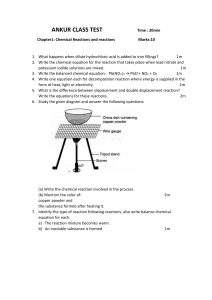
ONE- DIMENSIONAL KINEMATICS WATCH,LISTEN AND LEARN!! How well do you know these? ● ● ● ● What is motion? How are the different types of motion illustrated graphically? what equation are useful in solving different types of motion problems? How can the motion of different objects be represented and solved? ● To understand better the language of kinematics, lets review the six parameter of motion: distance,displacement, speed, velocity,acceleration, and time . Remember that distance, speed and time are scalars; while displacement, veloity, and acceleration are vectors quantities. The Motion of an object along straight path describe in one dimension. ● Distance and Displacement Distance is the total length cover from where the motion started. Dispalcement is the length of the line drawn from the object’s origin to it’s final position ,which indicate the overall direction of motion. It involves the starting position to serve as the reference point. How do we measures these two quantities? Consider the motion of a runner moving in a rectangular track as an example. 20 cm 3 10 cm 4 2 10 cm 1 20 cm Figure 3.1 The path (1-4) of a runner moving is a rectangular track 1. Distance and displacement from the origin to the end of path 1 Runner covered 20m. In this case, both distance and and displacement have a magnitude of 20m. The displacement now bears the direction to the right and should be complete described as 20m to the right. 2.Distance and displacement from the origin to the end of path 2. in this case, the total distance covered and the displacement are different. the total distance covered is simply the sum of the distance in path 1 and 2. 𝒅𝒕 = 𝒅𝟏 + 𝒅𝟐 𝒅𝒕 = 𝟐𝟎𝒎 + 𝟏𝟎𝒎 𝒅𝒕 = 𝟑𝟎𝒎 In getting the displacement, we use the concept of vector addition. To determine the resultant vector, we use Pythagorean theorem. 3. Distance and displacement from the origin to the end of path 3. We shall repeat the steps in the previous item, adding into the equation the distance covered by the runner from the end of path 2 to the end of path 3. 𝒅𝒕 = 𝒅𝟏 + 𝒅𝟐 + 𝒅𝟑 𝒅𝒕 = 𝟐𝟎𝒎 + 𝟏𝟎𝒎 + 𝟐𝟎𝒎 𝒅𝒕 = 𝟓𝟎𝒎 4. Distance and Displacement from the origin to the end of path 4. Add the total distance of each path. 𝒅𝒕 = 𝒅𝟏 + 𝒅𝟐 + 𝒅𝟑 + 𝒅𝟒 𝒅𝒕 = 𝟐𝟎𝒎 + 𝟏𝟎𝒎 + 𝟐𝟎𝒎 + 𝟏𝟎𝒎 𝒅𝒕 = 𝟔𝟎𝒎 Since the end point of path 4 is the same as the origin, the total displacement from the origin to the end of path 4 is zero. Thank you