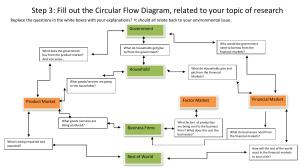
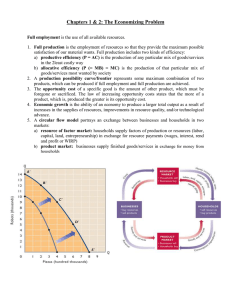
Operations Management Technique Section 1.1 An Overview of Statistics Section 1.1 Objectives • Define statistics • Distinguish between a population and a sample • Distinguish between a parameter and a statistic • Distinguish between descriptive statistics andinferential statistics - Notes By M Mbongo (1st Year Student At CPUT) 1.1 - Overview of Stats Data Sets Data Consist of information coming from observations, counts, measurements, or responses. Population - - The collection of all outcomes, responses, measurements, or counts that are of interest Sample - A subset of the population. Examples of data sets Identifying the population and the sample In a recent survey, 1500 adults in the United States were asked if they thought there was solid evidence for global warming. Eight hundred fiftyfive of the adults said yes. Suppose you are interested in studying the heights of all adult males living in a particular city. You randomly select 200 adult males from the city and measure their heights. You want to study the monthly electricity consumption of all households in a specific neighborhood. You randomly select 50 households and record their monthly electricity consumption. Population data set is US adults. Samples data sets is 1500 adults that have 855 yes`s and 645 no`s. Population data set is the adult males of the city. Sample data set is the 200 adult males. Population data set is the number of all the households in that specific neighborhood. Sample data set is the 50 households selected. Parameter and Statistic Parameter - A number that describes a population characteristic. Statistic - A number that describes a sample characteristic In between parameter and statistics, parameter represent the value of population and statistics represent the value of a sample. A parameter considers every individual in a population, whereas statistics consider the data it gets from a sample, not the entire population. Suppose you are interested in studying the heights of all adult males living in a particular city. You select 200 adult males amongst workingclass males from the city and measure their heights. You want to study the monthly electricity consumption of all households in a specific neighborhood. You select 50 households that have more than 3 or more people living in the household and record their monthly electricity consumption. - A recent survey of a sample of college career centers reported that the average starting salary for petroleum engineering majors is $83,121. The 2182 students who accepted admission offers to Northwestern University in 2009 have an average SAT score of 1442. - Sample statistic (the average of $83,121 is based on a subset of the population) - Population parameter (the SAT score of 1442 is based on all the students who accepted admission offers in 2009) - - - Parameter is the entire male population of that city. Statistics is the working-class males selected for measurements Parameter shows the monthly electricity consumption of the entire population of households in the neighborhood. Statistics show the monthly electricity consumption of 50 households that have 3 or more people living in them. - Definition Of Statistics - Statistics is the science of collecting, organizing, analyzing, and interpreting data to make decisions. Descriptive Statistics Descriptive statistics refers to the branch of statistics concerned with summarizing and describing the characteristics of a data set. This Inferential Statistics Inferential statistics refers to the branch of statistics concerned with making inferences or drawing conclusions about a population based on involves organizing, presenting, and analyzing data to provide insights into its key features, such as central tendency, variability, and distribution. Descriptive statistics techniques commonly used in operations management include measures such as mean, median, mode, range, standard deviation, and graphical representations like histograms, bar charts, and box plots. These techniques help operations managers understand the behavior of processes, identify patterns, and make informed decisions based on empirical evidence derived from the data. Descriptive Statistics Involves organizing, summarizing, and displaying data a sample of data from that population. In operations management, inferential statistics are used to generalize findings from a smaller subset of data (the sample) to a larger group or population. This involves estimating parameters, testing hypotheses, and making predictions about future outcomes or behavior of the population. Inferential statistics techniques commonly used in operations management include hypothesis testing, confidence intervals, regression analysis, analysis of variance (ANOVA), and chi-square tests. These techniques allow operations managers to make data-driven decisions, identify relationships between variables, and assess the effectiveness of process improvements or interventions Inferential Statistics Involves using sample data to draw conclusions about a population. > Difference between Descriptive statistics and inferential statistics A large sample of men, aged 48, was studied for 18 years. For unmarried men, approximately70% were alive at age 65. For married men, 90% were alive at age 65 Descriptive statistics involves statements such as “For unmarried men, approximately 70% were alive at age 65” and “For married men, 90% were alive at 65.” A possible inference drawn from the study is that being married is associated with a longer life for men. Suppose you are interested in studying the heights of all males studying in CPUT. You randomly select 200 males from the Bellville campus and measure their heights. Only to find that 20% of those who excel in sports are the tallest, 45% engineering students are taller and 35% of the other tall males. Descriptive statistics statement points out that “20% of males excelling are the tallest, 45% of taller males do engineering and 35% of tall males are in Bellville campus”. You want to study the monthly electricity consumption of all households in Delft. You select 50 households that have more than 3 or more people living in the household and record their monthly electricity consumption. Only to conclude that 17% of the households that consume the most electricity are households that have shops, the other 70% that consumed the most electricity had backrooms in their yard and the last 13% had at least more than 3 people. Descriptive statistics show that 17% of households that consume more electricity have shops, 70% of households that have backrooms consume most power and13% of households that have at least more than 3 people consume the least power. An inference drawn from this study points out that excelling athletics are often the tallest. In inferential statistics households with shops consume more power