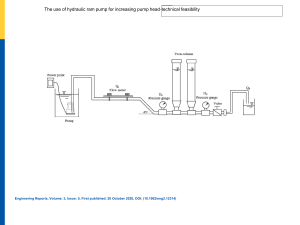
CE NTRIFUGAL PU MP TEST RIG (Multistage, Variable Sp eed, Series & Parallel) 1. OBJECTIVE: Study of centrifugal pumps in series & parallel mode. 2. AIM: 2.1 To determine: 2.1.1 Power input 2.1.2 Shaft output 2.1.3 Discharge 2.1.4 Total head 2.1.5 Pump output 2.1.6 Overall efficiency 2.1.7 Pump efficiency 2.12 To plot the following performance characteristics; 2.2.1 Speed vs. Discharge 2.2.2 Head vs Discharge 2.2.3 Pump efficiency vs Discharge 3. IN TRODUCTION: Thehydraulicmachines,whichconvertthemechanicalenergyintohydraulicenergy,arecalled pumps. The hydraulic energy is in the form of pressure energy. If the mechanical energy is converted into pressure energybymeansofcentrifugalforceactingonthefluid,thehydraulic machine is called a centrifugal pump. 4. TH EORY: The centrifugal pump acts as a reverse of an inward radialflowreactionturbine.Thismeans thattheflowincentrifugalpumpsisintheradialoutwarddirections.Thecentrifugalpumpworks on the principle of forced vortex flow, which means that when an external torque rotates a certain mass of liquid, the rise in pressure head of the rotatingliquidtakesplace.Therisein pressure head at any point of the rotating liquid is proportional to the square of tangential velocity of (i.e. rise in pressure head = V2/ 2g or ω2 r2/ 2g) the liquid at thatpoint.Thusatthe outlet of theimpellerwheretheradiusismore,theriseinpressureheadwillbemoreandthe liquid will be discharged at the outlet with a high- pressure head. Due to this high-pressure head, the liquid can be lifted to a high level. Centrifugal pump is a mechanical device, which consists of a body, impeller and a rotating meani.e.motor,engineetc. Impellerrotatesinastationarybodyandsucksthefluidthroughits axesanddeliversthroughitsperiphery. Impellerhasaninletangle,outletangleandperipheral speed, which affect the headanddischarge.Impellerisrotatedbymotorori.e.engineorany other device. MULTISTAGE CENTRIFUGAL PUMP: Acentrifugalpumpconsistsoftwoormoreimpellers;thepumpiscalledamultistagecentrifugal pump. A multi stage pump is having the following two important functions: 1. To produce a high head. 2. To discharge a large quantity of liquid. If a high head is to be developed, the impellersareconnectedinserieswhilefordischarging large quantities of liquid; the impellers are connected in parallel. 5. DE SCRIPTION: The present Centrifugal Pump Test Rig is a self-contained unit operated on a closed circuit basis containing a sump tank. Theset-upconsistsoftwoCentrifugalpumps.Bothpumpsare coupled with individual DC motors. Power inputs to these DC motorsarevariedbymeansof ThyristorcontrolledDCDrivestovarytheRPMofthemotor.TwoRPMIndicatorswithProximity sensors indicate the RPM of each Pump separately. Flow of water is measured by using a measuring tank and stopwatch. Vacuum Gauges are fitted on the suction line and Pressure Gauges are fitted on the delivery line of each pump to measure the pressure. Valves are provided at the outlets and inlets of pump to change the mode (i.e. Single Pump, Pumps in Parallel and Pumps in Series). Valve Operation to change mode are given in following table: - MODE V1 V2 V3 V4 V5 V6 Single Stage,Pump 1 Open Open Close Close Open Close Two Stage, Parallel Open Open Open Close Open Open Two Stage, Series Open Close Open Open Open Close 6. UT ILITIES REQUIRED: 6.1 Electricity Su pply: Single Phase, 220 V AC, 50 Hz, 5-15 Amp. combined socket with earth connection. Earth voltage should be less than 5 volts. 7. 6.2 Water Supply: Initial fill 6.3 Floor Drain Required. 6.4 Floor AreaRe quired: 2.0 m x 1.5 m EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE: 7.1 STARTING PR OCEDURE: 7.1.1 Clean the apparatus and make all tanks free from Dust. 7.1.2 Close the drain valve V10 & V11 are provided. 7.1.3 Fill the sump tank ¾ with clean water and ensure that no foreign particles are there. 7.1.4 Select mode of operation (Single Stage, Parallel or Series)andopenvalvesas per selected mode (Refer table given in description) 7.1.5 Ensure that all On/Off switches given on the panel are at OFF position. 7.1.6 Now switch on the main power supply (220 V AC, 50 Hz) and switch on the pump. 7.1.7 Set the desired RPM of the pump. 7.1.8 OperatetheflowcontrolvalveV1 toregulatetheflowofwaterdischargedbythe pump. 7.1.9 Record discharge pressure by partially open valve V1. 7.1.10Record suction pressure by partially open valves V8& V9. 7.1.11 Record the Pump input power supply on the watt meter. 7.1.12Measure the discharge by measuring the tank and stopwatch. 7.1.13Repeat the same procedure for different discharges with constant speed. 7.1.14Repeat the same procedure for different speeds of pump. 7.2 CL OSING PR OCEDURE: 7.2.1 When the experiment is over, open valve V1. 7.2.2 Reduce the RPM of the pump with the help of DC drive. 7.2.3 Switch OFF the pump. 7.2.4 Switch OFF power supply to panel. 8. OBSERVATION & CALCULATION: 8.1DA TA: Area of measuring tank A =0.148 m2 Acceleration due to gravity g = 9.81 m/s2 Motor efficiencyηm = 0.8 Density of water ρw = 1000 kg/m3 Area of measuring tank A = 0.148 m2 Height of pressure gauge from suction of pump hpg=1m 8.2OBSERVATION TABLE: Experiment 1: Centrifugal pump (Single Stage) Sr. No. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. N (RPM) PS1(m mHg) Pd 1(kg/cm2) R1(cm) R2(cm) t (s) Ei (w) Experiment 2: Centrifugal pump (Two stages - Parallel set-up) S2 P PS1 (mmHg)/ r. No. N1 (RPM) (mmHg) N2 (RPM) (kg/cm2) Pd (kg/cm2) R1 (cm) R2 (cm) t (s) Ei (w) S 1 2 3 4 5 Experiment 3: Centrifugal pump (Two stages - Series set-up) S2 P PS1 (mmHg)/ r. No. N1 (RPM) (mmHg) N2 (RPM) (kg/cm2) Pd (kg/cm2) R1 (cm) R2 (cm) t (s) Ei (w) S 1 2 3 4 5 8.3 CA LCULATIONS: Experiment 1: CentrifugalPu mp (SingleStage, Pump1) (kW) (m) (m3/ s) (m of water) (kW) (%) (%) Experiment 2: CentrifugalPu mp (TwoSt ages - ParallelSet-Up) (kW) (m) (m3/ s) (m of water) (kW) (%) (%) Experiment 3: CentrifugalPu mp (TwoStages- SeriesSe t-Up) (kW) (m) (m3/ s) (m of water) (kW) (%) (%) 9. NO MENCLATURE: Nom A Column Heading Area of measuring tank EMC Energy meter constant Units Type m2 Given Pulses/KW-hr Given Ei Pump input kW Calculated ES Shaft output kW Calculated Eo Pump output kW Calculated g Acceleration due to gravity m/s2 Given H Total Head m Calculated hpg Height of pressure gauge from suction of pump m Given N Speed of Pump RPM Measured P Pulses of energy meter * Measured Pd Delivery pressure kg/cm2 Measured PS1 Suction pressure of pump 1 mm of Hg Measured PS2 Suction pressure of pump 2 (mm of Hg)/ Measured 2 (kg/cm ) m3/ s Calculated Rise of water level in measuring tank m Calculated R1 Final level of water in measuring tank cm Measured R2 Initial level of water in measuring tank cm Measured s Measured s Measured Q Discharge R t Time taken for rise of water level in measuring tank tp Time taken for P pulses of energy meter ρ Density of fluid kg/m3 Given ηp Pump efficiency % Calculated ηo Overall efficiency % Calculated ηm Motor efficiency * Given * Symbols represent unitless quantity 10. PRECAUTION & MAINTENANCE INSTRUCTIONS: 10.1 Never fully close the delivery line (V1, V2 & V3 ) and suction line valves (V5 & V6) simultaneously. 10.2 Always use clean water. 10.3 If the apparatus will not be in use for more than half a month, drain the apparatus completely. 11. TR OUBLESHOOTING: 11.1 If the panel is not showing input, check the fuse and main supply. 11.2 Ifthepumpdoesnotliftthewater,opentheairventprovidedonthepumptoremovethe air from the pump. 11.3 If still water is not lifting the revolution of the DC motor may bereversed.Changethe electric connection of the motor to change the revolutions. 11.4 Iffieldfailure(FF)indicatesonthecontrolpanelandthemotorisnotmoving,checkthe fuses if burnt, change it. 11.5 If overload (OL) indicatesonthepanelandmotorstopsmoving,avoidclosingofoutlet valves (V1, V2 & V3) . 12. RE FERENCES: 12.1 Khurmi, R.S. (2008).Hydraulics, Fluid Mechanics andHydraulic Machines.11th Ed. ND: S. Chand & Company Ltd. pp 582-585, 587, 590. 12.2 Modi, P.N. Seth, P.N. (2005).Hydraulics and FluidMechanics including Hydraulic Machines.15th Ed. ND: Rajinder Kumar Jain. pp 1081-1083. 13. BLOCK DIAGRAM: