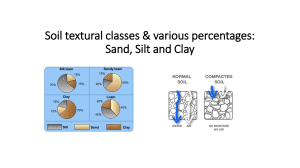
Soil and it’s characteristics Moroccan common core english option Horizons: vertical columns of soil exposure Color of soil depends on how the soil is formed and what it contains O. (Organic) Most living organisms carrie on their main activities remains of dead plants are found and slowly decomposing A. (Surface or topsoil) Most productive horizon, where most organisms and organic matter is found humus forms B. (Subsoil) Soil hasn’t quite formed yet, not enough organic matter to be productive, where root systems are penetrated C. (Substratum) Transition between bedrock and productive soils R. (bedrock) unweathered parent rock Soil’s roles growth releasing , absorbing gases. habitat, absorb animals hold release nutrients alter, Carbon, engineering media aquifer Living filter dynamic The same The same Soil’s physical characteristics : grain size • Soil's physical characteristics include grain size, which refers to the size of the mineral components within the soil. These mineral components are classified into three main types of grains based on their size." Clay Silt Sand granulometric analysis • The basic concept to get soil’s texture in a granulometric analysis of soil • Granulometric analysis refers to the process of determining the particle size distribution of a granular material, such as soil, sediment, or aggregate. It involves separating and measuring particles of different sizes within the material to understand its composition and characteristics • The analysis is typically performed through methods like sieving or sedimentation, where the sample is divided into fractions based on particle size. The weight or volume of each fraction is then measured, and the data is used to calculate the percentage or cumulative percentage of particles within specific size ranges. Soil’s physical characteristics : soil’s texture • Soil texture refers to the relative proportion of sand, silt, and clay particles in a given soil. It describes the physical composition of soil and is determined by the size of the mineral particles it contains • Given that we determine soil texture by calculating the percentages of clay, silt, and sand in a soil sample, we rely on a graphical approach in the form of a soil texture triangle. % Clay soil texture triangle • The soil texture triangle is a graphical representation that helps determine the texture of a soil sample by plotting the percentages of sand, silt, and clay in it. It consists of a triangular diagram divided into sections, with each section representing a different soil texture. By locating the point where the three percentages intersect on the triangle, one can determine the soil texture classification. % Clay How to use the triangle ? • Let’s suppose you have the following percentages. • Clay 30% • Silt 40% • Sand 30% • you project the percentage of each axis towards the complementary percentage of the contiguous axis and parallel to the third axis. • The meeting point of each projected line • Gives the soil texture Worked example • Let’s suppose you have the following percentages. • Clay 10% • Silt 40% • Sand 50% Worked example • Let’s suppose you have the following percentages. • Clay 30% • Silt 20% • Sand 50%