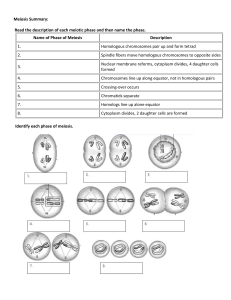
Heredity and Variation Cells behave the way they do because of the ____________ they contain which are made of proteins. Each protein in a cell is made according to the ___________ code that the cell ___________. The section of DNA that codes for an individual protein is known as a ___________ which are carried on long, thread-like structures called _______________. Genes occur in ____________. Cells may be divided into two types: diploid and ____________. Diploid cells contain __________ complete sets of chromosomes – written as 2n. ___________ cells contain _____________ complete set of chromosomes – written as n. Human body cells are ____________ while gametes are ____________. Human cells contain 23 different chromosomes. Human body cells contain two copies of these chromosomes totaling _____ while gametes contain _________ copy totaling ______. Homologous (partner) chromosomes are a pair of chromosomes with similar characteristics and the same types of genes and are found in human body cells. Human body cells therefore have _______ homologous chromosomes which is maintained when gametes fuse during ____________. Cell Division This occurs when the nucleus of a cell divides by one of TWO processes: mitosis and meiosis. During mitosis each chromosome becomes ___________ and duplicates itself into two ____________ which remain connected via the ______________. The nuclear envelope then disappears and the chromosomes align themselves along the center of the cell. Once there, the ________________ separate and move to opposite poles of the cell. The cell cytoplasm then divides into two along the equator resulting in two identical cells that are identical to the parent cell. The nuclear envelope then reforms. During meiosis each chromosome becomes __________ and duplicates itself into two ______________ which remain connected via the ________________. The nuclear envelope then disappears and the homologous chromosomes align themselves next to each other along the ____________ of the cell. Genetic information may then be exchanged between them – a process known as ______________ ____________. The homologous chromosomes then separate (each still made up of two ________________) and move to opposite ___________ of the cell. The cytoplasm then ___________ ________ _______ along the equator resulting in two non-identical cells. The chromosomes in each cell just formed now line up along the equator again. Once there, the _________________ separate and move to opposite __________ of the cell. The cell cytoplasm divides for both cells again resulting in ________ overall cells. These cells contain _________ the number of chromosomes found in the parent cell and they are not _____________ to it. Mitosis involves _______________ division while meiosis involves ______________ divisions. Page 1 of 2 Importance of Mitosis and Meiosis Mitosis ensures that every cell produced have the _____________ number of chromosomes and are genetically ________________. It is therefore used for growth, _____________ and ______________ of damaged cells. Meiosis ensures that the cells produced have the ______________ number of chromosomes and are genetically _________________. It is therefore used in the production of ______________. Variation Because meiosis produces genetically _________________ cells, variation is possible. Variation refers to the phenotypic (physical features) differences between individuals of a species. These differences may be due to genotype (the genetic make-up) or the environmental e.g. diet and living conditions. Identical twins, for example, have the same _____________ but based on exposure to their environment (eating habits, injury, even the formation of the finger prints) their phenotype may differ. Genetic (genotypic) variation may be continuous or _____________________. Continuous variation is where there is a complete range of forms for a particular characteristic within a population. Examples of features that show continuous variation include height, weight, skin colour, hair colour and size. Continuous variation usually occurs when a particular feature is controlled by a number of genes – it is polygenic. ______________________ variation is where there are clearly defined differences for a particular characteristic within a population. Examples of features that show ______________________ variation include ABO blood group, gender, fixed or free ear lobes and rhesus blood group. ______________________ variation usually occurs when a particular feature is controlled just one or two genes. Causes of genetic variation include random fertilization, crossing over during meiosis and mutation. Page 2 of 2