Entrance Note
Numbers
1. Integers
{…,−3,−2,−1,0,1,2,3,…}
2. Whole Number
{ 0,1,2,3,…}
3. Nature Number
{ 1,2,3,…}
4. Fraction
5. Rational
6. Irrational
7. Real Number
{
�� �
, , ,0.5,…}
�� �
�
� ��
{− ,0.54, , ,…}
�
{ e, �,�,
�
� �
−�� ,−7.4512,..}
{ −2,0,2.4,13,π,..}
8. Prime Number
{ 2,3,5,7,11,13,17,19,23,29,31,37,41,43,47,53,59,61,67,71,73,
79,83,89,97} E.g- 5 has factors 1,5 | 13 has factors 1,13
9. Composite Number
{ 4,6,8,9,10,12,14,15,16,18,20,…}
10. Positive Integer
{ 1,2,3,…}
11. Negative Integer
{ −1,−2,−3,…}
12. Non Positive Integer
{ 0,−1,−2,−3,…}
13. Non Negative Integer
{ 0,1,2,3,…}
14. Consecutive Integer
n,(n+1),(n+2),(n+3),…
15. Consecutive Odd Integer
3,5,7,9,….
16. Consecutive Even Integer
2,4,6,8,….
Rules For Fractions
Addition Fractions
�
�
�
+ =
�
�+�
�
�
�
Subtracting Fractions
�
+ =
�
��+��
��
�
�
�
− =
�
�−�
�
�
�
�
− =
�
��−��
��
Multiplying Fractions
Dividing Fractions
�
× � = �∙�
�
�
�∙�
Comparing Fractions Size
÷�=�×� =
�
Converting Fractions to Percentage
�
�
%
�
�
>
�∙�
�
= �� > ��
�
�
Squares of Fractions
� �
�
=
�
�
�
× ��� =
����
�
�∙�
Square Roots of Fractions
��
�
�
��
=
�
y
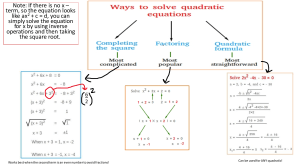
General Form of a Quadratic Equation
�
a� + �� + � = �
E.g1 -
�
� − �� −28 = 0
(� − �)(� + �) = 0
(� − �) = 0 (� + �) = 0
E.g2 -ab+ac =d
4x + 4y =7
X(x+100)=0
a(b=c)=d
4(x + y)=7
x=0 OR x+100=0
−�± �� −���
�=
��
Common Quadratic Identities
�+�
�
�−�
= (� + �)(� + �) = �� + ��� + ��
�
= (� − �)(� − �) = �� − ��� + ��
�� − �� = (� + �)(� − �)
�� + �� = (� + �)(�� − �� + �� )
�� − �� = (� − �)(�� + �� + �� )
�+�
�−�
�
�
= �� + ��� � + ���� + ��
= �� − ��� � + ���� − ��
Order of Operations in Algebra
����
���
����
����
���
+−×
+−
×÷
+−
×÷
���� = ����
��� = ����
��� = ����
��� = ���
��� = ���
+
−
+
−
Basic Words
×
÷
+ = +
������� ���� (��������) → >
×
÷
− = −
�� ����(�������) → ≤
×
÷
+
− = +
− = −
���� ÷ ���� = ���� �� ���
���� ����(�������) → <
�� �����(�������) → ≥
A Formula for Division
������� =
�������� − ���������
��������
�������� =
�������� − ���������
�������
�������� = (������� × ��������) + ���������
��������� = �������� − (������� × ��������)
2
3 7
6
Divisor
1
Quotient
Dividend
Remainder
Highest Common Factor (HCF) and Lowest Common
Multiple (LCM)
Divisibility Rules
Mean, Median, Mode and Range
Roots and Exponents
Sum of ‘n’ terms of Arithmetic Progression(AP)
�� =
�
�
{�� + (� − �)�} �� =
�� = the sum of the initial n terms
n = the total number of terms
�
�
{�+� }
a = the first term,
l = the last term
� = � + (� − �)�
d = the common difference
Ratio
Rate(Speed) & Work Formula
Rate-Time-Distance
Rate-Time-Work
�������� = ���� × ����
���� = ���� × ����
���� =
���� =
��������
����
��������
���� =
����
Average Rate
������� ���� =
���� =
����
����
��������
����
Converging/Diverging Rate
����� ��������
����� ����
����� ��������������� � ��� � = �������� + ��������
Round Trip Rate
Catch-up and Pass Rate
��������� = ���������
���� =
� ��������
� ����
Percentage
Example − 400 percentage of y =
400
100
× y = 4y
Percentage Increase/Decrease
Given Value
% = (Fraction) × 100 →
%=(
) × 100
Total Value
Example − 50% = 0.5; 120% = 1.2; 11% = 0.11 etc.
Calculating Percentage Change
Greater Than OR % Increase:
��� ����� = � + �������� × (�������� �����)
��� ����� =
�+
% ��������
���
× (�������� �����)
� �� �% ������� ���� � → � = �. �� × �
�
� �� �% ������� ���� � → � = (� + ��� ) × �
Less Than OR % Decrease:
��� ����� = � − �������� × (�������� �����)
��� ����� =
�−
% ��������
� �� �% ���� ���� � →
� �� �% ���� ���� � →
���
× (�������� �����)
� = �. �� × �
�
� = (� − ��� ) × �
Calculating Percentage Difference
Percentage Points
Reversed Percentages
Average
For example: the heights of students
in a classroom were measured. There
are 2 children at 1.20 m, 3 children at
1.25 m and 3 children at 1:30 m.
What is the average height of a
student in the classroom?
Solution:
Weight Average
(1.2 × 2) + (1.25 × 3) + (1.3 × 3)
=
2+3+3
= 1.256 m
Probability
�(�) =
������ �� ��������� �������� �� �
����� ������ �� �������� ��������
P(A) is the probability of an event 'B'.
n(A) is the number of favorable outcomes of an event 'B'.
�(�) =
n(S) is the total number of events occurring in a sample space.
�(�)
�(�)