REPUBLIC OF CAMEROON
REPUBLIQUE DU CAMEROUN
Peace-Work-Fatherland
Paix-Travail-Patrice
MINISTRY OF HIGHER
EDUCATION
MINISTRE DE L’ENSEIGNMENT
SUPERIEURE
UNIVERSITY OF BAMENDA
UNIVERSITE DE BAMENDA
COLTECH
COLTECH
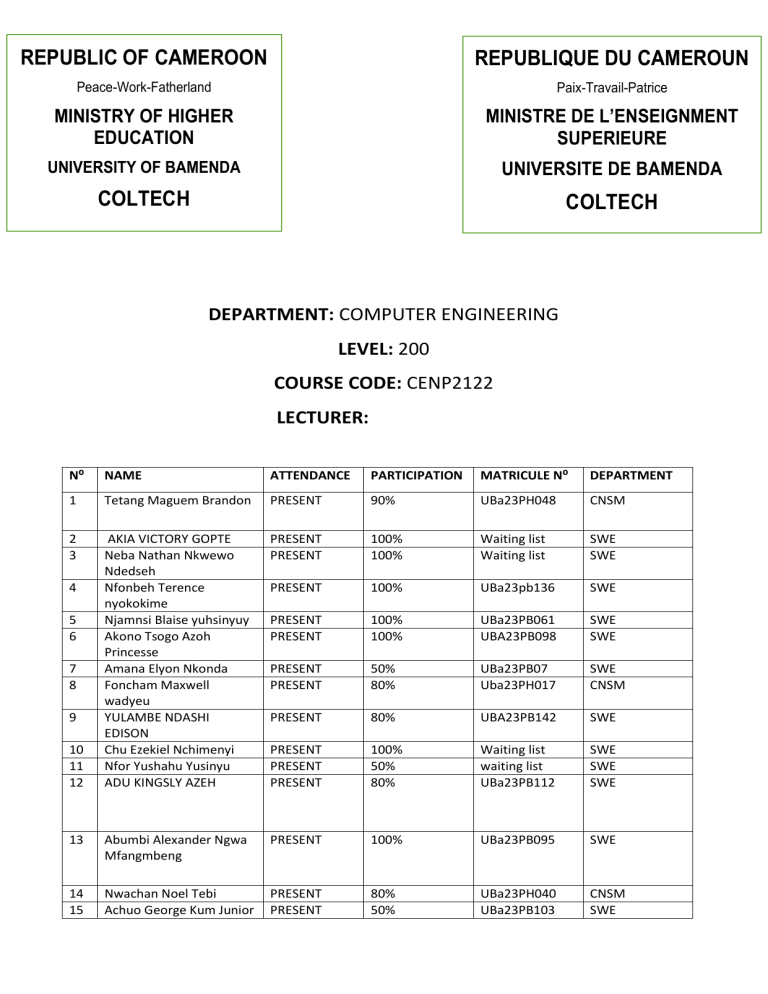
DEPARTMENT: COMPUTER ENGINEERING
LEVEL: 200
COURSE CODE: CENP2122
LECTURER:
N⁰
NAME
ATTENDANCE
PARTICIPATION
MATRICULE N⁰
DEPARTMENT
1
Tetang Maguem Brandon
PRESENT
90%
UBa23PH048
CNSM
2
3
AKIA VICTORY GOPTE
Neba Nathan Nkwewo
Ndedseh
Nfonbeh Terence
nyokokime
Njamnsi Blaise yuhsinyuy
Akono Tsogo Azoh
Princesse
Amana Elyon Nkonda
Foncham Maxwell
wadyeu
YULAMBE NDASHI
EDISON
Chu Ezekiel Nchimenyi
Nfor Yushahu Yusinyu
ADU KINGSLY AZEH
PRESENT
PRESENT
100%
100%
Waiting list
Waiting list
SWE
SWE
PRESENT
100%
UBa23pb136
SWE
PRESENT
PRESENT
100%
100%
UBa23PB061
UBA23PB098
SWE
SWE
PRESENT
PRESENT
50%
80%
UBa23PB07
Uba23PH017
SWE
CNSM
PRESENT
80%
UBA23PB142
SWE
PRESENT
PRESENT
PRESENT
100%
50%
80%
Waiting list
waiting list
UBa23PB112
SWE
SWE
SWE
13
Abumbi Alexander Ngwa
Mfangmbeng
PRESENT
100%
UBa23PB095
SWE
14
15
Nwachan Noel Tebi
Achuo George Kum Junior
PRESENT
PRESENT
80%
50%
UBa23PH040
UBa23PB103
CNSM
SWE
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
Exercise 1:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int a, b;
printf("Enter the first number (a): ");
scanf("%d", &a);
printf("Enter the second number (b): ");
scanf("%d", &b);
if (a == b) {
printf("a is equal to b\n");
} else if (a > b) {
printf("a is greater than b\n");
} else {
printf("a is less than b\n");
}
return 0;
}
Output
Enter the first number (a): 3
Enter the second number (b): 5
a is less than b
[Process completed - press Enter]
Exercise 2:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
void solveQuadratic(double a, double b, double c) {
double discriminant, root1, root2;
discriminant = b * b - 4 * a * c;
if (discriminant > 0)
root1 = (-b + sqrt(discriminant)) / (2 * a);
root2 = (-b - sqrt(discriminant)) / (2 * a);
printf("Two distinct real solutions:\n");
printf("Root 1 = %.2lf\n", root1);
printf("Root 2 = %.2lf\n", root2);
} else if (discriminant == 0) {
root1 = -b / (2 * a);
printf("One real solution (repeated root):\n");
printf("Root = %.2lf\n", root1);
} else {
printf("No real solutions.\n");
}
}
int main() {
double a, b, c;
printf("Enter the coefficients of the quadratic equation (a, b, c): ");
scanf("%lf %lf %lf", &a, &b, &c);
solveQuadratic(a, b, c);
return 0;
}
Output
enter the coefficients of the quadratic equation (a, b, c): 3 5 -7
Two distinct real solutions:
Root 1 = 0.91
Root 2 = -2.57
[Process completed - press Enter]
Exercise 3:
#include <stdio.h>
int xorGate(int a, int b) {
int result;
result = (a && !b) || (!a && b); // XOR gate logic
return result;
}
int main() {
int inputx, inputy, output;
// Prompt user to enter input x
printf("Enter input x (0 or 1)\n");
scanf("%d", & inputx);
// Prompt user to enter input y
printf("Enter input y (0 or 1)\n");
scanf("%d", &inputy);
// Call xorGate function to get the XOR result
output = xorGate(inputx, inputy);
// Display the output of the XOR gates
printf("Output: %d\n", output);
return 0;
}
Output
Enter input x (0 or 1)
0
Enter input y (0 or 1)
1
Output: 1
[Process completed - press Enter]
Exercise 4:
#include <stdio.h>
// Function to find the minimum of three values
int findMinimum(int a, int b, int c) {
int minimum;
if (a <= b && a <= c) {
minimum = a; // a is the smallest
} else if (b <= a && b <= c) {
minimum = b; // b is the smallest
} else {
minimum = c; // c is the smallest
}
return minimum;
}
int main() {
int a, b, c, minimum;
// Prompt the user to enter three values
printf("Enter value for a\n: ");
scanf("%d", &a);
printf("Enter value for b\n: ");
scanf("%d", &b);
printf("Enter value for c\n: ");
scanf("%d", &c);
// Call the findMinimum function to get the minimum value
minimum = findMinimum(a, b, c);
// Display the minimum value
printf("Minimum value: %d\n", minimum);
return 0;
}
Output
Enter value for a
: 12
Enter value for b
:5
Enter value for c
:7
Minimum value: 5
[Process completed - press Enter]
Exercise 5:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int number;
// Ask the user to enter an integer number between 1 and 50
printf(”Please enter an integer number between 1 and 50: “);
scanf(”%d”, &number);
// Check if the entered number is within the valid range
if (number >= 1 && number <= 50) {
printf(”You entered a valid number: %d\n”, number);
} else {
printf(”Invalid input: The number should be between 1 and 50\n”);
}
return 0;
}
Output:
Please enter an integer number between 1 and
50:
You entered a valid number: 30
Exited with status code: 0
Exercise 6:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main() {
int count = 0;
int sum = 0;
int sum_squares = 0;
int input;
while (count < 2) {
printf("Enter an integer between 1 and 9: ");
scanf("%d", &input);
if (input < 1 || input > 9) {
printf("Value is outside the allowed range. Please try again.\n");
continue;
}
count++;
sum += input;
sum_squares += input * input;
}
double average = (double)sum / count;
double root_mean_square = sqrt((double)sum_squares / count);
printf("Sum: %d\n", sum);
printf("Average: %.2f\n", average);
printf("Root Mean Square: %.2f\n", root_mean_square);
return 0;
}
Output
Enter an integer between 1 and 9: 4
Enter an integer between 1 and 9: 6
Sum: 10
Average: 5.00
Root Mean Square: 5.10
[Program finished]
Exercise 7:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int fatherAge;
int sonAge;
printf(”Enter the father’s age:\t\n”);
scanf(”%d”,&fatherAge);
printf(”Enter the som’s age:\t\n”);
scanf(”%d”,&sonAge);
if (sonAge >= fatherAge) {
printf(”Invalid input: Son’s age should be less than father’s age.\n”);
} else {
int years = 0;
while (fatherAge < 2 * sonAge) {
fatherAge++;
years++;
}
printf(”The number of years until the father’s age is double that of the son’s age: %d years.\n”,
years);
}
return 0;
}
Output:
Enter the father’s age:
25
Enter the som’s age:
15
The number of years until the father’s age is double that of the son’s age: 5 years.
Exited with status code: 0
Exercise 11: Casts
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
const char* sentence = "hello world!";
printf("%s\n", sentence);
// Casting the sentence pointer to an integer
int decimal_result = (int) sentence;
printf("%d\n", decimal_result);
return 0;
}
Output
hello
world!
1304
press
[Process
completed
Enter]
Exercise 12
#include <stdio.h>
void convertTime (int seconds)
{
int hours, minutes, remainingseconds;
hours = seconds/3600;
seconds %= 3600;
minutes = seconds/60;
remainingseconds = seconds % 60;
printf("%d seconds is equivalent to %d hours, %d minutes,
and %d
seconds.\n", seconds, hours, minutes,
remainingseconds);
}
int main ( ) {
int inputseconds ;
printf("Enter the number of seconds: ");
scanf("%d", &inputseconds);
convertTime (inputseconds);
return 0;
}
Output
Enter the number of seconds: 3665
65 seconds is equivalent to 1 hours, 1 minutes, and 5 seconds.
[Program finished]
Exercise 13: Constants and pi
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#define PI 3.14159
float computesurfaceArea(float raduis)
{
return PI * raduis * raduis;
}
int main()
{
float raduis;
printf("Enter the raduis of the disk: ");
scanf("%f", &raduis);
// using the constant value for pi
float area = computesurfaceArea(raduis);
printf("the surface area of the disk is : %.2f \n", area);
// using the M_PI from math.h
area = M_PI * raduis * raduis * raduis;
printf("the surface area of the disk using M_PI: %.2f\n", area);
return 0;
}
Output
Enter the raduis of the disk: 5
the surface area of the disk is : 78.54
the surface area of the disk using M_PI: 392.70
[Program finished]
Exercise 14:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int A, B, temp;
printf("Enter the value of A: ");
scanf("%d", &A);
printf("Enter the value of B: ");
scanf("%d", &B);
printf("\nBefore swapping: A = %d, B = %d\n",
A, B);
// Swapping using a temporary variable
temp = A;
A = B;
B = temp;
temp) to B
// Store the value of A in temp
// Assign the value of B to A
// Assign the saved value of A (in
printf("After swapping: A = %d, B = %d\n", A, B);
return 0;
}
Output
Enter the value of A: 2
Enter the value of B: 5
Before swapping: A = 2, B = 5
After swapping: A = 5, B = 2
[Process completed - press Enter]
Enter the value of A: 2
Enter the value of B: 5
Before swapping: A = 2, B = 5
After swapping: A = 5, B = 2
[Process completed - press Enter]
Exercise 15:
a) using 5 variables
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int num1, num2, num3, num4, num5;
int sum;
printf("Enter five integers: ");
scanf("%d %d %d %d %d", &num1, &num2, &num3, &num4, &num5);
sum = num1 + num2 + num3 + num4 + num5;
printf("Sum: %d\n", sum);
return 0;
}
Output
Enter five integers: 1,2,3,4,5
Sum: 2
[Process completed - press Enter]
b) Using 2 variables ( no memory of entries.kept )
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int num;
int sum = 0;
int count;
printf("Enter the number of integers: ");
scanf("%d", &count);
printf("Enter %d integers:\n", count);
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
scanf("%d", &num);
sum += num;
}
printf("Sum: %d\n", sum);
return 0;
}
Output
Enter the number of integers: 4
Enter 4 integers:
5,-4,3,1
Sum: 20
[Process completed - press Enter]
Exercise 16:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main() {
int x1, y1, x2, y2;
double distance;
//
Read
the
coordinates
of the first
point
printf("Enter the coordinates of the first point [X1, Y1]:
");
scanf("%d %d", &x1, &y1);
// Read the coordinates of the second point
printf("Enter the coordinates of the second point [X2, Y2]: ");
scanf("%d %d", &x2, &y2);
// Calculate the distance between the two points
distance = sqrt(pow(x2 - x1, 2) + pow(y2 - y1, 2));
// Display the result
printf("The distance between the two points is: %.2lf\n", distance);
return 0;
}
Output
Enter the coordinates of the first point [X1, Y1]: 8 9
Enter the coordinates of the second point [X2, Y2]: 6 7
The distance between the two points is: 2.83
[Process completed - press Enter]
Exercise 17:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int in[4];
int results[4];
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
printf("Enter binary number %d (0 or 1): ", i+1);
scanf("%d", &in[i]);
}
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
results[i] = in[i] ^ in[i+1];
}
printf("--------------------------------------------\n");
printf("| X | Y | Result |\n");
printf("--------------------------------------------\n");
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
if (i < 2) {
printf("| %7d | %7d | %6d |\n", in[i], results[i], in[i+1]);
} else {
printf("| %7d | %7d | %6d |\n", in[i], results[i], in[i+1]);
}
}
printf("--------------------------------------------\n");
return 0;
}
Output
Enter binary number 1 (0 or 1): 0
Enter binary number 2 (0 or 1): 0
Enter binary number 3 (0 or 1): 1
Enter binary number 4 (0 or 1): 1
-------------------------------------------| X | Y | Result |
-------------------------------------------|
0|
0|
0|
|
0|
1|
1|
|
1|
0|
1|
|
1|
1|
0|
----------------------------------------
Exercise 18
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main() {
double a, b, c,
discriminant, root1,
root2;
printf("Enter the coefficient a: ");
scanf("%lf", &a);
printf("Enter the coefficient b: ");
scanf("%lf", &b);
printf("Enter the coefficient c: ");
scanf("%lf", &c);
discriminant = (b * b) - (4 * a * c);
if (discriminant > 0) {
root1 = (-b + sqrt(discriminant)) / (2 * a);
root2 = (-b - sqrt(discriminant)) / (2 * a);
printf("Two distinct real roots exist: %.2lf and %.2lf\n",root1,root2);
} else if (discriminant == 0) {
root1 = root2 = -b / (2 * a);
printf("One real root exists: %.2lf\n", root1);
} else {
printf("No real roots exist.\n");
}
return 0;
}
Output 1
Enter the coefficient a: 3
Enter the coefficient b: 5
Enter the coefficient c: 7
No real roots exist.
Output 2
Enter the coefficient a: -1
Enter the coefficient b: -6
Enter the coefficient c: 8
Two distinct real roots exist: -7.12 and 1.12
Exercise 20:
#include <stdio.h>
int get_multiplication_sign(int A, int B) {
/*
Determine the sign based on the following rules:
- If both A and B have the same sign (both positive or both negative), the product is positive.
- If A and B have different signs (one positive and one negative), the product is negative.
- If either A or B is zero, the product is zero.
*/
if (A == 0 || B == 0) {
return 0; // If either A or B is zero, the product is zero.
} else if ((A > 0 && B > 0) || (A < 0 && B < 0)) {
return 1; // If both A and B have the same sign, the product is positive.
} else {
return -1; // If A and B have different signs, the product is negative.
}
}
int main() {
int A, B;
printf("Enter the value of A: ");
scanf("%d", &A);
printf("Enter the value of B: ");
scanf("%d", &B);
int sign = get_multiplication_sign(A, B);
printf("The sign of the multiplication of %d and %d is %d (1 for positive, -1 for negative, 0 for
zero).\n", A, B, sign);
return 0;
}
Output
Enter the value of A: 4
Enter the value of B: 8
The sign of the multiplication of 4 and 8 is 1 (1 for positive, -1 for negative, 0 for zero).
[Process completed - press Enter]
Exercise 23:
#include <stdio.h>
int calculateDayOfWeek(int day, int month, int year) {
int m1 = (month >= 3) ? month - 2 : month + 10;
int a1 = (month >= 3) ? year : year - 1;
int ns = a1 / 100;
int as = a1 % 100;
int fn = day + as + as/4 - (2*ns) + ns/4 + (26*m1 - 2)/10;
int dayOfWeek = fn % 7;
return dayOfWeek;
}
int main() {
int j, m, a;
printf("Enter day of the month: ");
scanf("%d", &j);
printf("Enter month of the year: ");
scanf("%d", &m);
printf("Enter year: ");
scanf("%d", &a);
int dayOfWeek = calculateDayOfWeek(j, m, a);
printf("The day of the week is: %d\n", dayOfWeek);
return 0;
}
Output
Enter day of the month: wednesday
Enter month of the year: Enter year: The day of the week is: 4
[Process completed - press Enter]
Exercise 24:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
// Assume the number is prime initially
int number, isPrime = 1;
// Taking input for the positive integer
printf("Enter a positive integer less than 1000: ");
scanf("%d", &number);
// Checking if the number is prime
if (number <= 1) {
// Numbers less than or equal to 1 are not prime
isPrime = 0;
} else {
for (int i = 2; i < number; i++) {
if (number % i == 0) {
// If the number is divisible by any number
//other than 1 and itself, it's not prime
isPrime = 0;
break;
}
}
}
// Displaying the result
if (isPrime) {
printf("%d is a prime number.\n", number);
} else {
printf("%d is not a prime number.\n", number);
}
return 0;
}
Output 1
Enter a positive integer less than 1000: 2
2 is a prime number.
[Process completed - press Enter]
Output 2
Enter a positive integer less than 1000: 4
4 is not a prime number.
[Process completed - press Enter]
Exercise 25:
#include <stdio.h>
unsigned long long factorial(int n) {
if (n < 0) {
printf("Factorial is not defined for negative numbers.\n");
return 0;
}
unsigned long long result = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
result *= i;
}
return result;
}
int main() {
int n;
printf("Enter a non-negative integer: ");
scanf("%d", &n);
unsigned long long fact = factorial(n);
printf("Factorial of %d is %llu\n", n, fact);
return 0;
}
Output 1
Enter a non-negative integer: 6
Factorial of 6 is 720
[Process completed - press Enter]
Output 2
Enter a non-negative integer: -4
Factorial is not defined for negative numbers.
Factorial of -4 is 0
[Process completed - press Enter]
Exercise 21:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int num;
printf("Enter a number: ");
scanf("%d", &num);
if (num % 2 == 0) {
printf("%d is even.\n", num);
} else {
printf("%d is odd.\n", num);
}
return 0;
}
Output 1
Enter a number: 6
6 is even.
[Process completed - press Enter]
Output 2
Enter a number: 5
5 is odd.
[Process completed - press Enter]
Exercise 22:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int number;
// Using if-else
printf("Enter an integer: ");
scanf("%d", &number);
if (number > 0) {
printf("Sign using if-else: 1\n");
} else if (number < 0) {
printf("Sign using if-else: -1\n");
} else {
printf("Sign using if-else: 0\n");
}
// Using switch
switch ((number > 0) - (number < 0)) {
case 1:
printf("Sign using switch: 1\n");
break;
case -1:
printf("Sign using switch: -1\n");
break;
default:
printf("Sign using switch: 0\n");
}
// Using ternary operator
int sign = (number > 0) ? 1 : (number < 0) ? -1 : 0;
printf("Sign using ternary operator: %d\n", sign);
return 0;
}
Output
Enter an integer: 5
Sign using if-else: 1
Sign using switch: 1
Sign using ternary operator: 1
[Process completed - press Enter]
Exercise 26:
# include <studio.h>
double powerUsingFor (double x, int n) {
double result = 1.0;
int i
for (i = 0; i <
result X;
RUN
return result
double powerUsingwhile(double x, int n) {
double result = 1.0;
int i = 0;
while (i < n) {
result *= x;
return result;
double powerUsingDoWhile(double x, int n) {
double result = 1.0;
int i = 0;
do § result *= x;
} while (i < n);
return result;
int main) {
double x = 2.0:
int n = 5;
printf("Using for loop: %1fin", powerUsingFor (x, n)); printf("Using while loop: %1fin", powerUsinghhile(x, n));
printf("Using do-while loop: %lf\n", powerUsingDoWhile(x, n))
Output
Enter the time in seconds: 40000
40000 seconds is equivalent to 11 hours, 6 mi
nutes and qU seconds
[Process completed - press Enter]




