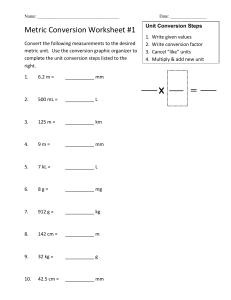
GRADE 7 School DAILY LESSON LOG Teacher Grade Level 7 Learning Area MATHEMATICS Teaching Dates and Time Session 1 Quarter SECOND Session 2 Session 3 Session 4 I. OBJECTIVES 1. Content Standards The learner demonstrates understanding of key concepts of sets and the real number system. The learner is able to formulate challenging situations involving sets and real numbers variety of strategies. Illustrates what it means Approximates the Approximates the 3. Learning to measure measures of quantities measures of quantities Competencies/ (M7ME-IIa-1) particularly length , particularly length , Objectives Describes the weight/mass, volume, weight/mass, volume, development of time, angle and time, angle and measurement from the temperature and rate temperature and rate primitive to the present (M7ME-IIa-3) (M7ME-IIa-3) international system of a. Describe what it a. Describe what it unit means to measure means to measure (M7ME-IIa-2) and approximate and approximate lengths measures of a. Describe what it means b. Convert length weight/mass to measure measurement from b. Convert weight/mass b. Identify the one unit to another. measurement s from development of c. Appreciate the one unit to another measurement from importance of including the English the primitive to the estimation/ system. approximation and c. Appreciate the present International measurements in importance of system of unit everyday life estimation/ 2. Performance Standards and solve these in a Approximates the measures of quantities particularly length , weight/mass, volume, time, angle and temperature and rate (M7ME-IIa-3) a. Describe what it means to measure and approximate the measures of volume b. Convert volume measurements from one unit to another including the English system. c. Appreciate the importance of estimation/ approximation measurements everyday life c. Apply accurate measurement in daily life situation II. CONTENT Measurement Measuring length and in Measuring weight/mass approximation measurements everyday life and in Measuring Volume III. LEARNING RESOURCES A. References 1. Teacher’s Guide pages pp.115-123 pp.117-121 2. Learner’s Materials pages pp. 91 – 98 pp. 91-98 3. Textbook pages 4. Additional Materials from Learning Resource (LR) portal Math Builders (Ulpina J.) p. Elem. Algebra pp.5-7. 117 Math Digest pp.6-7 e-math(Oronce,) p 83 http://www.discoveryeduc ation.com/teachers/freelesson-plans/discoveringmath-beginningmeasurement.cfm https://www.teachervision. com/measurement/teache r-resources/34507.html https://www.wyzant.com/r esources/lessons/math/ele mentary_math/measurem ent http://www.helpingwithmat pp.130-132 pp.124-130 pp. 104 -105 pp. 99-103 Elem. Algebra pp. 11-13. Math Digest 8-11 Elem. Algebra pp. 10-11. Math Digest 12-15 http://www.helpingwithmat h.com/by_grade/gr7_work sheets.htm http://www.dummies.com/ how-to/content/how-toconvert-metric-units-ofmeasurement.html http://www.regentsprep.or g/regents/math/algebra/a m2/leseng.htm http://www.enslow.com/re sources/978-0-7660-33696.pdf http://www.mathworksheet s4kids.com/capacity/estim ate-large.png http://www.mathworksheet s4kids.com/capacity.php http://www.mathsisfun.co m/volume-conversion.html http://worksheets.tutorvist a.com/volume-wordproblems.html?page=1 h.com/by_subject/word_pr oblems/wor_measurement 01_4md2.htm Grade 7 LCTG by DepEd B. Other Learning Resources / Materials Cavite Mathematics, 2016 Grade 7 LCTG by DepEd Grade 7 LCTG by DepEd Cavite Mathematics, 2016 Cavite Mathematics, 2016; Activity sheets rulers, tape measures, steel tape measure Grade 7 LCTG by DepEd Cavite Mathematics, 2016 shoebox, rubik’s cube, tin can, toblerone box, ball IV. PROCEDURES A. Reviewing previous lesson or presenting the new lesson Motivation Let the students identify the following pictures and describe how it can be used for measurement. Pre-Assessment: Identify the most realistic unit of measure for each of the following: Pre-Assessment: Fill in the blanks. Use as 1 unit of mass. 1. size of your waistline 2. length of Olympic pool 3. distance from Manila to Cavite 4. thickness of book 5. height of flagpole 1. The mass of the pineapple is _________. 2. The mass of the _________ is 2 units. 3. The mass of the broccoli is ________ . 4. The _________________ is 1 Pre Assessment Estimate the capacity of each object. Encircle your answer. unit lighter than the banana. 5. The total mass of the 4 items is ________. 6. The _________________ is lighter than the banana. 7. The _________________ is 3 times heavier than the banana. 8. The _________________ is 4 times heavier than the carrot. B. Establishing a purpose for the lesson Let the students do the following and write their answers on the notebook. a. Measure the length and width of your Math book using your thumb’s width and the ruler b. Measure the length of your classroom using foot length and meter stick c. Compare your measurement with those of your classmate (at least 3) and write your Estimate first. Record the object’s estimation, actual measurement and their difference on the table below. Use centimetre and inch. Activity A. Choose the most appropriate instrument to use in measuring the weights of the given objects. For the weight, check (√) only one of the given units. Determine the dimension of the following using the specified metric units only. Record your results in the table below and compute for each objects volume using the unit used to measure the object’s dimension. Complete the table by expressing/converting the volume using specified units. (For reference, see observations. Object LCTG, pp.99-103) 1. Length of the classroom 2. Height of the door 3. Length of a chalk 4. Length of shoe 5. Height of chair SHOE BOX l w h TIN CAN r h RUBICS CUBE l w h TOBLERONE BOX OBJECTS b 1. ₱5 - coin 2.a monoblock chair 3.barbie doll 4.A piece of brick 5.yourself BALL r h H WEIGHT -gram (g) -kilogram (kg) -pound (lb) C. Presenting examples/ Based from the activity, answer the following instances of the questions: lesson 1. Did you experience difficulty when you were doing the actual measuring? 2. What have you noticed on your results and of your classmates? 3. Can you relate an experience in your community where non – standard unit of measurement was Conversion of Metric System of Measure Study the metric converter illustrated below. km cm hm mm dam m dm To convert hectometer to decimeter, count the 1. What was your reason for choosing which instrument to use? 2. What was your reason for choosing which unit to use? 3. What other kinds of instruments for measuring weight do you know? 4. What other units of weight do you know? A. Metric System 1. Change 2.46 hL to cL Conversion Solution: To convert smaller unit to Since there are 4 spaces larger unit move to the left. between hL and cLm move the decimal point 4 1. Change 465 cg to dkg times to the right. 465 cg = 0.465 dkg To convert larger unit to smaller unit move to the right. 2. Change 7.95 kg to g 2. Change the volume of 45 000 milliliters of liquid to liter. Solution: There are 3 spaces between mL and used? 4. At present, what are some of the standard unit of measurement are used? Show to the class the different primitive ways of measurements spaces from hm to dm, and move the decimal point in the same direction as many spaces as indicated in the diagram. 7.95 kg =7 950 g English System Conversion Example 1. Convert 60 ounce into pounds Example: 1. 5.4321 hm = 5432.1 dm Example 2. Convert 3 2. 0.985 km = 985 m kg into pounds Similarly, move 5 spaces to the left or 5 decimal places to the left to convert centimeter to kilometer. The number of spaces corresponds to the powers of ten needed to convert one unit to another. Conversion of English System of Measure Proportions will help you make conversions when working with measurments Create a unit conversion ration, which is always equal to 1: L, thus move the decimal point 3 times to the left. A. For three dimensional unit, use the metric converter below. 1. Change 750 mm3 to cm3 Solution: There is only one space between the two units. Thus the decimal point is moved 3 times to the left. 2. Change 3.48 km3 to m3. Solution: There are 3 spaces between the two units. Thus the decimal point is moved 9 times to the right. For English Measures Illustrative Example 1. Convert 1 cubic yard into 1 cubic feet. We know that 1 yard = 3 feet 2. Convert the capacity of 30 cubic feet cylindrical tank into cubic meter. Example1: How many yards are in 15 feet? There are 3 feet in 1 yard, so the conversion ratio is Since 1 ft = 0.3048 m, therefore, . Solving algebraically gives an answer of 5 yards Example 2: Convert 2 miles into inches 1. What was your reason for choosing which unit to use? 2. How did you convert the metric units of volume (cc to m3) and vice versa? 3. How did you convert the English unit of volume? 4. How did you convert the Metric unit to English unit of volume and vice versa? Conversion of English system to Metric system or vice versa 1 inch = 2.54 cm 3.3 feet = 1 meter Example: Convert 60 inches into meter Since the given measurement was multiplied by conversion factors which are equal to 1, only the unit was converted but the given length was not changed D. Discussing new concepts and practicing new skills #1 Divide the class into five groups. Each group will get the measure of each item and share the results to the class after completing the table following Change the following to metric the indicated unit. 1. 21 g = _______ mg 2. 2.8 kg= _______ g 1. 7 m to dam 3. 9768 g= _______ kg 2. 9 km to m 4. 2340 mg=______ hg 3. 752 cm to mm 5. 0.553 kg =_____ mg 6. 3 lb = _______ oz 4. 57.3 m to mm Convert the using the converter. What is the water depth of each tank? (1 liter = 1 000 cm3) 5. 99 mm to km 1. 2. 3. 4. 6. 42.17 m to km 7. 8456 mm to m 7. 6 tons = ______oz 8. 5 000 lb =____ tons 9. 10 kg = _______ lb 10. 22 lb = _______ kg 8. 426 cm to mm 9. 15 dm to hm Item (1st Column) 10. 18 m to dam 1. length of the teacher’s table 2. height of the tallest student of the group 3. width of the blackboard 4. thickness of your Math book Hand of the tallest group member (2nd Column) Meter Stick or Ruler (3rd Column) Answer the following questions; 1. Which unit of measure is more accurate? Why? 2. What are the advantages of using meter stick or ruler? Volume: 4.8 liters Water Depth: ______ Volume: 32 liters Water Depth: ______ E. Discussing new concepts and practicing new skills #2 F. Developing mastery (Leads to Formative Assessment 3) Identify whether the unit of measure is expressed in standard form. If Yes write IWY and VOICE if No. 1. 15 paces 6. 7 hours 2. 10 gallons 7. 12 meters 3. 25 cubits 8.10 digits 4. 7 kilos 9. 8 meters 5. 10 spans 10. 12 liters Match each term with its meaning. Write the letter of your answer. ____1. The metric unit used for length ____2. The thickness or width of the index finger ____3. The distance of one full step ____4. A hundred meters Measure the length of each line segment and convert to the indicated unit. (For clearer view, see DLP/LCTG) Convert the following measures of length 1. 36 in = ________ ft 2. 21 ft = ________ yd 3. 3 yd = ________ in 4. 3 mi = ________ft 5. 6 ft = ________ in Encircle the best estimate of the weight of the following: 1. a cup of coffee a. 245 mg b. 245 g c. 250 kg 2. a 25 centavo coin a. 8 mg b. 8 g c. 8 kg 3. a glass of water a. 400 mg b. 400 g c. 400 kg 4. a thick book a. 1.5 mg b. 1.5 g c. 1.5 kg 5. a nail a. 0.5 mg b. 0.5 g c. 0.5 kg Convert the following measurements 1. 9.56 kg = ______ dg 2. 654.3 dg = ______ g 3. 9.268 mg = ____ cg 4. 3.54 kg = ______ hg 5. 455 g =_______ kg Convert the following to the indicated measures. 1. 459 mL = _____ L 2. 0.375 L = _____ mL 3. 396 L = _____ kL 4. 36 000 mm3= _____ dm3 5. 1 gal = _____ pt A. Convert the following: 1. 500 mL = _____ dL 2. 10 cm3 = _____ mm3 3. 120 oz = ______ qt 4. 3 ft3 = ______ in3 5. 150 m3 = ______ ft3 B. What is the water depth of each tank? (1 liter = 1 000 cm3) ____5. The distance from the elbow to the fingertips a.pace b.cubit c.digit d.hectometer e.meter f. hand span Volume: 1.8 liters Water Depth: ______ Volume: 8.25 liters Water Depth: ______ G. Finding practical applications of concepts and skills in daily living Use your span, palm and digit measures to estimate each length in inches. 1. The length of your Math notebook 2. The length of your classroom blackboard 3. The length of your Solve the following: Problem Solving 1. Gemma bought a 60 cm ribbon to accentuate her curtain but she needs to convert it in inches. How long is it in inch? 2. Maragondon Plaza 1. The mass of one sachet of coffee is 0.005 kilograms. What is its equivalent net weight in grams? Answer each of the ff. 1. Find the volume of balikbayan box with side length of 1 m. Convert into ft3. 2. Estimate the capacity of a cylindrical kiddie pool in cubic teacher’s table 4. The height of your chair H. Making generalizations and abstractions about the lesson The length of a foot, the width of a finger and the distance of a step were all accepted measurements. Primitive ways of measurements: 1. Inch 2. Hand 3. Span 4. Foot 5. Yard 6. Cubit 7. Lick 8. Pace Ancient Egyptians used units of measurement measures 25 meters in length and 12 meters in width. The Mayor asks its measurements in feet. What are its measures? 3. Will a cabinet of 60 inches in height fits into a door of 7.5 ft high? Show your answer. 4. My foot is 22 cm. What is the approximate shoe size should I buy if it is measured in inches? 5. If the school’s LCD TV is 40 inches, what is its measurement in meters? The results of measuring are merely near approximations since measurements are not always exact. There is often a relative error involve. Accuracy of measurements depends on two factors: 1. the skill of the person doing the measuring; and 2. the precision of the instrument used in measuring. 2. Carlo’s cell phone weighs 171 g, how much does it weigh in ounce? Points to remember in converting units: centimetres which is 2 ft high and 3 ft in diameter? 3. The school canteen bought a freezer which measures 60 cm in width, 80 cm in length and 150 cm in height. Find the volume of the freezer in cubic ft. Volume is the amount of space an object contains or occupies. It is often 1. Determine the large unit measured in terms of and the small unit. cubic centimeters (cm3) 2. Multiply when and cubic meter (m3). converting from large unit Capacity is used with to small unit. Divide when liquids and is often converting from a small measured in terms of liter unit to a large unit. Use the (L), milliliter (mL), conversion factor depending on the amount to be measured. The metric converter helps Volume Formulae for in changing one unit to some regularly shaped another. objects: To use the converter, simply count the spaces from the given unit to the based on body parts such as the cubit and the half cubit. The cubit is the length of the forearm from the elbow to the tip of the middle finger; that the inch and foot, the units for length of the English System of Measurement, are believed to be based on the cubit. The Metric System of Measurement became the dominant system in the 1900s and is now used by most of the countries with a few exceptions, the biggest exception being the United States of America. desired unit and move the The first factor can easily decimal point in the same Cube be developed through direction as the number of V=edge x edge x edge V= e3 constant practice while space counted. Rectangular prism the second factor is Mass is the amount of V=length x width x height totally dependent upon material in an object. V=lwh the measuring device. Mass is not weight! Triangular prism Weight is how heavy an V=1/2 x base x height x object is and can be Vocabulary: Length Meter – the fundamental affected by forces such as V=1/2 bhL unit of length in the metric gravity. You may weigh Cylinder less on the moon, where system. V= π x 〖radius〗2 x height there no gravity but your Metric System – it is a mass is the same! V=πr2h decimal system of Cone measurement where Gram is the basic unit for V=1/3 x π x 〖radius〗2 x multiples and fractions of measuring weight in the height the basic unit correspond metric system. V=1/3 πr2 h to powers of ten. Length - the distance The chart below shows Sphere V=4/3 x π x 〖radius〗3 from one end to the other you the metric mass units of the longest side of an from smallest to largest V=4/3 πr3 object. Context: The length of the SYMB Fraction Common Metric Measures or swimming pool is 12 OL (Volume) multiple meters and its width is 5 of 1 meter SYMBOL Fraction or meters multiple of 1 meter Approximate - fairly close 1 mg 0.001 g 1 ml = 0.001 L (1/1 000) to the actual but not (1/1 000) 1cl = 0.01L (1/100) accurate. 1dl = 0.1L (1/10) Context: Kim’s mother 1cg 0.01 g 1L =1L estimated that her (1/100) 1dal = 10 L approximate height is 5 1hl = 100 L 1kl = 1000 L feet. 1dg 0.1 g Estimate - to make a (1/10) Common English rough or approximate 1g 1 g Measures (Capacity) calculation. 3 teaspoons (tsp) = 1 Context: The sewer 1dag 10 g tablespoon (tbsp) estimated that the curtain 16 tbsp = 1 cup (c) 100 g for the window must be 2 1hg 8 ounces (oz) = 1 c meters in length 2 c = 1 pint (pt) 1kg 1000 g Exact - accurate, precise 2 pt = 1 quart (qt) Context: The carpenter 4 qt = 1 gallon (gal) used a steel tape measure to obtain an Common English Measure Metric Units of Volume and Capacity exact measurement of the (Weight) floor Weight 1 milliliter (ml) Points to remember in Ounces (oz) =1 cubic centimeter (cm3) converting units: 16 oz = 1 lb Pounds (lb) 1. Determine the large unit 1 liter (L) 2000 lb = 1t and the small unit. =1 000 cubic centimeter Tons (t) 2. Multiply when (cm3) = 2000 lb converting from large unit 1 t to small unit. Divide when converting from a small unit to a large unit. Use the conversion factor. Common Metric Measures 1 mm 000) 1cm 1dm 1m = 0.001 m (1/1 = 0.01 m (1/100) = 0.1 m (1/10) = 1m 1 kg = 2.2 lb 1 metric ton = 1 000 kg 1dam = 10 m 1hm = 100 m 1km = 1000 m Common English Measures Distance Inches (in) 12 in = 1 ft Feet (ft) 3 ft = 1 yd Yards (yd) 1760 yd = 1 mi Miles (mi) 1 mi I. Evaluating learning Tell what metric unit of measure is appropriate in measuring the following: 9. The height of your mother 10. The length of your ballpen 11. The distance of your home from your school 12. The length of a book 13. The thickness of this book = 5280 ft Compare each pair of measurements using <, > or =. 1. 1 m ___ 10 dm 2. 1 dm ___ 1 dam 3. 5 ft ____ 60 in 4. 2 000 cm ____2 m 5. 1 mi _____ 2 km Solve these problems. 1. A boy weighing 27.6 kilograms sits on one end of the seesaw. How many grams should another boy weigh if he is to balance the first boy on the opposite end? 2. Angel bought 3 kg of glutinous rice and 3.3 lb of brown sugar to make kalamay. Which of the ingredient did she Solve. A swimming pool in a park is 20 m wide, 30 m long, and 4 m deep. What is the capacity of the pool in liter? have more of? J. Additional activities for application or remediation V. REMARKS Use a tape measure to measure different parts of your body. Write each measurement to the nearest millimetre and centimetre. a. around your waist b. around your neck c. from your knee to your feet Solve: 1.Jose rode 2 km on his bike. His sister Lina rode 3000 meters on her bike. Who rode the farthest and how much farther did they ride (answer in km)? 2. Jasmin is measuring two extension cords. The first cord is 60 cm long and the other cord is 5 feet long. How longare the two cords together? (answer in cm) 3. Edna takes 500 milligrams of vitamin C every day. How many grams of vitamin C did Edna take in 30 days? Solve. Find the volume of the L A baby boy was born blocks below. exactly 9 pounds. He gained an average of 2 pounds in a month. How much will he weigh in kilogram on his first birthday? VI. REFLECTION 1. No. of learners who earned 80% on the formative assessment 2. No. of learners who require additional activities for remediation. 3. Did the remedial lessons work? No. of learners who have caught up with the lesson. 4. No. of learners who continue to require remediation 5. Which of my teaching strategies worked well? Why did these work? 6. What difficulties did I encounter which my principal or supervisor can help me solve? 7. What innovation or localized materials did I use/discover which I wish to share with other teachers?