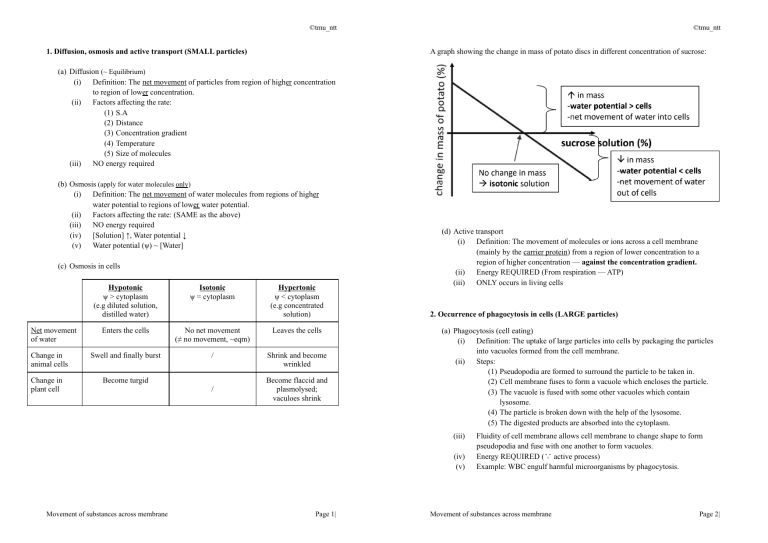
©tmu_ntt 1. Diffusion, osmosis and active transport (SMALL particles) ©tmu_ntt A graph showing the change in mass of potato discs in different concentration of sucrose: (a) Diffusion (~ Equilibrium) (i) Definition: The net movement of particles from region of higher concentration to region of lower concentration. (ii) Factors affecting the rate: (1) S.A (2) Distance (3) Concentration gradient (4) Temperature (5) Size of molecules (iii) NO energy required (b) Osmosis (apply for water molecules only) (i) Definition: The net movement of water molecules from regions of higher water potential to regions of lower water potential. (ii) Factors affecting the rate: (SAME as the above) (iii) NO energy required (iv) [Solution] ↑, Water potential ↓ (v) Water potential (ψ) ~ [Water] (c) Osmosis in cells Net movement of water Change in animal cells Change in plant cell Hypotonic ψ > cytoplasm (e.g diluted solution, distilled water) Isotonic ψ = cytoplasm Enters the cells No net movement (≠ no movement, ~eqm) Leaves the cells Swell and finally burst / Shrink and become wrinkled Become turgid / Hypertonic ψ < cytoplasm (e.g concentrated solution) Become flaccid and plasmolysed; vaculoes shrink (d) Active transport (i) Definition: The movement of molecules or ions across a cell membrane (mainly by the carrier protein) from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration — against the concentration gradient. (ii) Energy REQUIRED (From respiration — ATP) (iii) ONLY occurs in living cells 2. Occurrence of phagocytosis in cells (LARGE particles) (a) Phagocytosis (cell eating) (i) Definition: The uptake of large particles into cells by packaging the particles into vacuoles formed from the cell membrane. (ii) Steps: (1) Pseudopodia are formed to surround the particle to be taken in. (2) Cell membrane fuses to form a vacuole which encloses the particle. (3) The vacuole is fused with some other vacuoles which contain lysosome. (4) The particle is broken down with the help of the lysosome. (5) The digested products are absorbed into the cytoplasm. (iii) (iv) (v) Movement of substances across membrane Page 1| Fluidity of cell membrane allows cell membrane to change shape to form pseudopodia and fuse with one another to form vacuoles. Energy REQUIRED (∵ active process) Example: WBC engulf harmful microorganisms by phagocytosis. Movement of substances across membrane Page 2|