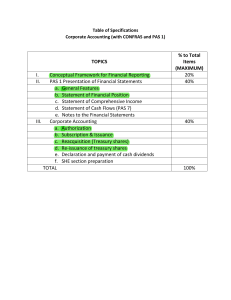
Conceptual Framework & Accounting Standards (ACCTG 103) Learning Objectives Transes By: @triciacababao Overview of Accounting 1. Define accounting and state its basic purpose. 2. Explain the basic concepts applied in accounting. 3. State the branches of accounting and the sectors in the practice of accountancy. 4. Explain the importance of a uniform set of financial reporting standards. Conceptual Framework for Financial Reporting 1. State the purpose, status, and scope of the Conceptual Framework. 2. State the objective of financial reporting. 3. Identify the primary users of financial statements. 4. Explain briefly the qualitative characteristics of useful information and how they are applied in financial reporting. 5. Define the elements of financial statements and state their recognition criteria and their derecognition. 6. State the measurement bases used in financial reporting. PAS 1 Presentation of Financial Statements 1. Enumerate and describe the general features of financial statement presentation. 2. Enumerate and describe the components of a complete set of financial statements. 3. State the acceptable methods of presenting items of income and expenses. 4. Differentiate between the statement of profit or loss and other comprehensive income and the statement of changes in equity. 5. State the relationship of the notes with the other components of a complete set of financial statements. PAS 2 Inventories 1. Define inventories. 2. Measure inventories and apply the cost formulas. 3. State the accounting for inventory write-down reversal thereof. PAS 7 Statement of Cash Flows 1. Describe the statement of cash flows. 2. Differentiate between the following: (1) Operating activities, (2) Investing activities, and (3) Financing activities. 3. State the classifications of the following in a statement of cash flows: (a) dividends received, (b) dividends paid, (c) interest paid and (d) interest received. PAS 8 Accounting Policies, Changes Accounting Estimates and Errors 1. Define the following and give examples: (1) Change in accounting policy, (2) Change in accounting estimate, and (3) Error. 2. Differentiate between the accounting treatments of the following: change in accounting policy, change in accounting estimate, and correction of prior period error. PAS 10 Events after the Reporting Period 1. Define events after the reporting period. 2. State the accounting requirements for events after the reporting period. PAS 12 Income Taxes 1. State the scope and the fundamental principle of PAS 12. 2. Interpret the terminology used in the accounting for current and deferred taxes. 3. State the recognition, measurement and presentation of current and deferred taxes. PAS 16 Property, Plant and Equipment 1. State the recognition criteria, initial measurement, and subsequent measurement of PPE 2. Apply the principles of PAS 16 in basic computations of a PPE's cost, depreciation, carrying amount, and revaluation surplus as well as the gain or loss on its disposal. PAS 19 Employee Benefits 1. Differentiate between benefits under PAS 19. 2. State the timing of the recognition of employee benefits. 3. Differentiate between a defined contribution plan and a defined benefit plan. 4. State the accounting procedures for defined benefit plans. PAS 20 Accounting for Government Grants and Disclosure of Government Assistance 1. Explain the recognition and measurement of government grants. 2. Explain the presentation of government grants in the financial statements. PAS 21 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates Learning Objectives @triciacababao | 1 1. 2. 3. Differentiate between the two ways of conducting foreign activities State the initial and subsequent measurements of foreign currency transactions. Describe the procedures in translating financial statements into a presentation currency. PAS 23 Borrowing Costs 1. State the core principle under PAS 23. 2. Compute for borrowing costs that are eligible for capitalization. PAS 24 Related Party Disclosures 1. Enumerate examples of related parties. 2. Describe the disclosure requirements for related parties. PAS 26 Accounting and Reporting by Retirement Benefit Plans 1. State the applicability of PAS 26. 2. Describe the accounting and reporting requirements of PAS 26. PAS 27 Separate Financial Statements 1. Describe the applicability of PAS 27. 2. Describe the measurement bases allowed under PAS 27. PAS 28 Investments in Associates and Joint Ventures 1. Define an investment in an associate. 2. Describe the accounting requirements for investments in associates and joint ventures. PAS 29 Financial Reporting in Hyperinflationary Economies 1. State the core principle under PAS 29. 2. Describe the restatement procedures under PAS 29. PAS 32 Financial Instruments: Presentation 1. State the definition of a financial instrument. 2. Give examples of financial assets and financial liabilities. 3. Differentiate between a financial liability and an equity instrument. 4. State the requirements for offsetting financial assets and financial liabilities. PAS 33 Earnings per Share 1. Explain how basic EPS is computed. 2. Explain how diluted EPS is computed. 1. 2. 3. Define an interim financial report. State the scope and applicability of PAS 34. Briefly describe the recognition and measurement principles applied in interim financial reporting. PAS 36 Impairment of Assets 1. State the core principle of PAS 36. 2. Account for the impairment of individual assets and cash generating units. 3. Account for the reversal of impairment. PAS 37 Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets 1. State the recognition criteria for provisions. 2. Differentiate the accounting requirements for a provision, a contingent liability and contingent asset. 3. Describe the measurement of a provision. PAS 38 Intangible Assets 1. Define an intangible asset. 2. State the initial measurement of intangible assets that are (a) externally acquired and (b) internally generated. 3. State the subsequent measurement of intangible assets that (a) have finite useful life and (b) indefinite useful life. PAS 40 Investment Property 1. Define an investment property. 2. State the initial and subsequent measurements of investment property. 3. Apply the fair value model of accounting for investment property. PAS 41 Agriculture 1. Differentiate the following: biological assets, bearer plants, agricultural produce and inventory. 2. State the initial and subsequent measurement of biological assets and agricultural produce. 3. State the accounting for government grants that are within the scope of PAS 41. PFRS 1 First-time Adoption of Philippine Financial Reporting Standards 1. Describe who a “first-time adopter” is and what the “first PFRS financial statements” are. 2. Describe the general requirements of PFRS 1. PFRS 2 Share-based Payment 1. Define a share-based payment transaction. PAS 34 Interim Financial Reporting @triciacababao | 2 2. 3. 4. State the measurement basis for share-based payment transactions with (a) non-employees and (b) employees. Compute for the salaries expense on share-based compensation plans. State the accounting for share-based transactions with cash alternatives. PFRS 3 Business Combinations 1. Define a business combination. 2. Explain briefly the accounting requirements for a business combination. 3. Make basic computations of good will. PFRS 5 Non-current assets Held for Sale and Discontinued Operations 1. Describe the criteria for held for sale classification. 2. State the initial and subsequent measurement of held for sale assets. 3. State the presentation requirements of a discontinued operation. PFRS 6 Exploration for and Evaluation o f Mineral Resources 1. Explain the accounting for exploration and evaluation expenditures. PFRS 7 Financial Instruments: Disclosures 1. State the two main categories of disclosures under PFRS 7. 2. State the types of risks required by PFRS 7 to be disclosed. PFRS 8 Operating Segments 1. Define an operating segment. 2. Describe the "management approach"to identifying reportable segments. 3. State the quantitative thresholds in identifying reportable segments. PFRS 9 Financial Instruments 1. State the classifications of financial assets and their initial and subsequent measurements. 2. State the classifications of financial liabilities and their initial and subsequent measurements. 1. 2. Define a joint arrangement and state its characteristics. Differentiate between a joint operation and a joint venture. PFRS 12 Disclosure of Interests in Other Entities 1. Describe the objective of PFRS 12. 2. State the types of investments that are within the scope of PFRS 12. PFRS 13 Fair Value Measurement 1. Define fair value. 2. State the principles used in measuring fair value. PFRS 14 Regulatory Deferral Accounts 1. Describe the applicability of PFRS 14. PFRS 15 Revenue from Contracts Customers 1. State the five steps in the recognition of revenue. 2. Describe how performance obligations are identified in a contract. 3. Describe how the transaction price is allocated to the performance obligations. 4. State the timing of revenue recognition and its measurement. 5. State the presentation of contracts with customers in the statement of financial position. PFRS 16 Leases 1. Identify a lease. 2. Describe the general recognition and recognition exemption relating to the accounting for leases by a lessee. 3. State the lease classifications by a lessor. 4. State the indicators of a finance lease. 5. Describe the accounting for finance leases and operating leases by a lessor. PFRS 17 Insurance Contracts 1. State the scope and applicability of PFRS 17. 2. Describe the level of aggregation and measurement of insurance contracts. PFRS 10 Consolidated Financial Statements 1. State the elements of control. 2. Describe the consolidation procedures. PFRS 1 Joint Arrangements @triciacababao | 3