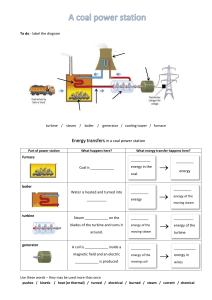
1. Explain the working principles of steam power plant. A steam power plant operates by burning fuel, usually coal, to produce heat. This heat is used to boil water, creating steam under high pressure. The steam then drives a turbine, causing it to spin. As the turbine rotates, it powers a generator, producing electricity. Finally, the steam is condensed back into water and returned to the boiler to repeat the cycle. 2. Identify the different cycles of steam power plants. The Rankine cycle is a thermodynamic cycle used in steam power plants where steam is generated at high pressure and temperature, expanded through a turbine, condensed, and then pumped back into the boiler to repeat the cycle. In a reheat cycle, after the steam expands through the high-pressure turbine, it is returned to the boiler to be reheated at constant pressure before being expanded again through a low-pressure turbine, increasing the overall efficiency of the cycle. In a regenerative cycle, feedwater is heated using steam extracted from the turbine at various stages, reducing the amount of fuel needed to generate steam and thus improving efficiency. In a reheat regenerative cycle, both reheat and regeneration techniques are employed, combining the benefits of reheating to increase efficiency and regeneration to utilize extracted steam for preheating feedwater. 3. What are the different components of steam power plant? Give each function. Boiler: Generates steam by heating water using fuel combustion, providing the energy source for the turbine. Turbine: Converts the energy from high-pressure steam into mechanical energy through rotation, driving the generator. Generator: Converts the mechanical energy from the turbine into electrical energy. Condenser: Condenses the steam exiting the turbine back into water, facilitating its reuse in the boiler. Feedwater Pump: Pumps condensed water from the condenser back into the boiler to maintain the steam generation cycle. Cooling Tower: Cools the water used in the condenser by dissipating heat into the atmosphere, allowing it to be reused in the condenser. 4. Draw the general layout of a steam power plant and explain the different working circuit. Boiler pump Turbine Condenser Generator Cooling Tower Boiler- The boiler generates high-pressure steam by heating water using fuel combustion. Turbine- The high-pressure steam from the boiler expands through the turbine, causing it to rotate and generate mechanical energy. Generator- The rotating turbine shaft is connected to a generator, which converts the mechanical energy into electrical energy. Condenser- The steam leaving the turbine enters the condenser, where it is condensed back into water by cooling it with water from the cooling tower. Cooling Tower- The cooling tower cools the water used in the condenser by dissipating heat into the atmosphere, allowing the water to be reused in the condenser. 5. What are the factors to be considered in selection of site for steam power plant? The selection of a steam power plant site considers proximity to fuel sources like coal or natural gas, ensuring cost-effective and reliable fuel supply. Accessibility for transportation of fuel, equipment, and electricity is crucial for efficiency and operational ease. Adequate water availability is vital for the cooling system and steam generation. Environmental impact assessments are conducted to minimize ecological disruptions and comply with regulations. Lastly, proximity to load centers ensures efficient electricity transmission and distribution, minimizing energy losses. 6. What are the following factors that can affect the choice of steam condition? Fuel Type- Different fuels may require specific steam conditions for optimal efficiency and combustion. Turbine Design- The design of the turbine influences the suitable steam conditions it can effectively utilize. Economic Considerations- Cost implications, including equipment and operational expenses, play a role in determining the appropriate steam conditions. Environmental Regulations- Compliance with environmental standards may dictate steam conditions to minimize emissions and environmental impact. Heat Recovery- Utilizing waste heat and implementing combined heat and power systems can influence the choice of steam conditions for enhanced energy efficiency. 7. What is the difference between the water tube boiler and fire tube boiler? Water tube boilers have water flowing inside the tubes while hot gases surround them externally. They are generally used for high-pressure applications and larger capacities. In contrast, fire tube boilers have hot gases flowing inside the tubes, surrounded by water externally, making them suitable for lower pressure and smaller capacity requirements. Water tube boilers provide faster steam generation due to their design, offering better efficiency. Fire tube boilers are simpler in construction and easier to maintain but may have slower steam production. The choice between them depends on factors like application, capacity, and operational preferences. 8. What are the advantages and disadvantages of water tube boiler and fire tube boiler? Water tube boilers offer advantages such as higher steam generation rates, increased efficiency, and the ability to handle higher pressures, making them suitable for industrial and power generation applications. They also provide better control over water quality. However, they tend to be more complex and expensive to manufacture and maintain. On the other hand, fire tube boilers are simpler in design and more costeffective, making them suitable for smaller applications with lower pressure requirements. They are also easier to clean and repair. However, fire tube boilers generally have a slower steam generation rate and may be less efficient than water tube boilers in certain scenarios. The choice between them depends on specific operational needs and priorities. 9. Give an example layout of a boiler and identify its accessories. Boiler Combustion Chamber Tubes Water Vessel Boiler Accessories Burner- Initiates and controls the combustion process. Tubes-Allow the passage of hot gases, facilitating heat transfer to the water. Combustion Chamber- Contains the burning fuel and ensures efficient combustion. Water Vessel- Holds the water to be heated and transformed into steam. Safety Valve- Releases excess pressure to prevent overpressure. Water Level Indicator- Monitors and displays the water level inside the boiler. Pressure Gauge- Measures the pressure within the boiler.