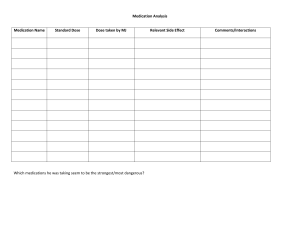
OUSSAMA BENKHYE (Mhtrf Gamer) Reading a Scientific Research Article scientific article: a piece of writing that reports the findings of a scientific experiment. Scientists use these types of articles to inform other scientists, as well as regular people, about their discoveries. good scientific article does several things: It explains why the experiment was done, how it was performed, what conclusion was reached, how the results support that conclusion. Why read a scientific paper? • I'm having trouble getting my experiments to work, and I think I might have the wrong concentration of NaCl in my solutions. I better check to see what other investigators have used. • Those folks at Your State University have been working on the same question as me. I wonder whether their work supports or contradicts mine? • I can't believe those folks at Your State University are claiming their results contradict my work. I'm going to scrutinize their data and analysis to see if they've made any mistakes. • That work sounds interesting, I wonder if I might be able to incorporate any of the ideas or approaches into my own work. • That Albert Einstein is a pretty bright guy, it's probably a good idea if I keep up with his work. • I'm trying to stay current with my field, I wonder what new work is out there. The typical “anatomy” of a paper: TITLE - title will help you to determine if an article is interesting or relevant for your project - Well-written titles: give a reasonably complete description of the study that was conducted, and sometimes even foreshadow the finding. included in a title are the species studied, the kinds of experiments performed, and perhaps a brief indication of the results obtained. - What – Who - Where Example : - The Effect of Strategy Training on Moroccan University Students Word Knowledge in an EFL Context - Knowledge Gaps on Paediatric Infections in Morocco, Norther Africa ABSTRACT - Abstracts provide you with a complete, but very succinct summary of the paper - An abstract contains brief statements of the purpose, methods, results, and conclusions of a study. OUSSAMA BENKHYE (Mhtrf Gamer) - Abstracts are often included in article databases, and are usually free to a large audience. Thus, they may be the most widely read portions of scientific papers. INTRODUCTION - You will find background information and a statement of the author's hypothesis in the introduction - An introduction usually describes the theoretical background, indicates why the work is important, states a specific research question, and poses a specific hypothesis to be tested. METHODS The methods section will help you determine exactly how the authors performed the experiment The methods describes both specific techniques and the overall experimental strategy used by the scientists. • The subjects: the people ,the participant of the study ,animals • The setting: time ,place, duration • The instruments: tools or equipment that the researcher has done to perform the experiment (habits lifestyle of subjects) • The research design : RESULTS - The results section contains the data collected during experimentation - The results section is the heart of a scientific paper. In this section, much of the important information may be in the form of tables or graphs. DISCUSSION The discussion section will explain how the authors interpret their data and how they connect it to other work. • What the work suggests : implication of the study • How it relates to other studies • Anticipate and address any possible objections to their work: limitations of the study • Suggest areas of improvement for future research. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS The acknowledgments tell you what people or institutions (in addition to the authors) contributed to the work. • Sources that provided financial support for the study. • The industry group or the federal government funded the study. LITERATURE CITED (not bibliography) - This section provides the sources cited throughout the paper Information about the range of other studies cited: • Does the author cite only his or her previous studies? • Are both classic and modern sources influencing this work? • Does the author look to the work of scientists in other disciplines? The literature cited section is also helpful for generating a list of background reading on the topic under study. How do expert readers approach a scientific paper? - Expert readers of scientific literature approach a paper with a critical mindset. - They do not automatically accept an author's conclusions. OUSSAMA BENKHYE (Mhtrf Gamer) - They examine whether an experiment and its data and analysis support the claims of the author. - They are persuaded by the data and its analysis, not by an author's writing. Types of graphs OUSSAMA BENKHYE (Mhtrf Gamer) Research studies Case control studies - In a case control study, a group of people suffering from a disease (the cases) is compared with a group who do not have the disease, but are similar in other ways (the controls). The two groups are compared to see if they were exposed to a possible risk factor (i.e. something which may contribute to the cause of a disease. - we search the comportment which causes the disease in the cases group Cohort studies - In a cohort study, a group (cohort) of people (subjects) who are similar is studied over a period of years (a longitudinal study) to determine if there is a relationship between exposure to a risk factor and development of a disease. At the beginning of a prospective study, none of the subjects has the disease. They are followed up for a number of years, and at the end of the period, those who have developed the disease are compared with those who have not. The subjects are only observed and there is no intervention. A cohort study is a more reliable method of identifying the cause of a disease than a case control study. Trials In a trial, a group of people who are suf fering from a dis ease ar e given a par ticular t r e a t m e n t . To d e t e r m i n e t h e e f f e c t i v e n e s s o f t h e t r e a t m e n t , a c o n t r o l l e d t r i a l i s p e r f o r m e d . Tw o g r o u p s a r e s t u d i e d : o n e g r o u p ( t h e s t u d y g r o u p ) i s g i v e n t h e t r e a t m e n t a n d t h e o t h e r ( t h e c o n t r o l g r o u p ) i s no t . T h e c o n t r o l s m a y b e g i v e n a p l a c e b o . Tr i a l s a r e u s e d t o te s t t r e a t m e n t s o r p r ev e n t i v e m e a s u r e s . longitudinal study: collect data from the same sample over an extended period of time. cross-sectional study: you collect data from a population at a specific point in time cases: A study that compares patients who have a disease or outcome of interest controls: patients who do not have the disease or outcome Risk factor: Something that increases a person's chances of developing a disease Cohort : is a group of people with similar characteristics Confounding: Something that might cause confusion about the cause of a disease meta-analysis is a statistical analysis that combines the results of multiple scientific studies. OUSSAMA BENKHYE (Mhtrf Gamer) Q.E the architecture of a scientific article : IMRAD introduction methods results and discussion IMRAD format The organization of a research report into four main sections: the Introduction, Method, Results, and Discussion sections. Methods the specific ways that scholars collect and analyze data which they then use to prove or disprove their theories Results data and observations gathered from the experiment Discussion the portion of a research report that restates the hypothesis, summarizes the results, and presents a discussion of the interpretation, implications, and possible applications of the results Open access publishing provides content online for readers for free but means that you can pay to be published what is the A in IMRAD sometimes abstract and includes an introduction and a brief summary Longitudinal study a study that observes the same participants on many occasions over a long period of time Cross-sectional study In medical research, social science and biology, a cross-sectional study is a type of observational study that analyzes data from a population, or a representative subset, at a specific point in time—that is, cross-sectional data. Clinical trials experiments that study the effectiveness of medical treatments on actual patients Case-control study A type of epidemiologic study where a group of individuals with the diseases, referred to as cases, are compared to individuals without the disease, referred to as controls cohort study design a study design that involves the examination of a large disease-free population over a period of several years Risk factors characteristics or behaviors that increase the likelihood of developing a medical disorder or disease what is research design a detailed plan or method for obtaining data scientifically Ethnographic Case Study Describes the activities of a specific group and the shared patterns of behavior the group develops over time OUSSAMA BENKHYE (Mhtrf Gamer) Experimental method a method of cause-and-effect relationships with a random assignment to experimental and control groups Meta-analysis combines the findings of multiple studies to determine the average impact of a similar intervention across studies Exploratory research Research conducted to gather more information about a problem or to make a tentative hypothesis more specific When is exploratory research used when the researcher sees additional information or desires more recent information about a problem Descriptive research designs describing patterns and finding connections True experimental research random assignment, active manipulation, Tx and control groups Quasi-experimental design Research method similar to an experimental design except that it makes use of naturally occurring groups rather than randomly assigning subjects to groups. Hypothesis a supposition or proposed explanation made on the basis of limited evidence as a starting point for further investigation. null hypothesis A prediction that there is no difference between groups or conditions, or a statement or an idea that can be falsified, or proved wrong. alternative hypothesis the hypothesis that a proposed result is true for the population Blinding a technique where the subjects do not know whether they are receiving a treatment or a placebo Double-blind procedure A research strategy in which neither subjects nor experimenters know which subjects are in the experimental or control groups. Randomization (random assignment) A sampling selection procedure in which each person or element in a population has an equal chance of being selected to either the experimental group or the control group. Setting The time and place of the action/experiment/research Funding money provided, especially by an organization or government, for a particular purpose. Capsule Cylinder shaped enclosure for medication, either gelatin or time-released coating OUSSAMA BENKHYE (Mhtrf Gamer) Drop Sterile solution that contains medication intended to be delivered directly into the area to be treated, e.g., eyes, ears, nose, etc. Inhalant Medications delivered in fixed or nonfixed dose breathed in through the nose or the mouth. May be oxygen, sprays or aeresols Liquid Medication suspended in liquid or alcohol to be administered through means of injection, intravenously, intrathecal, nasogastric or orogastric. Other means may be through wounds by irrigation. Powder Fine particles intended to be dissolved in liquids or foods just prior to be ingested. Suppository A bullet-shaped, solid drug that is inserted into a body opening: rectal, vagina or urethra that melts at body temperature. Tablet Medication that is bound together by substances that dissolve in stomach acids that are sometimes flavored to make them more palatable. Can be divided into two. OUSSAMA BENKHYE (Mhtrf Gamer) Transdermal Patch Adhesive patch with time-released dose of medication to be worn for a specific amount of time. Transdermal: Crossing through the skin Intradermal: pertaining to within the skin Ointment a smooth substance that you rub on the skin to heal a wound or sore place Lozenge (troche) A flat, round, or oval preparation that dissolves and releases a drug when held in the mouth Pill Mixture of a powdered drug with a cohesive material; may be round or oval IV injection injection of a substance directly into a vein OUSSAMA BENKHYE (Mhtrf Gamer) intramuscular injection an injection into deep muscle tissue, usually of the buttock, thigh, or upper arm Alimentary routes: Passes the GI organs and liver for drug metabolism Oral route of administration: the administration of medication through swallowing for absorption along the GI tract into systemic circulation buccal route of administration: a transmucosal route of administration in which a drug is placed between the gum and the inner lining of the cheek Sublingual: Drugs placed under tongue Rectal: Drugs inserted at anus parenteral route: dispensation of medications via a needle into the skin layers/non-oral means of administration Intradermal: pertaining to within the skin Subcutaneous: 45 deg Subq tissue Intramuscular: 90 deg muscle Intravenous: pertaining to within a vein Intraarterial: Direct route to artery Intraperitoneal: Direct route to peritoneal Intracardial: Direct route to heart Topical: Apply on skin or mucous membranes Eyes nose throat airways caging ears OUSSAMA BENKHYE (Mhtrf Gamer) Analgesics: alleviate pain Narcotics: decrease pain sensation in central nervous system Anesthetics: reduce or eliminate sensation Anticoagulants: prevent coagulation and formation of blood clots Antidiabetics: prevent or alleviate diabetes Antiemetics: relieve symptoms of nausea and prevent vomiting Antihistamines: prevent responses mediated by histamine; allergic and inflammatory reactions Antihypertensives: lower blood pressure by reducing cardiac output, dilating vessels, or promoting excretion of water by the kidneys anti-inflammatory drugs: counteract inflammation and swelling corticosteroids, nonsteroidal: types of anti-inflammatory drugs antibacterial, antibiotics, antifungals, antiparasitic, antivirals: types of anti-infective agents diuretics: promote excretion of water, sodium, and other electrolytes by the kidneys gastrointestinal drugs: act on the digestive tract antidiarrheals, histamine H2 antagonists, laxatives, proton pump inhibitors: types of gastrointestinal drugs antidiarrheals: treat or prevent diarrhea by reducing intestinal motility or absorbing irritants and soothing the intestinal lining laxatives: promote elimination from the large intestines muscle relaxants: depress nervous system stimulation of skeletal muscles antidepressants: relieve depression by raising brain levels of neurotransmitters respiratory drugs: act on the respiratory system antitussives: suppress coughing asthma maintenance drugs; bronchodilators: used for prevention of asthma attacks and chronic treatment of asthma; prevent of eliminate spasm of the bronchi by relaxing bronchial smooth muscle; used to treat asthma attacks and bronchitis expectorants: induce productive coughing to eliminate respiratory secretions sedatives/hypnotics: induce relaxation and sleep OUSSAMA BENKHYE (Mhtrf Gamer) QOD: every other day QD: daily BID: twice a day Q4h: every 4 hours Tab : tablet Cap: capsule Syr: syrup Gtt: drop Ung: ointment TID: three times a day QID: four times a day QAM: every morning QPM: every evening QHS: at bedtime Q#H: every ___ hours PO: by mouth IV: intravenous IM: intramuscular SL: sublingually OS: left eye OD: right eye OU: both eyes AS: left ear AD: right ear AU: both ears AC: before meals PC: after meals c food: with food WM: with meals qs: quantity sufficient prn: as needed 1 tsp: 5 mL 1 tbsp: 15 mL transcribe means putting verbal information into written form Pharmacokinetics the study of the bodily absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of drugs; looks at what the body does to drugs in its system Pharmacodynamics the study of the reactions between drugs and living systems Pharmacotherapeutics the study of the therapeutic uses and effects of drugs toxicology OUSSAMA BENKHYE (Mhtrf Gamer) the study of poisonous chemicals, drugs, and other substances, and how a person or other living things react to them. focuses on negative effects of drugs on the body prescription is a legal document that provides information regarding the medication to be dispensed to a patient a prescription always includes: the medication name, how to use the medication (frequency and route of administration) and the patient's information Medical Orders provide the same information found on prescriptions; however, they are used for inpatient settings and include the number of doses generic Drug Name the official drug name that's found in the US parmacopeia (USP) National Formulary Trade Name (brand name) the name given to a drug by its manufacturer; this info doesn't appear if the drug is generic chemical name of drug Describes the drug's chemical composition and molecular structure Drugs facts labeling Tells you what the medicine is supposed to do, who should or shouldn't take it, and how to use it. It contains usage and safety information for consumers. National Drug Code (NDC) a drug's unique 10 or 11 digital identification number Dosage Strength the amount of active ingredient found in the medication Drug Manufacturer the name of the company that made the medication Storage Instructions instructions on how to store the medication, such as the temperature or humidity Expiration Date the date after which a medicine should not be sold because of an expected decline in quality or effectiveness Bioavailability is the fraction of the unchanged drug that enters the circulation and is available to have a therapeutic effect What are some factors that affect bioavailability? what patient eats, if the patient's stomach is empty, quantity, ect dose is the amount of medication that is taken at one time Dosage is the total amount of a medication to complete the prescription order OUSSAMA BENKHYE (Mhtrf Gamer) Scored Tablet tablet with a linear indentation (scoring) that acts as a guide for splitting into equal parts Unscored Tablet tablet without linear indentation (scoring) Parenteral medications aren't administered or absorbed through the gastrointestinal tract Tinctures formulated by dissolving the active ingredient in alcohol Elixirs sweetened alcohol-based medications Suspensions mixtures of an insoluble active ingredient uniformly distributed in a liquid but not dissolved in it. Syrups saturated sugar solutions containing dissolved medical ingredients Solutions medications completely dissolved in a liquid Infusion medication is introduced into the body at a slow, continuous rate through a needle or catheter Topical medication is applied to the skin. generally, topical medications treat the area of skin with which they come in contact. sometimes they're creams instead of true liquids Ophthalmic medication is introduced through the eye Intranasal medication is introduced through the nose Ophthalmic delivery system where medication is introduced through the eye Infusion delivery system where medication is introduced into the body at a slow, continuous rate through a needle or catheter International Unit (IU) is a measurement of the amount of substance in a medication, but this type of measurement caries across different types of medications Anticoagulant a type of drug that prevents blood from clotting, such as heparin Insulin a medication (a hormone) used to control type 1 & 2 diabetes. OUSSAMA BENKHYE (Mhtrf Gamer) An anti-epileptic medication is one that prevents seizures : 2) An antihypertensive medication is used to prevent or control high blood pressure. 3) An anticancer medication is one that prevents the growth of cancer cells or prevents the spread of cancer in the body. 4) An antitoxin medication is one that reduces or eliminates the harmful effects of a toxin. 5) An anti-anginal medication is one that alleviates angina or chest pain. 6) An antiviral medication prevents the spread of a virus. 7) An antibacterial medication eliminates bacteria. Compendium: a comprehensive list and collection of knowledge and information Formulary: a list of drugs approved for prescription and their formulas Therapeutic: able to treat, ameliorate, or cure Potential: is capable of action but not yet doing so Gross: large or coarse and visible to the eye Poison: a substance that enters the body that is injurious to health or potentially fatal Tremors: abnormal, repetitive, involuntary shaking movements Medication order: identifies a drug the doctor wants the patient to take and gives instructions on how to take the drug Transcribe: copy and interpret something spoken or written into a document Obligation: duty and responsibility OUSSAMA BENKHYE (Mhtrf Gamer) Safe practice: actions, knowledge, and competencies that will not harm patients or clients Follow-up care: a phase of care that continues in the community after discharge from the hospital or a series of treatments Best practice: procedures and treatments of high standards that have been proven to be effective in care delivery Grave: very serious and possibly dangerous, harmful, or life threatening Measures: steps in a procedure or process Verifying: checking the truth, accuracy, or interpretation Wristband: bracelet that wraps around the wrist that includes identifying data Systematic: organized, methodical, step-wise chest pain: angina 1) What is the main focus of this reading? 2) In what types of situations are these strategies occurring? 3) What is meant by the term the “7 Rights”? 5) The title of the reading mentions preventative action. What is being prevented? 6) Two preventative actions are discussed in this reading. Name them.