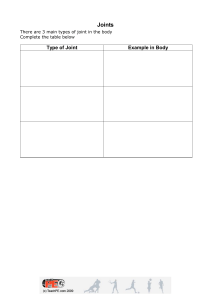
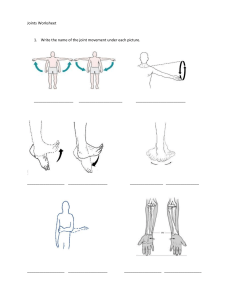
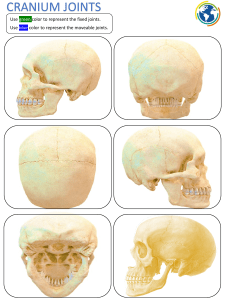
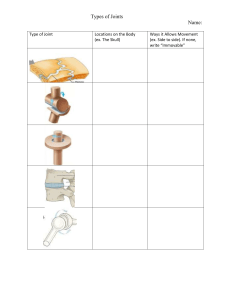
Movement Lesson 1 COURSE LEARNING OUTCOME Students should be able to meet the following intended learning outcomes: ●To gain knowledge and understanding of the different types of joints in the body, and to learn their structure. ●To explain the movement, giving Practical examples of what movement is uses during specific actions. Demonstrate the different types of body movements. Movement is the change in the position of a body part with respect to the whole body. It is one of the significant features of all living beings. The blinking of the eyes, breathing, eating are all examples of movement. So we can say that every second some or the other part of our body exhibits some or other kind of movements. The human body movements get polished as we grow in age. The movement starts from crawling and with the increase in age the person starts walking leading to the movement of the whole organism. Joints Joints are points in our body where two or more skeleton parts are connected. Different joints help our body carry out different activities and movements. FUNCTIONAL CLASSIFICATION OF JOINTS STRUCTURAL CLASSIFICATION OF JOINTS FIBROUS JOINTS Fixed joints, also called immovable joints, are found where bones are not flexible. In such joints, bones have been fused together in such a way that they are fixed to that part, most commonly to create a structure. A prominent example of a fixed joint is the skull, which is made up of a number of fused bones. Examples upper jaw, rib cage, backbone, and pelvic bone, etc CARTILAGINOUS JOINTS Cartilaginous joints are partly movable joints comprising of symphysis or synchondrosis joints. These joints occur only in those regions where the connection between the articulating bones is made up of cartilage. Synchondrosis are temporary cartilaginous joints which are present in young children and last until the end of their puberty. Examples spinal column and the ribcage. SYNOVIAL JOINTS The synovial joints are the most common type of joint because this joint helps us to perform a wide range of motion such as walking, running, typing and more. Synovial joints are flexible, movable, can slide over one another, rotatable and so on. Example These joints are found in our shoulder joint, neck joint, knee joint, wrist joint, etc. ACTIVITY 1.Why learning fundamental movements so important? 2.Aside from the above mentioned fundamental movement patterns, identify atleast 5 movement patterns that are evident in your day-to-day life activities and describe each.