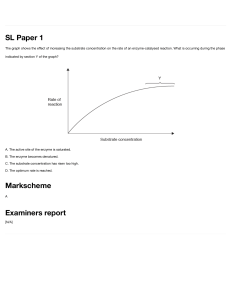
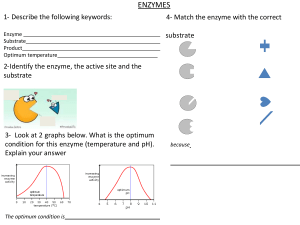
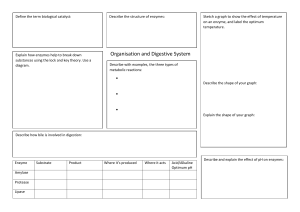
log Be ↑ ↳ * gen 84 . 84 . 23 2 5 Enzymes . What is Enzymes sional an are protein molecules with . shape The On the surface a of three dimensa enzyue every a known the active , shape an site as enzyme binds to the enzyme-substrate complex - form active site . It is in the active into An enzyme is a biological catalyst and is almost always a protein. It speeds up the rate of a specific chemical reaction in the cell. The enzyme is not destroyed during the reaction and is used over and over active site ? region subthispecial or the to Enzyme defenition: revision . products syte that substrates are converted How do enzymes and substrates meet ? Most biological reactions and substrate molecules take place a collision a in with one another When a emdecule Orientation the substral site in similar way to a . , Nature of science The lock and to analogy A e onspenze cours in the fits correct into the active key fitting into a lock . : key hypothesis has been used model or explain enzyme-substrate interactions , the induced fit model has refined our as a . second theory . Models like these unable of the process understanding Scientists to make predictions and describe the proces's in simple turMS - E G - How O enzymes Catalyses down · W fa substrate molecule into two product molecules active site strate enzyme products G A substrate molecule is drawn into the active site . of the enzyme The products arereleased and the is to receive another substrate molecule enzyme enzyme ready , ↳ strat Biological detergents definition: Biological detergents contain enzymes that help break down the fatty, greasy, and starchy compounds that are found in some of the most common clothing stains such as pasta sauces, bike oil, and hamburger grease. Protease definition: An enzyme which breaks down proteins and peptides. They do this by cleaving the peptide bonds within proteins by hydrolysis, a reaction where water breaks bonds Amylases definition: An enzyme that catalyses the hydrolysis of starch into sugars. Amylase is present in the saliva of humans and some other mammals, where it begins the chemical process of digestion. Inert material definition: Inert materials are classed as 'waste that does not undergo any significant physical, chemical or biological transformations and is unlikely to adversely affect other matter with which it comes into contact'. Substrate definition be the surface on which an organism (eg: plant, fungus, or animal) lives or the substance on which an enzyme can act Codon definition a sequence of three nucleotides which together form a unit of genetic code in a DNA or RNA molecule. Genes definition a unit of heredity which is transferred from a parent to offspring and is held to determine some characteristic of the offspring Allele Definition each of two or more alternative forms of a gene that arise by mutation and are found at the same place on a chromosome. Genetic Mutation Definition a change in the sequence of bases in a gene Genome definition the whole genetic information of an organism Eukaryotic Chromosome definition long threads of DNA and protein that carry the genetic material of the cell. In prokaryotes the DNA in a chromosome is not associated with proteins Definitions Diploid nucleus: contains two copies of each chromosome in homologous pair Haploid nucleus: contains one chromosome of each homologous pair Homologous pair: a pair of matching chromosomes that carry the same genes but not necessarily the same alleles of those genes Somatic cell: a body cell that is not a gamete Gamete: a haploid sex cell, for example, sperm, ovum or pollen Karyotype Definition the number of types of chromosomes in the nucleus Meiosis definition The type of cell division that takes place in ovaries and testes of animals, and in the anthers and ovaries of plants to produce haploid gametes for sexual reproduction Definitions Axon: the long threadlike part of a nerve cell along which impulses are conducted from the cell body to other cells Synapse: a short branched extension of a nerve cell, along which impulses received from other cells at synapses are transmitted to the cell body Motor Neuron: a nerve cell forming part of a pathway along which impulses pass from the brain or spinal cord to a muscle or gland