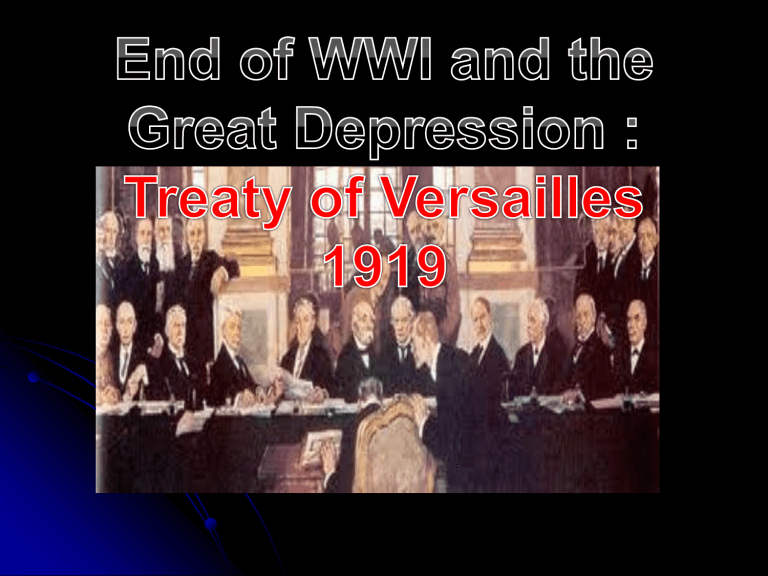
A Review • Russia left the war by 1917, as the Communist Revolution of Lenin’s Bolsheviks took hold • War of Attrition continued (more than 9 million soldiers died and huge amounts of products were expended in the war efforts) • USA entered the war, with fresh men and resources in late 1917 •Germany decided to surrender from a position of strength (it could have still kept fighting!) Goal: get good treaty results •Kaiser is no longer the emperor of Germany! Abdicated and exiled. •Weimar Republic of Germany, the new democratic government. The Treaty of Versailles In Paris 1919, the leaders of the victorious countries met to discuss peace settlement. They were dominated by “The Big Three.” Germany and Russia were not invited to the peace conference. Georges Clemenceau [France] David Lloyd-George [Great Britain] Woodrow Wilson [USA] Treaty of Versailles Allies have a desire to “get back at Germany” = reparations Flaws in the treaty sowed the seeds of postwar international problems that eventually lead to WWII Treaty humiliated Germany War-Guilt Clause-forced Germany to admit sole responsibility for starting WWI No way Germany could pay the bill- $33 Billion Dollars!!!!! Russia was excluded from the peace conference and lost more territory than Germany (Russia had the most causalities in war and fought for 3 years) Some believed treaty was too harsh Officially signed on June 28, 1919-- !!! 1914 1919 When did Germany make the last payment for it’s WWI reparations? October th 10 …. Guess The Year …2010 The German’s made the final payment of 60 million dollars on th October 10 , 2010. Discontent Germans were bitter! Arabs upset that Ottoman rule was replaced by British and French control rather than independence (Mandate System) Colonial people who fought in the war were angry that their nations remained colonies (wanted nation-states). What is the political message of this cartoon? What is being represented by the ‘hand’? ‘Who’ / or, ‘what’ is the man representing? What does the plank represent THE FINISHING TOUCH Vengeance! German Nation Today in the Hall of Mirrors of Versailles the disgraceful Treaty is being signed. Do not forget it! The German people will with unceasing labour press forward to reconquer the place among nations to which it is entitled. Then will come the vengeance for the shame of 1919. From the ‘Deutsche Zeitung’ [‘The German Express’] newspaper. Only fools, liars and criminals could hope for mercy from the enemy. In these nights hatred grew in me, hatred for those responsible for the dead. By Adolf Hitler, who had served in the army. Wilson Presents His Plan Fourteen Points-Plan for World Peace 14 Points = document giving 14 points to ensure peace after WWI’s end Self-determination- what is this? League of Nations The League of Nations Encourage cooperation Stop aggression AIMS Disarmament Improve social conditions Powers of the League If a country ignored the ruling of the League it could: Put pressure on Refuse to trade - sanctions Send in troops (but no fighting) member countries join together Many countries supported it in early days - they wanted peace U.S. Response A few felt that the League of Nations threatened US isolationism and the constitutional right of Congress to declare war Wilson set out in the US and spoke about the League of Nations Became ill on October 2, 1919 and suffered a stroke US Senate rejected the League of Nations and signed a separate treaty w/ Germany in 1921 Membership 42 members - by 1930’s 59 Defeated countries could not join (e.g. Germany) Russia excluded because communist USA did not join - isolation from world affairs A club for the victorious? Weaknesses of League USA didn’t join No real power - relied on goodwill and persuasion No permanent army Disarmament not realistic Structure a disaster - everyone had to agree before any action taken!!! The Great Depression Financial Crisis In Germany Inflation •During the war the German gov’t didn’t raise taxes •Government simply printed money to pay for wartime expenses • This drastically lowered the value of the peoples’ money. The Cost of Bread in the German Weimar Republic 1918- less than 1 mark 1922- 160 marks 1923- 200 billion marks Causes of the Global Great Depression WWI Ends, production shrinks, men become unemployed - European countries in debt to US - Germany cannot pay reparations or the loans for the reparations High inflation 2. Crash of the U.S. stock market - Panic about the economy 3. Overproduction Mass production plus shrinking wages after WWI meant factories couldn’t sell all of the goods they made Example: Unemployment reached 50% in Germany and 36% in USA 1. Capitalism Challenged Major result of the Great Depression = capitalist countries were challenged and criticized Capitalist countries = claimed the economy would regulate itself and self-correct itself if any problems arose But this wasn’t happening during the Great Depression The Great Depression: Capitalism Challenged Some countries became interested in communism and looked twice at the Soviet Union USSR continued to experience economic growth throughout the Depression because of 5 Year Plans (centralized gov’t control) III. Government Reactions Some governments became less laissez faire Governments that held colonies exploited them even more to try to improve their own economy Governments of non-industrial countries became even stronger autocratic gov’t’s to try to keep control Ex: Latin America- military officers (caudillos) seized power







