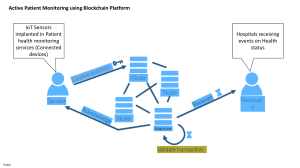
TRACKING CARBON FOOTPRINT USING AI By S.Wali, S.Mahad, Zayan.U, Muneeb.A, Muhibullah.S, M.Ibrahim.Z PROBLEM Rising carbon emissions contribute to global climate change, escalating the frequency and severity of extreme weather events like hurricanes, droughts, and heatwaves, while also accelerating the melting of ice caps and raising sea levels. The Hindu Kush glaciers are particularly vulnerable, melting rapidly and facing potential collapse, with projections indicating they could lose over 80% of their ice in this century. Health implications arise from high carbon emissions, including headaches, dizziness, and respiratory issues. Economically, there are challenges such as infrastructure damage, disruptions in supply chains, and increased insurance claims. Transitioning to cleaner technologies is crucial, but it poses economic challenges for carbon-intensive industries. Furthermore, agriculture and labor sectors suffer from climate impacts, risking crop yields, food security, and workforce productivity. Health costs associated with air pollution strain economies, emphasizing the urgency for action to mitigate these dire consequences and transition towards a low-carbon economy. CONCEPT We will integrate the Non-Dispersive Infrared (NDIR) sensor with a microcontroller or a small computing device capable of performing data preprocessing before storing it securely on a blockchain for analysis and subsequent actions. Among existing blockchain technologies, Ethereum and Bitcoin best align with our requirements. Subsequently, we will implement AI systems or algorithms to analyze the collected data and provide feedback. Alternatively, we can develop an AI system capable of predicting emissions by detecting changes in data patterns. Following this, we will design a user interface using HTML and JavaScript, if the web route is chosen. This interface will display real-time sensor data through live graphs and provide AIgenerated recommendations in textual format. CONTRIBUTION TO THE SOCIETY There are numerous benefits associated with this initiative, including a reduction in our carbon footprint, resulting in a more hospitable and livable climate. Solutions to carbon emissions, such as improved public transportation, offer societal advantages, while NDIR sensors facilitate the detection and mitigation of CO2 levels in the environment. Additionally, this effort not only enhances national well-being but also contributes to the global community by mitigating climate change and improving public health. Furthermore, it fosters ecosystem preservation, ensuring the safety of wildlife habitats. Our project stands to positively impact millions worldwide by improving living conditions through the reduction of harmful carbon dioxide emissions, which are linked to various issues such as global warming and respiratory diseases like pneumonia, asthma, and lung cancer. By addressing these challenges, our initiative plays a crucial role in combating the ongoing climate crisis. CONTRIBUTION TO QATAR Qatar is one of the most affected countries from high carbon emissions. In fact it has the highest carbon emissions per capita in the world. Our project helps by tracking the footprint live making it more efficient, also accessible to everyone. So everyone can track their carbon footprints and act on it. WHAT IS UNIQUE IN OUR PROJECT We implemented using AI which is not a very common practice in this field. Ai has great potential to strive in this field as proven in several other fields, giving as a strong recommendation about the air quality. Secondly we implemented the blockchain technology in this project which is something innovational and new for this field making our theory stand out amongst the others. HOW DID WE IMPLEMENT AI IN THIS PROJECT. In the era of the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR), abundant data from sources such as the Internet of Things (IoT), cybersecurity, mobile devices, business operations, social media, and healthcare are available for analysis. Artificial intelligence (AI), particularly machine learning (ML), plays a pivotal role in intelligently analyzing this data and developing smart, automated applications. Various machine learning algorithms, including supervised, unsupervised, semi-supervised, and reinforcement learning, along with deep learning, offer sophisticated data analysis capabilities. This paper provides an extensive overview of these machine learning techniques and their applicability across diverse domains such as cybersecurity, smart cities, healthcare, e-commerce, and agriculture. Additionally, it discusses challenges and potential research directions. Ultimately, this paper aims to serve as a valuable resource for academia, industry professionals, and decision-makers, offering insights and guidance on leveraging machine learning in real-world scenarios from a technical perspective. QATAR’S CO2 EMISSIONS Qatar is one of the most affected countries from high carbon emissions. In fact, it has the highest carbon emissions per capita in the world. Our project helps by tracking the footprint live making it more efficient, also accessible to everyone so they can track their own carbon footprintFossil fuel combustion and industrial processes in Qatar produced 102.6 million metric tons of carbon dioxide (MtCO₂) emissions WHY BLOCK CHAIN. integrating blockchain technology into this project offers significant advantages. Blockchain's decentralized structure ensures the security and integrity of data through cryptographic techniques, rendering it tamper-resistant and providing a transparent, verifiable ledger. The consensus mechanism and immutability of blockchain records enhance trust and reduce the risk of fraudulent activities, creating a reliable and auditable trail of information. The elimination of intermediaries and the use of smart contracts make blockchain a cost-effective solution, reducing administrative overhead and automating processes for greater efficiency. In the context of addressing global issues such as carbon emissions and climate change, blockchain's transparency and collaborative nature provide a robust framework for collecting, sharing, and validating environmental data. This not only aligns with the project's goal of fostering international cooperation but also ensures that diverse stakeholders can contribute and access information securely. Overall, incorporating blockchain technology into the project not only guarantees the security and integrity of data but also brings efficiency, transparency, and cost-effectiveness, contributing significantly to the project's success in addressing complex global challenges. WHAT IS BLOCKCHAIN Blockchain technology, renowned for its decentralized and distributed ledger system, revolutionizes record-keeping by ensuring secure and transparent transactions across a network of computers. Beyond its association with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, blockchain operates on decentralized nodes, providing a synchronized database accessible to all participants. Transactions are grouped into blocks, forming an immutable chain with sequential linking, ensuring integrity. Consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Work or Proof of Stake, validate and add new blocks, ensuring agreement among nodes on transaction validity. Utilizing cryptographic techniques, public and private keys secure transactions and access control. Smart contracts, self-executing agreements with coded terms, enhance efficiency by automatically enforcing conditions upon fulfillment. Blockchain's immutability reinforces security and trustworthiness, making alterations exceptionally challenging once a block is added. For this project, Ethereum and Bitcoin are selected as the most suitable options among existing blockchain technologies, meeting our requirements effectively. SMART CONTRACTS Operating on blockchain, revolutionize contract execution by replacing or augmenting traditional legal agreements with code. These self-executing contracts automatically enforce terms and conditions when predefined criteria are met, streamlining processes across various industries. The decentralized and distributed nature of blockchain ensures transparency and reduces reliance on central authorities for execution and verification. Smart contracts' immutability secures terms throughout execution, while cryptographic security and trustless transactions enhance reliability. The automated, transparent, and tamper-resistant nature of smart contracts not only saves time and costs but also finds applications in finance, supply chain, healthcare, and beyond, showcasing their versatility in transforming diverse sectors SENSOR We will be using an ndir sensor (non dispersive infrared) sensor. An NDIR (Non-Dispersive Infrared) sensor detects gases like carbon dioxide by emitting infrared radiation through a gas sample chamber. If the target gas is present, it absorbs specific infrared wavelengths. The remaining radiation reaches an infrared detector, which measures the intensity, proportional to the gas concentration. A reference channel compensates for variations in the light source or detector, ensuring accurate readings. NDIR sensors are efficient, low-power devices commonly used for precise gas concentration measurements in applications such as climate control