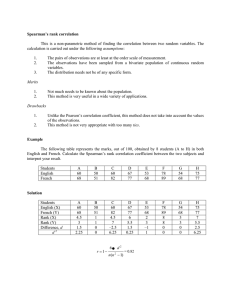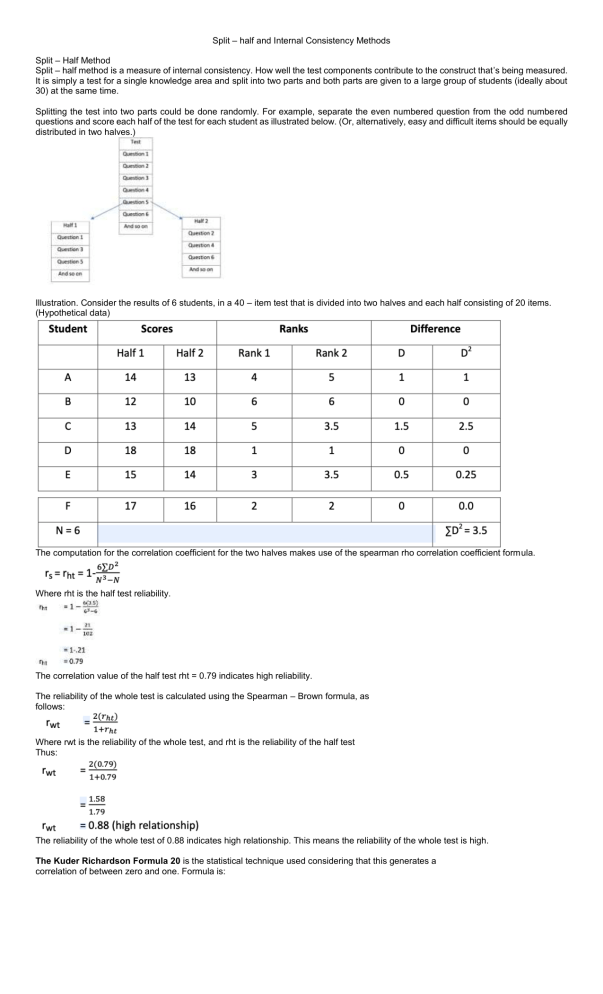
Split – half and Internal Consistency Methods Split – Half Method Split – half method is a measure of internal consistency. How well the test components contribute to the construct that’s being measured. It is simply a test for a single knowledge area and split into two parts and both parts are given to a large group of students (ideally about 30) at the same time. Splitting the test into two parts could be done randomly. For example, separate the even numbered question from the odd numbered questions and score each half of the test for each student as illustrated below. (Or, alternatively, easy and difficult items should be equally distributed in two halves.) Illustration. Consider the results of 6 students, in a 40 – item test that is divided into two halves and each half consisting of 20 items. (Hypothetical data) The computation for the correlation coefficient for the two halves makes use of the spearman rho correlation coefficient formula. Where rht is the half test reliability. The correlation value of the half test rht = 0.79 indicates high reliability. The reliability of the whole test is calculated using the Spearman – Brown formula, as follows: Where rwt is the reliability of the whole test, and rht is the reliability of the half test Thus: The reliability of the whole test of 0.88 indicates high relationship. This means the reliability of the whole test is high. The Kuder Richardson Formula 20 is the statistical technique used considering that this generates a correlation of between zero and one. Formula is: Where rxx = correlation coefficient N = number of items SD2 = variance ∑piqi = the sum of the product of pi and qi, where pi = proportion of passing item i qi = proportion of failing item I, and qi = 1 – pi (Legend: 1 – correct answer; 0 – incorrect answer) Computation for pi & qi: Computation for variance, SD2 Computing for the correlation coefficient value The reliability coefficient of 0.85 indicates a high relationship. Thus this means that the test is highly reliable.