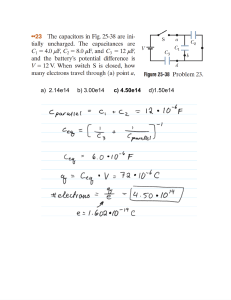
UNIVERSITY OF PRETORIA DEPARTEMENT OF CHEMICAL ENGINEERING KINETICS (CKN 321) November 2018 EXAM TIME : 3 HOURS TOTAL 60 Read this before you start: THE PAPER CONSISTS OF 4 QUESTIONS AND 5 PAGES, MAKE SURE YOU HAVE A COMPLETE QUESTION SET All Python graphs should be redrawn on your script. No printouts allowed Any form of communication on your computer will result in serious consequences. There are more ways to monitor this than you are aware of. Take care in presenting your scripts. Remember that only the scripts will be marked and not the pynb files! Remember that Python is only a tool to help you with calculations. This is not an exam to test your computer/programming skills, it is an exam to test your insight in the subject. Remember to illustrate your insight neatly on the script! Remember to give intermediate calculated values on the script, the pynb-file will not be marked. 1 Question 1 [15] The following liquid phase irreversible reaction is studied in various continuous reactor configurations with feed compositions CAo = 1 mol/L, CBo = 2 mol/L: 𝐴 + 2𝐵 → 3𝐶 The reactor configurations and the corresponding conversions of species A are shown in the following table: Description Configuration CSTR Overall measured conversion of A xA = 45.25% PFR xA = 60.15% Two CSTRs in series xA = 64.39% PFR followed by CSTR xA = 71.99% The volumes of all the individual reactors are identical (1L). I.e. a single PFR volume is the same as a single CSTR. Additionally, two CSTRs in series as well as the PFR followed by the CSTR would have double the combined volume of a single CSTR/PFR. The volumetric flowrate through all reactors are the same: Q = 8.3 L/min Determine the kinetics of the reaction (give the units of the kinetic constant in mol, L and min). 2 Question 2 [15] A complex reaction involving the limiting reagent A takes place in a liquid phase batch reactor. 1 0.9 0.8 CA (mol/L) 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Time (hours) y = 0.000175x5 - 0.0044136x4 + 0.037515x3 - 0.11643x2 - 0.02033x + 0.999108 R² = 0.9995 The curve is described nearly perfectly (r2 = 0.9995) by the fifth-order polynomial: 𝐶𝐴 = 0.000175𝑡 5 − 0.0044136𝑡 4 + 0.037517𝑡 3 − 0.11643𝑡 2 − 0.02033𝑡 + 0.999108 You may assume that the conditions used to determine the relationship between C A and t, will hold in any continuous operation system. a) Use the data provided for the system and draw qualitative sketches of –rA vs t and −rA vs CA (6) b) Determine the minimum residence time (or combined residence time for multiple reactors) that will yield a final conversion of 95% during continuous operation. (9) 3 Question 3 [15] The following reversible gas phase reaction is studied in a batch reactor: 𝐴 + 𝐵 ⇋ 𝐶 + 30𝐷 The reactor is a piston reactor with a minimum volume of 5 L, a maximum volume of 70 L and applies a constant pressure between these volume limits. Outside the volume limits the reactor volume is constricted and consequently becomes a constant volume reactor. The following information about the system is known: CAo CBo CIo (inert) T Vo EA ko,A1 ΔH Kc,20°C 0.1 mol/L 0.1 mol/L 0.1 mol/L 123 °C 7.5 L 60 kJ/mol 1×109 L/(mol.min) +40 kJ/mol 3 (mol/L)29 a) What is the pressure in the reactor at the start of the experiment in bar? b) What is the pressure in the reactor at equilibrium in bar? 4 (3) (12) Question 4 [15] A system consisting of the following two gas phase reactions are studied: 𝐴 + 2𝐵 → 6𝐵 (1) 10𝐵 → 𝐶 (2) The first reaction happens spontaneously and is known to be elementary while the second reaction is a first order reaction and requires the presence of catalyst in the reactor. To determine the kinetics of the system a PBR was setup and the concentration of B in the outlet was measured for two different masses of catalyst, the catalyst is diluted by the substitution with inert packing. The operating conditions and the measurement results from the system are summarized in the following table (only species A and B are fed to the reactor): Parameter/Variable Value Units Qo 10 L/min CAo 1 mol/L CBo 1 mol/L ρB1 (catalyst packing density 450 g/L in PBR in run 1) ρB2 (catalyst packing density 900 g/L in PBR in run 1) VPBR = 1 L CB,ρB1 1.487 mol/min CB,ρB2 0.102 mol/min What are the values of the kinetic constants kA1 and k’B2 in units of mol, L, min, and mol,g, min, respectively? 5