced in the stomach and thus, relieve gas pressure. (iii) It is used to remove colour from crude sugar and turns it white. (iv) It is used in water filters and removes bacteria from drinking water. (v) It adsorbs the foul smelling gas produced by decaying food particles in the mouth. Thus, it is used in ayurvedic dental powders. Bone charcoal - It is obtained by the destructive distillation of animal bones. The solid product in the retort is thoroughly washed with hydrochloric acid. Bone charcoal mainly contains calcium phosphate. It contains only 10-12% carbon. Carbon is separated from bone charcoal by treating it with hydrochloric acid. Hydrochloric acid dissolves the calcium phosphate. Carbon is filtered from the solution. In this form, it is called ivory black or bone black. Animal charcoal is highly porous and is a good adsorbent. Uses of animal bone charcoal 1.It is used in sugar industry as a decolourising agent to remove brown colour of cane sugar. It is also used for removing coloured impurities from solutions. 2. Ivory black is used in artistic paintings due to its deep black colour. 3. Animal charcoal is used to remove excess fluoride from water. Excessive intake of fluorinated water may cause dental fluorosis. 4. Animal charcoal is used in manufacturing a large number of phosphorus compounds. 5. Filter aquarium water: It is used to filter aquarium water. 8 9987652729 SHEETAL SHAH TUTORIALS CARBON NOTES STD:8 Sugar charcoal - Sugar charcoal is the purest form of amorphous carbon. It is made by heating sugar in the absence of air. It can also be obtained by dehydrating sugar with concentrated sulphuric acid. Uses of sugar charcoal: 1. Decolourising agent: It is used in the removal of coloured impurities from solutions. 2 Artificial diamonds: Sugar charcoal is used in the preparation of artificial diamonds. 3. Reducing agent: It is used as a reducing agent in the extraction of metals. Lamp black Lamp black is an amorphous form of carbon. It has 98-99 percent carbon. It is prepared by heating carbon rich substances like turpentine oil or kerosene oil in limited supply of air. The oil burns with a sooty flame. The smoke contains a large amount of free carbon. The black smoke collects in form of black powder. It is called lamp black or soot. Lamp black is used in our country as kajal. Uses of lamp black 1. Making various articles: It is used for making black shoe polish, black paints, black carbon papers, black ribbons used in typewriters, printer's ink and kajal. 2. Rubber industry: It is used in rubber tyres to increase their hardness and durability. 3. Gunpowder: It is used In the manufacturing of gunpowder. Gas Carbon During destructive distillation of coal or other organic matter (at high temperature), the carbon particles deposit on the walls of the container. These carbon particles are gas carbon. It is a greyish solid. It is a good conductor of electricity. Uses of gas carbon: 1.It is used for making carbon rods for arc lamps and electrodes of dry cells. 9 9987652729 SHEETAL SHAH TUTORIALS CARBON NOTES STD:8 General chemical Properties of Carbon 1. Affinity for Oxygen: Carbon has a great affinity for oxygen a) If the supply of oxygen is limited, it forms a poisonous gas carbon monoxide. Carbon monoxide oxidises further to form carbon dioxide. b) If it burns in excess of oxygen, it forms carbon dioxide. 2. Reducing Property: A reducing agent helps other substance to get reduced. Carbon has a great affinity for oxygen, thus a) it (coke and charcoal) acts as a reducing agent to obtain metals from metallic oxides. ZnO + C → Zn + CO FeO + 3C → 2Fe + 3CO SnO + 2C → Sn + 200 PbO + C → Pb + CO CuO + C → Cu + CO Metallurgy: The science of extracting metals from their ore and modifying them for use. b) It (coke) reduces steam to form water gas. Water gas is a great industrial fuel as both the components are combustible. C + H₂0 →H₂ + CO CARBON DIOXIDE: Occurence: 1. Found naturally as a mixture in air, about 0.03%, water and volcanic rocks. 2. Found in combined state in some minerals like lime stone/ marble (CaCO₃), Dolomite (MgCO₃.CaC0₃), Calamine(ZnCO₃) etc. Preparation of CO₂: 1. Burning Carbon based fuels: a) if the supply of oxygen is limited, it forms a poisonous gas carbon monoxide. Carbon monoxide oxidises further to form carbon dioxide. 2C+0₂ → 2CO (Carbon monoxide) 2C0 + O₂→ 2CO₂ 10 9987652729 SHEETAL SHAH TUTORIALS CARBON NOTES STD:8 b) If it burns in excess of oxygen, it forms carbon dioxide. 𝑖𝑔𝑛𝑖𝑡𝑒 C+ O₂ → CO₂ c) Burning of CNG (mainly methane) 2CH₄ + 2O₂ → 2CO₂ + 2H₂0 + ∆ d) Burning of LPG (mainly butane) 2C₄H₁₀ + 13O₂ → 8C0₂ + 10H₂0 + ∆ 2. Thermal decomposition of carbonates: (Na₂CO₃ and K₂CO₃ do not decompose) pg no. (132) 3. Action of an acid on a carbonate or bicarbonates. (pg no. 133) Reactants: Marble chip with hydrochloric acid Or sodium carbonate with sulphuric acid. CaCO₃ + 2HC1 → CaCl₂ + H₂0 +CO₂ + ∆ Na₂CO₃ + H₂SO₄ → Na₂SO₄ + H₂0 + CO₂ + ∆ Q: Can we use sulphuric acid with CaCO₃ marble chip for lab preparation of CO₂? Explain Ans: No, because calcium sulphate formed during the reaction is insoluble in water. It covers the marble chips and stops the reaction. Marble chips (CaCO₃) are preferred over other metallic carbonates to prepare CO₂……. because it is cheap and easily available. Carbon dioxide is fairly soluble in water. So it is not collected over water. Q: How is the impurity of HCl vapour are removed from the mixture of CO₂ & HCI? The impurity of HCl vapour can be removed by passing the mixture of CO₂ & HCI through water. HCl gas is highly soluble in water, hence dissolves in water leaving behind only gaseous carbon dioxide. 11 9987652729 SHEETAL SHAH TUTORIALS CARBON NOTES STD:8 Physical properties of CO₂ Density: colourless, odourless and non poisonous gas which is 1.5 times heavier than air. Dry ice: Gas carbon dioxide solidifies directly at -78°C to form dry ice. Solid CO; is used in cold storages. It is a sublime substance. It is used to produce a false effect of clouds on stage. Soda water: under high pressure CO₂ is highly soluble in water forming soda water or fizzy drink. When the cap is opened, the pressure gets released and dissolved C0₂ bubbles out vigorously forming Fizz. Chemical properties: 1. Combustion: CO₂ gas is neither combustible nor supports combustion. 2. Reaction with active metals: Active metals like Na, K or Mg abstracts oxygen from CO₂ and when burnt in the gas. 2Mg+ C0₂ → 2Mg0 + C Q-What happens when burning strip of magnesium metal is lowered in the jar containing CO₂ gas? Ans- The metal continues to burn in the gas. White smoky scales of magnesium oxide are deposited on the inner walls of the jar and some black carbon particles are also formed. 3. Reaction on litmus: CO₂ gas turns moist blue litmus paper red CO₂ gas turns moist blue litmus paper red. Give reason. Ans- C02 dissolves in water, to form carbonic acid. It is a weak acid hence turns moist blue litmus paper red. CO₂ + H₂0 → H₂CO₃ ( carbonic acid) 4.Reaction with metal oxides: CO₂ slowly reacts with metal oxides to form metal carbonates. Na₂O + CO₂ → Na₂C0₃ MgO + CO₂ → MgC0₃ 12 9987652729 SHEETAL SHAH TUTORIALS CARBON NOTES STD:8 5. Reaction with limewater: Limewater is a dilute solution of calcium hydroxide. limewater turns milky when CO2 gas is passed through it. This is because the insoluble, white salt calcium carbonate is formed. Ca(OH)₂ + CO₂ → CaC0₃ ↓ + H₂0 when an excess of CO₂ gas is passed through this milky liquid, the milkiness disappears. This is because the soluble, colourless compound calcium bicarbonate is formed. CaCO₃ + H₂0 + CO₂ → Ca(HCO₃) ₂ Milkiness reappears on boiling the clear liquid. This is because the bicarbonate, on being heated, decomposes back to give the carbonate which is insoluble. Ca(HC0₃)₂ → CaCO₃ + H₂0 + CO₂ Q- What do you observe when CO₂ gas is passed first little and then excess through lime water? Ans- lime water turns milky first ( due to formation of insoluble calcium carbonate) but on passing excess of CO₂ gas, it once again becomes clear (due to formation of soluble calcium bicarbonate). 6.Reaction with Alkalis: Carbon dioxide reacts with alkalis (like sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide) to produce salt and water. 2NaOH + CO₂ → Na₂CO₃ + H₂0 2KOH + CO₂ → K₂CO₃ + H₂0 Potassium hydroxide (caustic potash) and sodium hydroxide (caustic soda) can absorb a large amount of carbon dioxide Thus, they are used to remove carbon dioxide However, potassium hydroxide is preferred because of better absorbing capacity. On passing excess of carbon dioxide, respective bicarbonates are formed. Na₂C0₃ + C0₂ + H₂O → 2NaHCO₃ K₂CO₃ + CO₂ +H₂O → 2KHCO₃ 13 9987652729 SHEETAL SHAH TUTORIALS CARBON NOTES STD:8 Tests For Carbon Dioxide 1. When a burning matchstick is introduced in a gas jar containing carbon dioxide, it gets extinguished. 2. Carbon dioxide gas turns limewater milky. Uses of CO₂: 1) In the manufacture of washing soda and baking soda. Carbon dioxide is used in the manufacturing of baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) and washing soda (sodium carbonate). Mixture of sodium bicarbonate and potassium hydrogen tartarate forms baking powder. Baking powder is used to make cakes and bread spongy as it releases carbon dioxide. 2) For making fertilizer like Urea. 3) Used by plants during photosynthesis. 4) For making fizzy (aerated) drinks. 5) In the form of dry ice as a coolant and for creating smoky background on stage. 6) It is used in fire extinguisher. 7) In Hospitals: Carbon dioxide is used in the form of carbogen for artificial respiration. Carbogen is a mixture of 5% carbon dioxide and 95% oxygen. FIRE EXTINGUISHERS A fire extinguisher s a device used to extinguish fire. Carbon dioxide is used in this device to put off fire. The common types of fire extinguishers are: 1 Foam-type fire extinguisher –. In this type of fire extinguisher, Aluminium sulphate is made to react with sodium bicarbonate They react to produce carbon dioxide gas and aluminium hydroxide. A substance called saponin is added to sodium bicarbonate solution to produce a foam of carbon dioxide. The foam of carbon dioxide comes out through the nozzle that is directed towards the fire. This type of fire extinguisher is used to extinguish fires caused by petrol and kerosene. 6NaHCO₃ + Al₂(SO₄)₃ → 3Na₂SO₄ + 2Al(OH)₃ + 6CO₂ 14 9987652729 SHEETAL SHAH TUTORIALS CARBON NOTES STD:8 2. Soda-acid fire extinguisher – In this type of fire extinguisher, sulphuric acid is made to react with sodium bicarbonate to form carbon dioxide. 2NaHCO₃ + H₂S0₄ → Na₂SO₄+ 2H₂0 + 2C0₂(1) 3. Liquid-carbon dioxide fire extinguisher – In liquid carbon dioxide fire extinguisher, Carbon dioxide is stored in a steel cylinder under high pressure. When we open the valve of the cylinder, the pressure reduces and liquid carbon dioxide changes into dry ice. It is used to extinguish both oil-fed fires and electrical fires. Soda-acid and foam-type fire extinguishers cannot be used to put off electrical fire because in these fire extinguishers, water is also produced along with carbon dioxide. Water conducts electricity and may cause an electric shock. CO₂ gas is used in fire extinguisher. Give reason. Ans- CO₂ does not support combustion, it is heavier than air, so it settles down and displaces air from the vicinity of fire. Due to lack of supply of oxygen, fire gets extinguished. CARBON CYCLE The percentage of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is about 0.03%. It remains balanced through carbon cycle. Carbon dioxide is introduced in atmosphere and consumed continuously. Thus, the addition of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is balanced by its removal. 15 9987652729 SHEETAL SHAH TUTORIALS CARBON NOTES STD:8 Addition of Carbon Dioxide in The Atmosphere 1. By respiration of human beings, animals and plants 2. By decay of dead plants and animals 3. By combustion of fuels 4. By industries 5. By sea water when percentage of carbon dioxide increases in water 6. By volcanic eruptions Removal of Carbon Dioxide From The Atmosphere 1. By photosynthesis (plants use carbon dioxide to make their food) 2. By dissolution of carbon dioxide in water from atmosphere. Greenhouse effect: Warming up of the Earth's atmosphere due to the trapping of heat radiations by greenhouse gases in the atmosphere is called greenhouse effect. Greenhouse gas - A gas that traps heat in the environment and keeps the surroundings warm is known as a greenhouse gas. Eg. carbon dioxide, methane, chlorofluorocarbons, ozone, oxides of nitrogen and water vapour. Global warming – It is the rise in the average temperature of the earth's atmosphere. Effects of Global Warming 1.The average temperature of earth increases, 2. The polar ice caps and glaciers are melting. 3. Rise in sea level. 4. Submerging islands and coastal cities. 5. Change in the pattern of seasons 6. Acid rain 16 9987652729 SHEETAL SHAH TUTORIALS CARBON NOTES STD:8 Steps To Prevent Global Warming 1.Reducing the use of fossil fuels. 2. Using renewable source of energy like solar energy biogas etc. 3. Use filters in the chimneys of factories. 4. Grow more trees. CARBON MONOXIDE Occurrence: It does not occur freely in nature. It is formed due to incomplete combustion of fuels. It is found in tobacco smoke, coal gas and exhaust fumes of automobiles. It burns with the blue flame. Carbon monoxide is a highly poisonous gas, Give reason. Reason: As it is an odourless gas, it can spread undetected and therefore, is very dangerous. CO has 325 times greater affinity for Haemoglobin than that of oxygen. It forms carboxyhaemoglobin which reduces level of oxygen in blood. Therefore, adverse effects are seen due to cut off of supply of oxygen to the body cells. Properties of Carbon Monoxide 1. It is a colourless gas. 2. It has a faint odour and is highly poisonous gas. 3. It is a non-supporter of combustion. However, it is combustible and burns with a blue flame to form carbon dioxide. 4. It is sparingly soluble in water. 5. It does not decompose even at high temperatures because it is thermally stable. Reducing Action of Carbon Monoxide: It reduces the oxides of less reactive metals to their respective oxides. Examples pg no. 141 17 9987652729 SHEETAL SHAH TUTORIALS CARBON NOTES STD:8 1. Sleeping in a closed room with a coal fire is dangerous. Ans. Sleeping in a closed room with a coal fire is dangerous because coal burns with a limited supply of oxygen and produces carbon monoxide. When we inhale carbon monoxide, it combines with haemoglobin to form a very stable compound called carboxyhaemoglobin which reduces the oxygen carrying capacity of blood and results in headache and suffocation. It may even cause death. 2. Asphyxia is caused by severe lack of oxygen in the body. When the lack of oxygen is prolonged, it results in unconsciousness and can lead to death. Remedies For Carbon Monoxide Poisoning: 1. The victim should be given artificial respiration with carbogen (mixture of 95% Oxygen and 5% carbon). 2. The victim should be brought into open. Precautions To Prevent Carbon Monoxide Poisoning: When the concentration of carbon monoxide increases, we should wear gas masks that absorb carbon monoxide and oxidise it to carbon dioxide. Such masks are made of hopcolite. 18