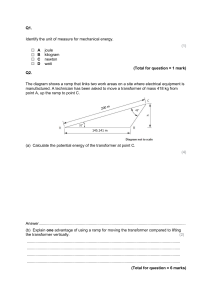
Republic of the Philippines BATANGAS STATE UNIVERSITY The National Engineering University Alangilan Campus Golden Country Homes, Alangilan Batangas City, Batangas, Philippines 4200 Tel Nos.: (+63 43) 425-0139 local 2121 / 2221 E-mail Address: ceafa@g.batstate-u.edu.ph | Website Address: http://www.batstate-u.edu.ph College of Engineering EE 422 Laboratory Report Transformer Parts and Functions Leading Innovations, Transforming Lives Republic of the Philippines BATANGAS STATE UNIVERSITY The National Engineering University Alangilan Campus Golden Country Homes, Alangilan Batangas City, Batangas, Philippines 4200 Tel Nos.: (+63 43) 425-0139 local 2121 / 2221 E-mail Address: ceafa@g.batstate-u.edu.ph | Website Address: http://www.batstate-u.edu.ph College of Engineering I. Introduction The following report discusses different types of electrical transformers: step-up and step-down transformers, single-phase and three-phase transformers, power transformers, distribution transformers, current transformers, and potential transformers. II. Objectives The objective of this report is to define the parts, and functions of the different types of transformers mentioned above. III. Background Electrical transformers are machines that transfer electricity from one circuit to another with changing voltage levels but no frequency change. Because they are designed to use alternating current, changes in supply voltage are influenced by changes in supply current. They either increase or decrease voltage levels, ensuring a safe and efficient power system in both industrial and residential areas. (Industrial Quick Search, n.d.) IV. Discussion The following discusses the types of electrical transformers. a. Step-up Transformer and Step-down Transformer Definition: A step-up transformer is a transformer that increases the voltage from primary to secondary by having more secondary winding turns than primary winding turns. Moreover, its primary current is greater than its secondary current. The primary winding of the transformer is the LV winding, and the secondary winding is the HV winding. In most cases, a step-up transformer is used for power transmission and its example is the one found in a power plant. (Kuphaldt & Haughery, 2020) Leading Innovations, Transforming Lives Republic of the Philippines BATANGAS STATE UNIVERSITY The National Engineering University Alangilan Campus Golden Country Homes, Alangilan Batangas City, Batangas, Philippines 4200 Tel Nos.: (+63 43) 425-0139 local 2121 / 2221 E-mail Address: ceafa@g.batstate-u.edu.ph | Website Address: http://www.batstate-u.edu.ph College of Engineering On the other hand, a step-down transformer is designed to do just the opposite. It has a primary voltage greater than the secondary voltage. On the other hand, the HV winding of the transformer is the primary, and the LV winding is secondary. Also, the number of turns in the primary winding is more than in the secondary winding. The secondary current is more than the primary current. A stepdown transformer is used in power distribution. One of its examples is the transformer in a residential colony. (Kuphaldt & Haughery, 2020) Parts: The step-up transformer and step-down transformer both have 2 parts: (Linquip Team, 2021) • Core A high permeability substance can be used to mimic the core of the transformer. Its core material enables magnetic current to flow more efficiently. When compared to the air, the core material has a high permeability. As a result, the magnetic flux lines passing through the core material will be limited by this core substance. As a result, decreasing transformer waste can enhance transformer efficiency. • Windings The step-up transformer's windings will aid in the transfer of the current generated by the transformer. These windings are generally designed to keep the transformer cool during operation and testing. The windings include primary and secondary windings. The primary part of the coil has a high density but fewer turns. Similarly, the coil density in the second part is thin but contains a large number of turns. This can be modeled by assuming that the major part contains less energy than the secondary side. b. Single-phase Transformer Definition: A single-phase transformer is an electrical device that converts alternating current (AC) from one voltage level to another. It is a static (or stationary) electric Leading Innovations, Transforming Lives Republic of the Philippines BATANGAS STATE UNIVERSITY The National Engineering University Alangilan Campus Golden Country Homes, Alangilan Batangas City, Batangas, Philippines 4200 Tel Nos.: (+63 43) 425-0139 local 2121 / 2221 E-mail Address: ceafa@g.batstate-u.edu.ph | Website Address: http://www.batstate-u.edu.ph College of Engineering machine with two or more windings, and transformers are classified according to the number of windings they have. Transformers are used in electric power applications to increase or decrease alternating voltages. Single-phase transformers are the most common type of transformer. Single-phase transformers are used in a wide range of applications, including power distribution, electronic equipment, and lighting. (Sorting Hat Technologies Pvt Ltd, n.d.) Parts: The single-phase transformer parts work together to provide a safe and efficient way to transfer electrical energy. The single-phase transformer have 3 parts: (Sorting Hat Technologies Pvt Ltd, n.d.) • Core The core of the transformer is made of iron or steel. It provides a path for the magnetic flux. • Winding The winding is a coil of wire that is wound around the transformer core. It carries the current that flows through the transformer. The primary winding is winding on the transformer's side that is connected to the alternating current power source. When an alternating current voltage is applied to the primary winding, it generates a magnetic field. The winding on the side of the transformer connected to the load is known as secondary winding. When an alternating current voltage is applied to the primary winding, a voltage is induced in the secondary winding. • Isolation Isolation is necessary to protect the transformer winding from the core. It is done by using an insulation material such as glass, mica, varnish, etc. Leading Innovations, Transforming Lives Republic of the Philippines BATANGAS STATE UNIVERSITY The National Engineering University Alangilan Campus Golden Country Homes, Alangilan Batangas City, Batangas, Philippines 4200 Tel Nos.: (+63 43) 425-0139 local 2121 / 2221 E-mail Address: ceafa@g.batstate-u.edu.ph | Website Address: http://www.batstate-u.edu.ph College of Engineering c. Three-phase Transformer Definition: A three-phase transformer, also known as a 3-phase or 3-transformer, is made up of three primary coils and three secondary coils. A three-phase system can be built using three identical single-phase transformers, and this type of three-phase transformer is known as a bank of three transformers. The three-phase transformer, on the other hand, can be built on a single core. A transformer's windings can be connected in either a delta or a wye configuration. The operation of a three-phase system is similar to that of a single-phase transformer, and they are commonly used in power plants. (Elprocus, 2020) Parts: The most important parts used in the three-phase transformer are windings and core. • Laminated Steel Core Silicon steel is used in the construction of three-phase transformer cores. Its high permeability, low magnetic reluctance, and low hysteresis loss make it useful. The core is made up of stacks of laminated thin steel sheets that are electrically insulated from one another thanks to a thin coat of varnish. To reduce eddy current loss, the core is laminated. • Windings The cylindrical coils (windings) are arranged concentrically around the same limb, with the low-voltage winding inside and the high-voltage winding outside. Because it is easy to insulate a low voltage winding from the core, it is Leading Innovations, Transforming Lives Republic of the Philippines BATANGAS STATE UNIVERSITY The National Engineering University Alangilan Campus Golden Country Homes, Alangilan Batangas City, Batangas, Philippines 4200 Tel Nos.: (+63 43) 425-0139 local 2121 / 2221 E-mail Address: ceafa@g.batstate-u.edu.ph | Website Address: http://www.batstate-u.edu.ph College of Engineering placed close to the core. Both windings are properly insulated from one another and from the core. Three high-voltage and three low-voltage windings are used in the construction of a three-phase transformer. • Transformer Oil Transformer oil is a mineral oil obtained by fractional distillation of crude petroleum that is used in transformers. This oil transports the heat generated by convection in the transformer from the windings and core to the transformer tank. This oil also improves and maintains transformer winding insulation. • Conservator It's a small cylindrical tank that sits on top of oil-cooled transformers and is linked to the main tank by a small pipe. It allows for the expansion and contraction of oil, which expands when heated and contracts when cooled. It reduces oil oxidation by reducing the surface area of oil in contact with air. • Breather It is the device through which all air movement from and into the transformer occurs. When the oil expands due to the heating of the transformer, air is expelled and drawn in when the oil cools. It's mounted at one end of the conservatory. • Thermometer A thermometer is installed on all large-capacity transformers to indicate the temperature of the hot oil. Temperature-indicating devices are installed in the winding of very large transformers to record the winding temperature. A temperature-sensitive alarm system is also installed to sound the alarm whenever the temperature rises dangerously. • Explosion Vent Pipe It's a twisted pipe with a glass cap at the end. It is mounted on top of the transformer tank. It protects against excessive pressure buildup within a transformer. In the absence of this device, the transformer may explode. • Valves Each transformer has a number of valves for filling and draining the transformer oil. • Buchholz Relay Buchholz relay is a type of gas relay. When a fault develops inside the transformer, the relay sounds an alarm, and if the fault is dangerous, the relay Leading Innovations, Transforming Lives Republic of the Philippines BATANGAS STATE UNIVERSITY The National Engineering University Alangilan Campus Golden Country Homes, Alangilan Batangas City, Batangas, Philippines 4200 Tel Nos.: (+63 43) 425-0139 local 2121 / 2221 E-mail Address: ceafa@g.batstate-u.edu.ph | Website Address: http://www.batstate-u.edu.ph College of Engineering disconnects the transformer circuit. On large-capacity transformers, this relay is installed between the main tank and the oil conservator. d. Power Transformer Definition: Power transformers are generally used in transmission networks for stepping up or down the voltage level. It operates mainly during high or peak loads and has maximum efficiency at or near full load. A power transformer is a passive electromagnetic device that uses inductive coupling to transfer energy from one circuit to another. (Power Transformers, 2020) Parts: The power transformer has the following parts: (Parts Of A Power Transformer, 2011) • Transformer Tank (1) This houses the transformer windings as well as the insulating medium (oilfilled). Transformer tanks must be airtightly sealed in order to isolate their contents from any environmental contaminants. • High Voltage Bushing (2) This is where the transformer's primary windings terminate and serve as an insulator from the transformer tank. Its creepage distance is determined by the transformer's voltage rating. Leading Innovations, Transforming Lives Republic of the Philippines BATANGAS STATE UNIVERSITY The National Engineering University Alangilan Campus Golden Country Homes, Alangilan Batangas City, Batangas, Philippines 4200 Tel Nos.: (+63 43) 425-0139 local 2121 / 2221 E-mail Address: ceafa@g.batstate-u.edu.ph | Website Address: http://www.batstate-u.edu.ph College of Engineering • Low Voltage Bushing (3) This is the terminal where the secondary windings of the transformer terminate and serve as an insulator from the transformer tank, similar to the highvoltage bushing. Because low-voltage bushings are typically smaller in size than high-voltage bushings, they can be easily distinguished from their high-voltage counterparts. • Cooling Fins/Radiator (4) Cooling fins and radiators are typically attached to transformer tanks in order for the transformer to dissipate the heat generated in its oil-insulation. The capacity of the transformer is affected by its temperature, so it must have a cooling mechanism for improved performance and efficiency. • Cooling Fans (5) It is commonly found attached to the cooling fins. Cooling fans can be controlled by a timer or by winding/oil temperature. Cooling fans assist in increasing transformer capacity when the temperature of the transformer rises due to loading. Cooling fans on the transformer are activated by a relaying device that detects a relatively high temperature and causes the fan to run automatically. • Conservator Tank (6) An oil preservation system in which the oil in the main tank is isolated from the atmosphere over a specified temperature range by an auxiliary tank partially filled with oil and connected to the fully filled main tank. • System Ground Terminal (7) When the connection type of the transformer windings includes a wye, system ground terminals are usually present. This terminal is located in line with the transformer's main terminals. • Drain Valve (8) It is typically found at the bottom of the transformer tank. Drain valves are used whenever oil needs to be replaced. This valve allows for the simple replacement of oil in an oil-filled transformer by simply opening it like a faucet. • Dehydrating Breather (9) Dehydrating breathers are used to keep normal air moisture from contacting the oil in electrical equipment as the load or temperature changes. This helps to keep the oil's insulation capability and reduces degeneration. It reduces moisture accumulation in the cell when used with a conservator system and a rubber air Leading Innovations, Transforming Lives Republic of the Philippines BATANGAS STATE UNIVERSITY The National Engineering University Alangilan Campus Golden Country Homes, Alangilan Batangas City, Batangas, Philippines 4200 Tel Nos.: (+63 43) 425-0139 local 2121 / 2221 E-mail Address: ceafa@g.batstate-u.edu.ph | Website Address: http://www.batstate-u.edu.ph College of Engineering cell. Some breathers are intended for sealed tank transformers and only breathe at predetermined pressure levels. • Oil Temperature/Pressure gauges (10) These are used to monitor the transformer's internal characteristics, particularly its windings. These gauges assist the operator in determining the temperature and pressure levels within the transformer (oil & winding). This will also serve as an alarm if a certain level is reached that may be hazardous to the transformer windings. • Bushing Current Transformers (11) These are typically found near transformer terminals that will later be used for metering and relaying. Its terminals are located in the transformer's control panels. • Control Panel (12) This contains all of the transformer's monitoring devices, terminals, and auxiliary devices, as well as the terminals of the bushing current transformers and cooling fans. Control panels are extremely useful, especially when constructing a remote control house; this will serve as their connection point. • Surge Arresters (13) This type of arrester is installed directly before and after the transformer terminals to reduce the transformer's exposure. Its purpose, like any other surge arrester, is to clip sudden voltage surges that can damage the transformer winding. e. Distribution Transformer Definition: A distribution transformer is also mentioned as a common type of isolation transformer. The basic function of this transformer is to convert high voltage to standard output voltages such as 240/120 V for use in electric energy distribution. In the distribution system, transformers of various types are available, including single-phase, three-phase, pad-mounted, underground, and pole-mounted distribution transformers. (Linquip Team, 2021b) Leading Innovations, Transforming Lives Republic of the Philippines BATANGAS STATE UNIVERSITY The National Engineering University Alangilan Campus Golden Country Homes, Alangilan Batangas City, Batangas, Philippines 4200 Tel Nos.: (+63 43) 425-0139 local 2121 / 2221 E-mail Address: ceafa@g.batstate-u.edu.ph | Website Address: http://www.batstate-u.edu.ph College of Engineering Parts: The distribution transformer has the following parts: (Distribution Transformer | MBT Transformer, 2020) • Oil Tank The oil tank is used to soak the coils by placing it in. • Conservator On the outside of the transformer frame, above the oil tank, is a conservator. It is linked to the main tank through a metal tube. The oil in the tank can be easily contacted and expanded during loading, allowing the oil's temperature to rise and fall. • Buchholz relay When using a conservator tank, the Buchholz relay is used. Because it indicates errors such as oil loss when it runs low, the flow of oil between the tank and transformer is incorrect. • Dehydrating Breather The oil in the breather unit contains desiccant silica gel. It will not be hygroscopic in oil if its color changes from blue to pink. • Oil Level Indicator The oil indicator displays the level of oil in the conservatory unit. • Temperature Detector The temperature detector keeps track of the oil's temperature. When the oil temperature reaches a certain threshold, the transformer is turned off. • Pressure relief device Leading Innovations, Transforming Lives Republic of the Philippines BATANGAS STATE UNIVERSITY The National Engineering University Alangilan Campus Golden Country Homes, Alangilan Batangas City, Batangas, Philippines 4200 Tel Nos.: (+63 43) 425-0139 local 2121 / 2221 E-mail Address: ceafa@g.batstate-u.edu.ph | Website Address: http://www.batstate-u.edu.ph College of Engineering The pressure relief device reduces the pressure inside the transformer to prevent it from exploding. • Thermal relay The thermal relay serves as a temperature indicator for the winding. • Radiators Radiators are used to improve the transformer's cooling efficiency. • Bushings Bushings are used to connect a transformer's inner windings to an external electrical network. f. Current Transformer Definition: Current transformers are measurement transformers that are used to measure the amount of current flowing through a circuit. Direct measurement of high currents with measuring instruments is not only costly but also dangerous and difficult at times. As a result, in order to be measured, the current passing through the circuit must be reduced to a specific value. The current transformer, which is connected in series to the circuit, reduces the magnetic field created by the current passing through the primary circuit and transfers it to the secondary circuit. The amount of current flowing in the primary circuit can be measured by the measuring device connected in parallel to the secondary winding due to the cyclic current occurring in the secondary circuit. (Entes, 2023) Leading Innovations, Transforming Lives Republic of the Philippines BATANGAS STATE UNIVERSITY The National Engineering University Alangilan Campus Golden Country Homes, Alangilan Batangas City, Batangas, Philippines 4200 Tel Nos.: (+63 43) 425-0139 local 2121 / 2221 E-mail Address: ceafa@g.batstate-u.edu.ph | Website Address: http://www.batstate-u.edu.ph College of Engineering Parts: Current transformers are made up of three parts: a magnetic iron core, a primary winding wound on this core, and a secondary winding wound in the opposite direction on this primary winding. The primary winding current generates a magnetic flux on the magnetic iron core. The magnetic flux in the core induces a voltage on the secondary winding. Because the current passing through the secondary circuit is opposite to the winding direction, the measuring device connected in parallel to the secondary winding generates a magnetic flux in the magnetic iron core in the opposite direction. The magnetic flux created by the current passing through the primary winding is balanced by this magnetic flux. As a result, the current transformers' secondary ends must be short-circuited by a measuring device or a load. Otherwise, there will be no magnetic flux in the opposite direction, and because the flux is unbalanced, the magnetic iron core will heat up and fail. Furthermore, this situation endangers users by increasing the voltage at the secondary ends. (Entes, 2023) g. Potential Transformer Definition: A potential transformer is a type of instrument transformer (also known as a voltage transformer). It is a step-down voltage transformer that converts high-level voltage to lower-level voltage. An ordinary voltmeter can be used to measure the potential transformer's output voltage. (Electrical Technology, 2021) Parts: The potential transformer has the following parts: (Construction of Potential Transformer, 2017) • Core The potential transformer's core can be either a core or a shell. The windings surround the core in a core-type transformer, while the core surrounds the winding in a shell-type transformer. The shell-type transformer is intended for low-voltage applications, whereas the core-type transformer is intended for highvoltage applications. • Windings The primary and secondary windings are coaxially placed to reduce the potential transformer's leakage reactance. Leading Innovations, Transforming Lives Republic of the Philippines BATANGAS STATE UNIVERSITY The National Engineering University Alangilan Campus Golden Country Homes, Alangilan Batangas City, Batangas, Philippines 4200 Tel Nos.: (+63 43) 425-0139 local 2121 / 2221 E-mail Address: ceafa@g.batstate-u.edu.ph | Website Address: http://www.batstate-u.edu.ph College of Engineering • Insulation Cotton tape and cambric materials are used as insulation between the potential transformer's windings. Low voltage transformers do not use compound insulation. Oil is used as an insulation medium in high voltage transformers. Porcelain is used as an insulator in transformers with ratings greater than 45kVA. • Bushing The bushing is an insulated device that connects the transformer to the external circuit. The transformer's bushings are made of porcelain material. The oil-filled bushing is used in transformers that use oil as an insulating medium. When the line through which it is connected is not at ground potential, a two bushings transformer is used in the system. The transformer that connects to the neutral ground uses only one high voltage bushing. V. Reference Construction of Potential Transformer. (2017, December 7). Circuit Globe. https://circuitglobe.com/construction-of-potential-transformer.html Distribution Transformer | MBT Transformer. (2020). Vietnamtransformer.com. https://vietnamtransformer.com/our-news/distribution-transformer-mbttransformer Electrical Technology. (2021). Potential Transformer (PT) - Types of Voltage Transformers. ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY. https://www.electricaltechnology.org/2021/09/voltage-potentialtransformer.html Elprocus. (2020). Three-Phase Transformer - Working Principle and Its Construction. ElProCus Electronic Projects for Engineering Students. https://www.elprocus.com/what-is-three-phase-transformer-construction-andits-working/ Entes. (2023). What is current transformer? Where do we use current transformers? ENTES Elektronik. https://www.entes.eu/what-is-current-transformer-wheredo-we-use-currenttransformers/#:~:text=Current%20transformers%20basically%20consist%20of Leading Innovations, Transforming Lives Republic of the Philippines BATANGAS STATE UNIVERSITY The National Engineering University Alangilan Campus Golden Country Homes, Alangilan Batangas City, Batangas, Philippines 4200 Tel Nos.: (+63 43) 425-0139 local 2121 / 2221 E-mail Address: ceafa@g.batstate-u.edu.ph | Website Address: http://www.batstate-u.edu.ph College of Engineering Industrial Quick Search. (n.d.). Electric Transformers: Types, Applications, Benefits, and Components. Www.iqsdirectory.com. https://www.iqsdirectory.com/articles/electrictransformer.html#:~:text=Electric%20transformers%20are%20basically%20ma chines Kuphaldt, T. R., & Haughery, J. (2020, June 1). TRANSFORMERS. Iastate.pressbooks.pub; Iowa State University Digital Press. https://iastate.pressbooks.pub/electriccircuits/chapter/transformers/ Linquip Team. (2021a). Step Up Transformer: Construction & Working Principles | Linquip. Linquip. https://www.linquip.com/blog/what-is-step-up-transformer/ Linquip Team. (2021b, May 23). Distribution Transformer: Parts, Types & Working Principles. Linquip. https://www.linquip.com/blog/what-is-a-distributiontransformer/#:~:text=The%20main%20components%20of%20this Power Transformers. (2020). Power Transformers. Arrow.com. https://www.arrow.com/en/categories/magnetics/transformers/powertransformers PARTS OF A POWER TRANSFORMER. (2011, June). Blogspot.com. https://powersystemsloss.blogspot.com/2011/06/parts-of-powertransformer.html Sorting Hat Technologies Pvt Ltd. (n.d.). Parts Of A Single-Phase Transformer. Unacademy. Retrieved from https://unacademy.com/content/upsc/studymaterial/physics/parts-of-a-single-phasetransformer/#:~:text=The%20single%2Dphase%20transformer%20is%20comp osed%20of%20the%20following%20parts Leading Innovations, Transforming Lives