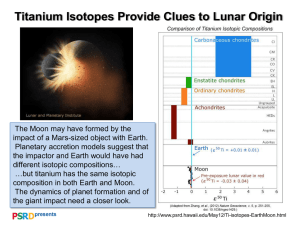
Jet Engine Trevon Richardson, Gerrell Williams, Dhavalkumar savaliya Material: Titanium Alloy Reason we chose This Material: Our selected material was Titanium grade 5 (Ti 6Al-4v) as for jet engines(non propeller) typically require a very strong and ductile material. The strength to weight ratio is what makes this material the perfect selection to support a Jets engine. Jet engines are very complex and easy to mess up. So it is necessary to build the parts in isolated areas. Alot of aircrafts typically use this material but the military uses it the most for their aircraft. Unlike aluminum titanium has allowed aircraft to become much more efficient. Titanium has been mixed with other metals such as aluminum and nickel to allow for “unique characteristics” and properties to let engineers build more efficient engines.This includes the durability and ability to resist heat corrosion while staying relatively lightweight. The cost of developing these engines could cost roughly up between $12-35 million per unit. Strength Mechanisms: Titanium has a variety of mechanisms to allow for such great ductility and low elastic modulus. Solid solution and strain hardening methods are used to quantify the Ti alloys allowing for such material to be durable. Micro structure Properties Metric Imperial Tensile strength: 220 MPa 52.2136 Modulus elasticity: 116 GPa 15.229 Shear Modulus: 39 GPa 5.65647 Hardness: 1250 181.297 JET ENGINES - BASIC OPERATION •Air enters the through the intake duct (cowl). • Air compressed by passing through the compressor. • Mixed with fuel in the combustion chamber. • Fuel is ignited, Pressure and Temperature raised • Some of the pressure used to turn a turbine; • Turbine shaft drives the compressor. • Hot, high pressure air forced through the exhaust. • The reaction force is the engine thrust. How a CFM56-7B jet engine works (2:58)(1.25x) Titanium Grade 5 Titanium Grade 5 (aka Ti6Al4V) is a non-magnetic alloy, Ti6Al4V consists of: 90% Titanium 6% Aluminum 4% Vanadium & traces of other elements. Depending on its processing it is able to withstand high temperatures alongside its low elastic modulus, high corrosion resistance, and high strength. When titanium is exposed to oxygen it forms an oxide layer between the metal and the air, allowing for its high corrosion resistance. IMPORTANT OF TITANIUM Most engines use titanium because it has a high strength-to-weight ratio, is corrosion and fatigue resistant, and would be able to withstand the impact of a bird strike. ESTIMATE IMPACT OF SOCIETY 1.Titanium is being increasingly used in our modern society. It is light, strong and corrosion-resistant. These properties allow it to be used in the aerospace industry, building industry, sports goods industry and as implants in a number of surgical procedures. 2. Titanium is used to alloy with different metals such as iron, aluminum, and manganese where it helps to produce strong and lightweight alloys for use in spacecraft, naval ships, missiles, and as armor plating. Its resistance to corrosion makes it especially useful in sea water applications. 3. Titanium is a familiar metal. Many people know that it is used in jewelry, prosthetics, tennis rackets, goalie masks, scissors, bicycle frames, surgical tools, mobile phones and other high-performance products. Titanium is as strong as steel but weighs about half as much. JET ENGINE - COMMON TYPES Turbojets : - Turbine used to drive the compressor. - All thrust produced by hot, high-speed exhaust gases. Turbofans (Fan-Jet): - A large propeller in the intake cowl, in front of compressor. - Dramatically increases the amount of air pulled in the intake. - High bypass ratio are most commonly used in larger commercial aircraft. Turboprops: - Jet engine used to turn a large propeller, which produces most (90% or more) of the thrust. Used in smaller aircraft.They use titanium for all common types. Use of the titanium in 787 Sources ● ● ● ● ● Ren, Junqiang, et al. “Deformation Behavior of Pure Titanium With a Rare HCP/FCC Boundary: An Atomistic Study.” Materials Research, Materials Research, www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1516-14392020000100218. Ti 6al-4v Titanium Bar Stock, Sheet and Plate - Grade 5 - AMS 4911, 4928, 4967, 6932, www.upmet.com/products/titanium/ti-6al-4v#:~:text=Commonly%20referred%20to%20as%20Ti,and%20it%20is %20heat%20treatable. America, From Heidolph North, et al. “Properties: Titanium (Ti) - Properties, Applications.” AZoM.com, 13 Apr. 2021, www.azom.com/properties.aspx?ArticleID=712. “Titanium and the Aerospace Industry.” TMS Titanium, 22 Aug. 2014, tmstitanium.com/titanium-and-the-aerospace-industry/. Zhao, G.-H., et al. “Modelling Strengthening Mechanisms in Beta-Type Ti Alloys.” Materials Science and Engineering: A, Elsevier, 11 Apr. 2019, www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0921509319304733. THANK YOU