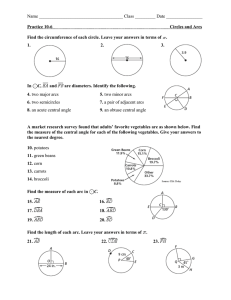
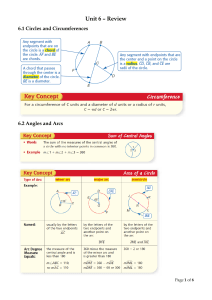
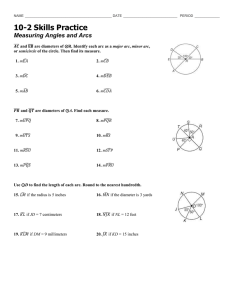
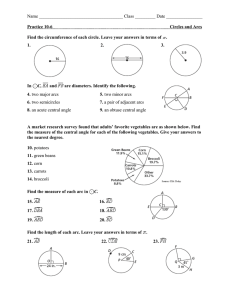
A Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics Grade 10-2 Learning Competency: Proves theorems related to chords, arcs and central angles. I. Objectives: At the end of the lesson, the students are expected to be able to: a. define central angles, arcs and chords, b. determine relationship between minor arc and major arc, c. apply the arc addition postulate in solving problems involving circles, and d. prove theorems involving arcs and chords. II. Subject Matter a. Topic: Central Angles, Arcs, and Chords b. Reference: SAP Education. 2014. Synergy for Success in Mathematics - New Edition. Singapore Asia Publishers Pte Ltd. c. Materials: Chalk and Board Marker Manila Papers Teaches Activity A. Preliminary 1. Daily Routines a. Greetings b. Checking of orderliness and neatness of the class and the classroom. c. Implementing of House Rules. Students' Activity B. Pre - Lesson Activities 1. Review a. Have the students recall about their last topic on introduction of circles. b. Emphasize that last time they focused more on the outside properties of a circle. C. Lesson Proper 1. Given a circle ABC, discuss what are central angles. Prepared By: SUPANGA, Joe Angelo D. 2. Recall the basic terms of a circle. 3. Then discuss what is a minor arc. 4. Show what are major arcs. 5. Differentiate the property of the two arcs. 6. Emphasize the proper labeling of the minor and major arcs. 7. Add a point D on the circle then have the students determine 2 minor and major arcs. 8. Add another line that bisects the circle and discuss semicircles. 9. Emphasize central angles of an arc and show that minor arcs are less than 180 degrees, major arcs are greater than 180 and semicircles are equal. 10. Using the same figure, discuss Adjacent non-overlapping arcs. 11. Test the student by asking if the pair of minor arc and major arc forming the circle is considered adjacent nonoverlapping arcs. 12. Emphasize the definition why it is false. 13. Assign values to some of the 1-2: AB, BC, CD, AD 3-4: ABC, BCD, ACD, ABD 5. False Prepared By: SUPANGA, Joe Angelo D. central angles then show that the values for the other can be obtained by angle addition, and same will be applied with the arcs. 14. Emphasize that all arcs within the circle must add up to 360 arc degree. 15. Referring to the same figure, discuss congruent arcs. 16. Using another figure, show relationship between arcs and chords. i. AB is the arc of chord AB and AB is the chord of arc AB. 17. Point out that congruent chords have congruent arcs and vice versa. 18. Bisect the chord by a diameter. 19. Emphasize point m is a midpoint of arc AB using definition. 20. Ask students whether it’s true that if the minor arc is bisected by a diameter then the other major arc is also bisected. 21. Explain answer by using theorem 4.5. True D. Generalization Briefly discuss the key points and definitions of: Central Angles Arcs Minor and Major Arcs Semicircle Central Angle of Arcs Adjacent Non-Overlapping Arcs Arc Addition Postulate Prepared By: SUPANGA, Joe Angelo D. Midpoints and Bisectors E. Assessment Given a circle, Find the following: 3 Minor Arcs 3 Major Arcs A Semicircle Central Angle of Arc F. Agreement Read on the next topic Prepared By: SUPANGA, Joe Angelo D.