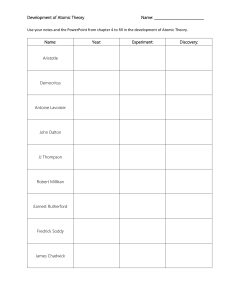
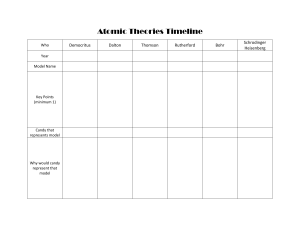
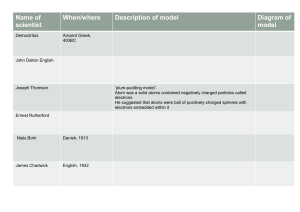
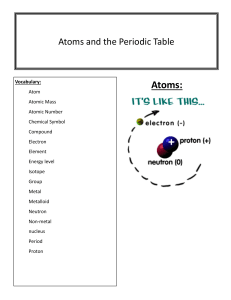
TIMELINE Atomic Theory By, Varsha, Divya, Avikshit , Aaditya menon , Aditya ram C. 460 BCE - C. 370 BCE DEMOCRITUS Theory : Proposed the concept of atomism, suggested that all of matter is consisted of indivisible & indestructible particles called atoms. Democritus also believed that atoms were uniform & solid. Also believed atoms moved in infinite numbers through empty space until stopped. Model: Democritus atomic model envisioned as tiny,solid, & indivisible particles that combined in various ways to form different substances 1856 CE - 1940 CE 1766 CE - 1844 CE SOLID SPHERE - JOHN DALTON Discovery : (1803- 1808) Dalton formulated the modern atomic theory, which proposed that elements are composed of atoms and that chemical reactions involve the rearrangement of atoms. Model: Dalton's atomic model described atoms as indivisible and indestructible spheres, each with a unique mass and combining ratio in compounds.Those of given element are identical. Compounds are combinations of different types of atoms. PLUM PUDDING MODEL JJ THOMPSON Theory (1897 CE): Thomson discovered the electron through his cathode ray experiments and proposed the "plum pudding" model of the atom. Model: Thomson's atomic model depicted atoms as a positively charged sphere with negatively charged electrons embedded within, resembling plums in a pudding. 1885 CE - 1962 CE PLANETARY MODEL NIELS BOHR Theory: Bohr expanded upon Rutherford's model and proposed the planetary model of the atom. . Model: Bohr's atomic model incorporated the idea of quantized energy levels. Electrons occupy specific orbits or energy levels around the nucleus, and they can jump between these levels by absorbing or emitting energy. Electron energy was quantized. Explained emissions spectra of some elements 1871 CE - 1937 CE NUCLEAR MODEL - ERNEST RUTHERFORD Theory : Rutherford conducted the famous gold foil experiment and proposed the nuclear model of the atom.. Model: Rutherford's atomic model suggested that atoms have a tiny, dense, and positively charged nucleus at the center, with electrons orbiting around it like planets around the sun. 1891 CE - 1974 CE DISCOVERY OF NEUTRON JAMES CHADWICK Theory: Chadwick discovered the neutron, an uncharged subatomic particle, which completed the picture of the atomic nucleus. Model: Chadwick's discovery led to the refinement of the atomic model, indicating the presence of neutral neutrons alongside protons in the nucleus. Note: The timeline extends until World War II, but there were significant advancements in atomic theory beyond that period as well. . COMPARISONS AND CONTRASTS: Democritus' model was based on philosophical reasoning, proposing the existence of indivisible particles. In contrast, the atomic models developed in the late 19th and early 20th centuries were based on experimental evidence and scientific principles. Dalton's model emphasized the idea of atoms as fundamental building blocks with distinct properties. Thomson's model introduced the concept of subatomic particles and the electron's presence within the atom. Rutherford's model further refined the structure of the atom, highlighting the existence of a small, dense nucleus. Bohr's model introduced the idea of quantized energy levels and explained the stability of atoms, which earlier models couldn't account for. It provided a bridge between classical physics and the emerging field of quantum mechanics. Tools and Technologies: The development of atomic theory required advancements in experimental techniques and tools, such as the cathode ray tube (used by Thomson), the gold foil experiment (performed by Rutherford), and spectroscopy (used by Bohr). These tools enabled scientists to observe and analyze the behavior of atoms and subatomic particles. The emergence of more sophisticated instruments, like the electron microscope and particle accelerators, in later years facilitated further discoveries and detailed investigations into atomic structure and behavior. REFRENCES: OpenStax Chemistry. "2.2 Atomic Theory and Atomic Structure." OpenStax CNX. Accessed 14 July 2023. "Democritus." Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Accessed 14 July 2023. "John Dalton." Encyclopaedia Britannica. Accessed 14 July 2023. "J.J. Thomson." NobelPrize.org. Accessed 14 July 2023. "Ernest Rutherford." NobelPrize.org. Accessed 14 July 2023. "Niels Bohr." NobelPrize.org. Accessed 14 July 2023. "James Chadwick." NobelPrize.org. Accessed 14 July 2023. Heathcote, William. MYP Physics: a Concept Based Approach. Oxford University Press, 2018. Accessed 14 July 2023