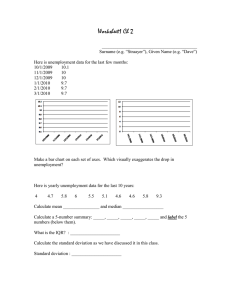
LABOUR MARKET: CONCEPT OF UNEMPLOYMENT LESSON OBJECTIVES: Key Words: 1. To define unemployment Unemployment rate 2. To list and explain types of unemployment Self-employment 3. To outline the causes and consequences of unemployment 4. To outline the solutions to the problem of unemployment DEFINITION OF UNEMPLOYMENT • It is defined as a situation in which persons of working age, able and willing to work are unable to find paid employment. Unemployment is the stock of all those individuals who are not engaged in any productive activity and who are either unable to find work at the prevailing real wage or which are in the process of switching to a new job. UNEMPLOYMENT RATE • Unemployment rate is the percentage of the labour force that is unemployed but actively seek employment with the willingness to work. 𝑁𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟 𝑜𝑓 𝑢𝑛𝑒𝑚𝑝𝑙𝑜𝑦𝑒𝑑 𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑠𝑜𝑛𝑠 • Unemployment rate = 𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑛𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟 𝑜𝑓 𝑤𝑜𝑟𝑘𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝑝𝑜𝑝𝑢𝑙𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑋 100 1 • Example: A country has a working population or labour force of 4.8 million of which 3.6 million people are employed. Calculate the unemployment rate of the country. • Solution: • Labour force = 4.8 million • No of employed = 3.6 million • No of unemployed = 4.8m - 3.6m = 1.2m 𝑁𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟 𝑜𝑓 𝑢𝑛𝑒𝑚𝑝𝑙𝑜𝑦𝑒𝑑 𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑠𝑜𝑛𝑠 • Unemployment rate = 𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑛𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟 𝑜𝑓 𝑤𝑜𝑟𝑘𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝑝𝑜𝑝𝑢𝑙𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑋 • Unemployment rate = • 1.2 4.8 𝑋 = 25% 100 1 100 1 CLASS WORK • If the labour force of a country is 2.5 million and 2 million are employed , what is the unemployment rate? • (WAEC 2011, objectives No27) TYPES OF UNEMPLOYMENT 1. Structural Unemployment: Arises as a result of changes in the pattern of demand of certain commodity leading to changes in industrial structures. This calls for readjustment in production pattern. It takes time for readjustment and some workers will be asked to leave. 2. Cyclical Unemployment. Occurs during the depression or recession stage of the business or trade cycle. During this time, demand is very low so business wants to adjust to decrease in demand and lay off some workers. 3. Seasonal Unemployment: People are employed in one season and unemployed in another season. 4. Residual Unemployment.Arises as a result of physical or mental disabilities some could not get job. 5. Disguised Unemployment:This is the same as under-employment i.e. when a worker is not working in his full capacity. 6. Frictional Unemployment. People are unemployed because they have no information of employment opportunities elsewhere. It is a time lag between losing one job and getting another one. 7. Voluntary Unemployment: Arises from the deliberate refusal of labour to work, even though employment opportunities exist. 8. Casual Unemployment: Involves jobs that are not permanent. This is common with the unskilled type of labour, e.g. part time jobs. CAUSES OF UNEMPLOYMENT 1. Inadequate educational system 2. Lack of industrial growth: 3. More people than available jobs 4. Immobility of labour 5. Wage rate 6. Seasonal changes 7. Choice of technology 8. Inadequate demand for goods services (deficiency in demand CONSEQUENCES OF UNEMPLOYMENT 1. Increase in crime rate 2. Threat to peace and stability 3. Reduction in investment 4. Emigration 5. Waste of human resources 6. High rate of dependency 7. Loss of potential output SOLUTIONS TO THE PROBLEM OF UNEMPLOYMENT 1. Industrialization 2. Population control 3. Encouraging geographical mobility of labour 4. Re-designing educational system 5. Proper development plans 6. Expansionary fiscal policy: 7. Diversifying the economy 8. Improvement in the provision of high standard infrastructure 9. Creating an enabling investment environment 10. Encouraging self-employment CONCEPT OF SELF-EMPLOYMENT • The Meaning of Self Employment: • Self-employment refers to the status of an individual who instead of accepting a position as an employee of another person or organization, chooses to go into business for himself or herself. ADVANTAGES OF SELF EMPLOYMENT 1. Freedom to work without supervision 2. Flexibility in working hours 3. Your success is based on you 4. You are the boss and you need no other boss 5. You are able to pursue your own dreams and goals DISADVANTAGES OF SELF EMPLOYMENT 1. Uncertain levels of income 2. Long working hours 3. Isolation 4. The need to fund one's own retirement plans HOMEWORK • Outline 10 factors to consider before embarking on self-employment.