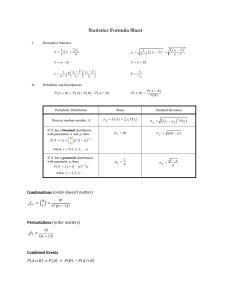
Applied Mathematics 40S Final Review Unit A: Logic and Set Theory 1. Know how to write conditional statements. 2. Know how to write negation statements. 3. Know how to write converse statements. 4. Know how to write contrapositive statements. 5. Be able to provide counterexamples to disprove a statement. 6. Know how to write biconditional statements 7. Be able to use a Venn Diagram to compare two sets. 8. Know the difference between a union and an intersection of two sets. 9. Know the meaning of the complement of a set. Unit B: Permutations and Combinations 1. Be able to use the fundamental counting principle. 2. Be able to use factorial notation to solve problems. 3. Be able to calculate the number of permutations of an event (nPr). 4. Be able to calculate the number of permutations of repeated events. 5. Be able to calculate the number of permutations of grouped events. 6. Be able to use cases to determine the number of permutations. 7. Know the difference between combinations and permutations and when to use each. 8. Be able to calculate the number of combinations of an event (nCr) 9. Be able to determine the number of combinations when selecting from two groups 10. Be able to use cases to determine the number of combinations. 11. Be able to solve "at most" and "at least" problems 12. Know when to use complements to solve permutations and combinations. 13. Be able to create a situation that fits a given permutation or combination. Unit C: Probability 1. Know the difference between mutually exclusive, non-mutually exclusive, independent, and dependent events. 2. Be able to calculate a probability as a fraction, decimal and percent. 3. Know the acceptable values of a probability. 4. Know how a probability and its complement are related. 5. Be able to use a tree diagram to solve the probability of dependent events. 6. Be able to use a Venn Diagram to solve probabilities. 7. Know how to count the number of routes between two points. 8. Be able to use permutations and combinations to solve probabilities. Unit D: Design and Measurement 1. Be able to convert units within the metric and imperial systems including squared and cubed units. 2. Be able to convert units from metric to imperial and vice versa including squared and cubed units. 3. Be able to draw diagrams to scale. 4. Be able to calculate surface area and volume of various objects. 5. Be able to solve real problems such as amount of paint needed to paint a house. Unit E: Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 1. Know the behaviour and shape of exponential and logarithmic graphs. 2. Know the common points of exponential and logarithmic graphs. 3. Know the domain and range of exponential and logarithmic functions. 4. Know the effects of changing values of a and b in y = a log bx. 5. Know the effects of positive and negative values of a and b in y = a log bx. 6. Be able to use Desmos to set appropriate windows and graph functions. 7. Be able to use Desmos to create regression equations that fit a table of values. 8. Be able to use Desmos graphs to solve problems. Unit F: Polynomial and Sinusoidal Functions 1. Know the behaviour and shape of linear, quadratic, and cubic graphs. 2. Know the domain and range of linear, quadratic, and cubic graphs. 3. Be able to determine the direction, range, and whether there is a maximum or minimum in a parabola by looking at only the equation. 4. Know the effects of changing values of a, b, and c in y = ax2 + bx + c 5. Know the effects of positive and negative values of a and c in y = ax2 + bx + c. 6. Know the effects of a, b, c, and d in y = a sin (bx + c) + d. 7. Know the effects of positive and negative values of a and d in y = a sin (bx + c) + d. 8. Be able to use Desmos to set appropriate windows and graph functions. 9. Be able to use Desmos to create regression equations that fit a table of values for polynomial functions. 10. Be able to use the TI-83 to create regression equations that fit a table of values for sinusoidal functions. Unit G: Finance 1. Know how appreciation affects the value of a home. 2. Be able to solve for any of the variables in the TVM solver. 3. Know the difference between simple interest and compound interest. 4. Understand the risk levels of various investments and make recommendations based on one's age and lifestyle. 5. Be able to use the rule of 72 to estimate doubling time. 6. Be able to calculate the rate of return on an investment portfolio. 7. Know how depreciation affects the value of a vehicle. 8. Be able to give reasons why one should buy or lease a vehicle.