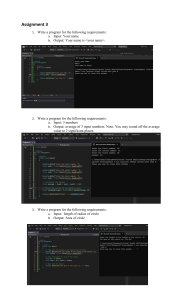
THE CIRCLE THEROM GROUP MEMBERS Alicia Phillips Ann-Marie Thompson Kishawnie Sewell Deshaun Walker Davihano Pottinger 10s THE CIRCLE T H E O R E M o A circle is a round plane figure whose boundary (the circumference) consists of points equidistant from a fixed point (the centre) o The Circle Theorem is the angle that lies between a tangent and a cord is equal to the angle subtended by the same chord in the alternate segment. When two angles are subtended by the same arc, the angle at the centre of a circle is twice the angle at the circumference. So angle AOB = 2 × angle ACB. Angles subtended by the same arc at the circumference are equal. This means that angles in the same segment are equal . THE PROPERTIES OF THE CIRCLE Lines and circles are the important elementary figures in geometry. We know that a line is a locus of a point moving in a constant direction, whereas the circle is a locus of a point moving at a constant distance from some fixed point. The theoretical importance of the circle is reflected in the number of amazing applications. Some properties of a circle CIRCLE THEOREM 1 Angle At The Centre What is the angle at the centre? The angle at the centre is twice the angle at the circumference of a circle. In the diagram above, the two points B and D on the circumference are joined to the centre, C, and to another point on the circumference, A. Circle Theorem 2 Angles In The Semi Circle (Thales' Theorem) What are angles in the semicircle? Angles in a semicircle are created when you join the two ends of the diameter to one point on the arc using cords. In the diagram below, A B AB is the diameter of a circle that divides the circle into two. Circle Theorem 3 Angles In The Same Segment Angles in the same segment are equal. The angle in the circumference subtended by the same arc are equal. More simply, angles in the same segment are equal. Circle Theorem 4 Cyclic Quadrilateral A cyclic quadrilateral is a four sided shape that can be inscribed into a circle. Each vertex of the quadrilateral lies on the circumference of the circle and is connected by four chords. The opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral have a˚ total of. 180˚ Circle Theorem 5 Radius To A Tangent A line that touches the circle at a single point is known as a tangent to circle. The point where tangent meets the circle is called point of tangency. The tangent is perpendicular to the radius of the circle, with which it intersects.