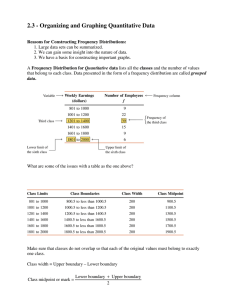
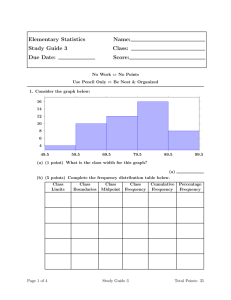
Organizing and Graphing Quantitative Data Sections 2.3 – 2.4 Frequency Distribution for Quantitative Data Frequency Distribution for Quantitative Data • Lists all the classes (intervals) and the # of values in each class (frequency). • Class Boundary – midpoint between upper limit of one class and lower limit of next class. • Class width = upper boundary – lower boundary. • Class Midpoint = lower limit + upper limit 2 Example: Constructing Frequency Distribution Tables • Number of classes - usually 5-20. • Class width. – To approximate class width: Largest value – smallest value Number of classes Example: Start with Data Frequency Distribution of Data Relative Frequency Distribution Histograms • Classes on x-axis, frequencies/relative frequencies/percentages on y-axis. Truncation Relative Frequency Histogram Polygon • Graph formed by joining midpoints of bars. Frequency Distribution Curve • As the # of data and classes increase the polygon becomes more of a smooth curve. Shapes of Histograms • Symmetric Shapes of Histograms • Skewed Shapes of Histograms • Uniform