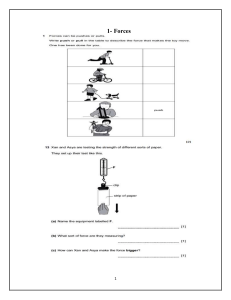
**Physics: Unraveling the Mysteries of the Universe** Physics, often dubbed the "fundamental science," is a discipline that seeks to understand the fundamental principles governing the behavior of the universe. From the smallest subatomic particles to the vast expanses of space-time, physics endeavors to unravel the mysteries of the cosmos through observation, experimentation, and theoretical modeling. **Historical Foundations** The roots of physics can be traced back to ancient civilizations such as Mesopotamia, Egypt, and Greece, where early thinkers pondered the nature of the world around them. However, it was during the scientific revolution of the 16th and 17th centuries that physics emerged as a distinct field of study. Pioneering figures like Galileo Galilei, Isaac Newton, and Johannes Kepler laid the groundwork for modern physics with their groundbreaking theories of motion, gravity, and celestial mechanics. **Classical Physics** Classical physics, which encompasses the theories developed prior to the 20th century, provided a comprehensive framework for understanding the behavior of macroscopic objects. Newton's laws of motion, Maxwell's equations of electromagnetism, and the laws of thermodynamics were among the cornerstones of classical physics. These principles revolutionized fields such as engineering, technology, and astronomy, laying the foundation for the Industrial Revolution and the modern world. **The Rise of Modern Physics** The early 20th century witnessed a paradigm shift in physics with the advent of quantum mechanics and relativity theory. Quantum mechanics, pioneered by luminaries like Max Planck, Albert Einstein, and Niels Bohr, revolutionized our understanding of the microscopic world of atoms and subatomic particles. It introduced concepts such as wave-particle duality, uncertainty principle, and quantum entanglement, challenging conventional notions of determinism and causality. **Relativity theory, developed by Albert Einstein, introduced a new understanding of space, time, and gravity. His groundbreaking work on special relativity and general relativity reshaped our conception of the cosmos, leading to profound insights into the nature of black holes, gravitational waves, and the expanding universe.** **Contemporary Frontiers** Today, physicists continue to push the boundaries of knowledge, exploring phenomena at the forefront of scientific inquiry. Particle physics, which delves into the fundamental constituents of matter and forces, seeks to unravel the mysteries of the universe's origins and composition. Experiments conducted at particle accelerators such as the Large Hadron Collider shed light on the elusive Higgs boson and probe the nature of dark matter and dark energy. **Astrophysics and cosmology, meanwhile, probe the origins, evolution, and fate of the universe on the largest scales. Observational astronomy, coupled with theoretical modeling, provides insights into the birth of stars and galaxies, the formation of black holes and neutron stars, and the structure of the cosmic web.** **Furthermore, interdisciplinary fields such as biophysics, nanotechnology, and quantum computing bridge the gap between physics and other scientific disciplines, offering new avenues for technological innovation and discovery.** **Conclusion** Physics, as the cornerstone of scientific inquiry, continues to inspire wonder and curiosity about the nature of reality. From the subatomic realm to the cosmic expanse, physicists strive to unravel the mysteries of the universe and unlock its deepest secrets. As we stand on the brink of a new era of exploration and discovery, the quest to understand the fundamental laws governing the cosmos remains an enduring and awe-inspiring endeavor.