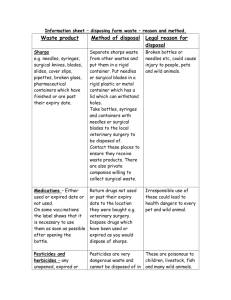
Worksheet in Agri-crop NC I Grade 10/Quarter 2 Week 1 Storing waste material and debris in the designated area according to workplace procedure TLE_AFAC912CW-IIa-e-3 Name of Learner: ___________________________________ Date of Delivery: ________________ Date of Retrieval: ________________ Adviser/Subject Teacher: MARY JANE S. MOLINA_ Checked by: MITO V. MACABEO HT III T.L.E. Department Head 1 Review Directions: Loop 5 hand tool and equipment commonly used in the farm X M M E V V Q X W X B M D X V W X X R O T A V A T O R S L X P W X X W A S O X S W E X W K X M S N X X X W E Presentation and Discussion There are 5s which are written in Japanese words which are good to adopt or practice in any workplace and it was proven effective. The purpose of the 5s is to reduce waste and increase efficiency thereby reducing production costs while increasing productivity, safety and workers satisfaction. 5S in Japanese In English Definition 1. Seiri Sort segregation of the workplace contents and removing unnecessary items. 2. Seiton Systematize is putting the necessary items in their place and providing easy access. In other words, these is orderliness. 3. Seiso Shine 4. Seiketsu Standardize if the workplace is orderly it follows cleanliness and these two were maintain and it provides good atmosphere for the workers. always follow and observe the standard. 5. Shitsuke Sustain workers should always set the workplace safe before starting to work and leave the workplace clean and orderly 2 Why is 5S important to your workplace? 1. It helps to eliminate waste stream line production 2. Make a commitment to post safety organization and effectiveness ahead of prevention, deadliness, profits, and outputs. 3. Increase efficiency but reduce production costs. In addition to the 5S here are the ten rules to follow to keep safety in a workplace. 10 Rules to follow for workplace safety: 1. You are responsible for your own safety and for the safety of others. 2. All accidents are preventable. 3. Do not take short cuts, always follow the rules. 4. If you are not trained, don’t do it. 5. Use the right tools and equipment and use them in the right way. 6. Assess the risks before you approach your work. 7. Never wear loose clothes or slippery footwears. 8. Do not indulge horse paly while at work. 9. Practice housekeeping. 10. Always wear PPE’s Finally, the key to Safety is in your hands. What are the basic rules of safety? Always put away the tools when they are not in use. Keep the floors clean, pick up scraps and wipe up spills. A slip or trip can be fatal. Reporting is important. Never fail to report accidents, defective equipment and or unsafe conditions. In case there are problems arises, make a report immediately using the required forms. 12 forms to be use in reporting depending the kind of problem happen or arises in working areas. 1. Waste Segregation Plan- This is the form use if there are different waste material that are found in the work place that needs to be segregated. 2. Maintenance Inspection Checklist- This is the form use if there is a machine that needs inspection and maintenance. 3. Breakdown or Repair Report- This form is used when there is a facility that needs repair or replacement. 4. Housekeeping Maintenance Schedule- This is the form used for housekeeping activities in a particular area. 5. Equipment Maintenance Schedule- This form is used if there is equipment that needs checkup and inspection. Parts of the machine to be checked should be indicated. Other than machines, other working area, like storage room and tool room that needs maintenance. 6. Work Request- This is 7prepared if there is a machine, tool that needs replacement due to damage. 3 7. Housekeeping Inspection Checklist- This is prepared when a particular working area needs to be inspected to keep safe for working. 8. Salvage Report- A form used if a certain equipment is for future use or back-up. 9. Equipment Record with Code and Drawing- In this form, specifically equipment was listed including their complete description, equipment number, quantity, drawing reference, and locations. 10. Inspection Report- This form is to be filled out if something happens in the working area. 11. Tag-out Bill- in this form, damage, warning, and certain was tag for a certain equipment or a certain part of the working area to keep safe/ 12. Housekeeping Maintenance Schedule- A form where in housekeeping schedule are indicated, the activities, responsible person are specified for a certain area in a working place. Materials storage Safe and efficient materials storage depends on good co-operation and coordination between everyone involved including, client, contractors, suppliers and the construction trades. Top tips for materials storage on smaller projects: 1. Storage areas - designate storage areas for plant, materials, waste, flammable substances e.g. foam plastics, flammable liquids and gases such as propane and hazardous substances e.g. pesticides and timber treatment chemicals; 2. Pedestrian routes – do not allow storage to ‗spread in an uncontrolled manner on to footpaths and other walkways. Do not store materials where they obstruct access routes or where they could interfere with emergency escape; 3. Flammable materials - will usually need to be stored away from other materials and protected from accidental ignition; 4. Storage at height - if materials are stored at height e.g. on top of a container, make sure necessary guard rails are in place if people could fall when stacking or collecting materials or equipment; 5. Tidiness - keep all storage areas tidy, whether in the main compound or on the site itself; and Safety tips for the storage tools, materials and outfits 1. 2. Store protective equipment and clothing in a nearby location that provides immediate access but is away from pesticides and their fumes, dusts or possible spills. Provide an immediate supply of clean water and have an eyewash dispenser immediately available for emergencies. Soap and a first aid kit are also necessary. Establish procedures to control contain and clean up spills. Familiarize everyone with the procedures and provide tools and absorbent materials to clean up spills. Prevent pesticide fires. Some pesticides are highly flammable. The labelling of the pesticides that require extra precautions often will contain a warning statement in the "Physical and Chemical Hazards" section or the "Storage and Disposal" section. 4 3. 4. Install fire detection systems in large storage sites and equip each storage site with a working fire extinguisher that is approved for all types of fires, including chemical fires. If you store highly toxic pesticides or large amounts of any pesticides, inform your local fire department, hospital, public health officials and police of the location of your pesticide storage facility before a fire emergency occurs. Storage & Disposal of Farm Wastes If farm wastes, including dead stock, are managed inappropriately, they can cause contamination of the premises, livestock, inputs and food. The accumulation of farm waste can also provide habitats and food for pests. General Farm Waste. All garbage and waste materials generated through normal production processes. Storage: Locate farm waste storage areas away from food handling, input storage and livestock housing areas to prevent cross-contamination and avoid attracting pests. Make sure farm waste storage areas and containers are adequate for the amount of waste generated between disposal times. Clean farm waste storage areas often enough to avoid creating conditions that can cause cross-contamination or attract pests. Where possible, use containers with lids for the storage of farm waste until removal. Disposal: Remove farm waste often enough and in a manner to prevent crosscontamination and avoid attracting pests. Dispose of all materials according to municipal laws and provincial regulations. If farm waste can be used by other sectors, store and ship them so as not to pose a food safety hazard. Unless properly sanitized, vehicles used for transporting farm waste should not be used to transport food products and farm inputs. Note: Crops grown on-farm can be fed to livestock housed on the same farm. Follow pesticide label instructions regarding grazing and feeding crops to livestock. Medical Waste. Used medical equipment (for example, needles), unused or expired medicated feed, animal health products, packaging and/or containers. 5 Storage: Store used needles, empty medicine containers and unwanted or expired animal health products in rigid, leak-proof containers and labelled NONHAZARDOUS WASTE (medicine bottles) or BIOMEDICAL WASTE (needles, scalpels and other “sharp” equipment). Disposal: Follow suppliers’ or manufacturers’ instructions for disposal of syringes, medications and other items as well as outdated medical supplies. Another viable disposal option may be your veterinarian. Disposal on your property or in burn barrels are not desirable disposal options. Contact local Environmentalist. Make sure medicated feed and water are disposed in a manner that does not contaminate the environment. Used Pesticide Containers Storage: Triple-rinse all empty pesticide containers by following these steps: 1. 2. 3. 4. Fill empty containers with water to a minimum of one-tenth of the container size. Rinse by recapping the container and shaking or rolling. Empty pesticide container contents into sprayer tank. Repeat steps 1 to 3 two times. Do not reuse pesticide containers for storage of other items. Disposal: Take rinsed containers to a pesticide container collection site for recycling. There are four options to dispose of unwanted pesticides: 1. 2. 3. 4. Return unopened pesticide container to the dealer before winter. Apply pesticide to another crop specified on the label. Pay a Hazardous Waste Disposal Company to dispose of the pesticide. Participate in the local government programs on waste management. Occasionally, the government, pesticide industry and Agricultural Council coordinate special unwanted pesticide collection programs. Be prepared for the auditor to observe or inquire about storage activities to ensure that: Adequate and proper waste storage areas and/or containers are clearly designated on the farm, Farm waste storage containers and areas are well kept and maintained, Farm waste is removed on a regular basis, Medical waste containers are clearly marked, Empty pesticide containers and unwanted pesticides are stored in a designated area labeled for disposal, and 6 Dead stock is stored and/or disposed of according to provincial regulations. ENVIRONMENTAL LAWS Presidential Decree (PD) 1152 The Philippine Environmental Code,‖ which took effect in 1977, provides a basis for an integrated waste management regulation starting from waste source to methods of disposal. PD 1152 has further mandated specific guidelines to manage municipal wastes (solid and liquid), sanitary landfill and incineration, and disposal sites in the Philippines. In 1990, the Philippine Congress enacted the Toxic Substances, Hazardous and Nuclear Wastes Control Act, commonly known as Republic Act (RA) 6969, a law designed to respond to increasing problems associated with toxic chemicals and hazardous and nuclear wastes. RA 6969 mandates control and management of import, manufacture, process, distribution, use, transport, treatment, and disposal of toxic substances and hazardous and nuclear wastes in the country. The Act seeks to protect public health and the environment from unreasonable risks posed by these substances in the Philippines. Apart from the basic policy rules and regulations of RA 6969, hazardous waste management must also comply with the requirements of other specific environmental laws, such as PD 984 (Pollution Control Law), PD 1586 (Environmental Impact Assessment System Law), RA 8749 (Clean Air Act) and RA 9003 (Ecological Solid Waste Management Act) and their implementing rules and regulations. Are you familiar with the 3R’s (Reuse, Reduce, Recycle)? 3Rs refers to three terms often used when talking about waste: Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle. Reducing is cutting back on the amount of trash we make, reusing is finding a new way to use trash so that we don't have to throw it out, and recycling is using trash to remake new goods that can be sold again. https://gltnhs-tle.weebly.com/lesson-46.html https://www.veolia.co.uk/nottinghamshire/recycling/recycle-nottinghamshire/3rsreduce-reuse-and-recycle https//www/ccohs.ca https//www.betterhealth.vicgov.au https//www.southerncouncil.org.c https//www.hazardouswasteexperts.com.ph.understandingthe4 characteristics hazardous waste (January 16,2020) https//disposal.uk/articles/difference.betweenhazardousandnonhazardouswaste. https://www.google.com/search?q=dustbin+clipart+black+and+white&tbm=isch&hl=e n&tbs=rimg:CbzuXkCh0eILYQxgzqxKg5k4&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwjxirnNhevsAhWaA aYKHU3hA0kQrNwCKAB6BQgBEPsB&biw=1686&bih=710 7 Activity 1 Directions: Supply the missing word/s by writing the correct answer in the space provided on how to Store Farm Wastes, medical waste and used pesticide containers. 1. input storage and livestock housing areas to prevent ______-contamination 2. Make sure __________waste storage areas and containers are adequate 3. Clean farm waste _______ areas often 4. use containers with ________ for the storage of farm waste until removal. 5. Fill ______ containers with water to a minimum of one-tenth of the container size. 6. Rinse by____________ the container and shaking or rolling. 7. Empty pesticide container contents into__________ tank. 8. Repeat steps 1 to 3________times. 9. label ________-hazardous waste on used medicine bottles/containers 10. label non-_____________ waste or biomedical waste empty medicine containers 8 Activity 2 Directions: complete the concept map below. Answer what is being ask on the different waste disposal in the farm. Write the proper disposal of the following Disposal of Farm Waste 1.________________________________________ 2.________________________________________ 3.________________________________________ Medical Waste 4.________________________________________ 5.________________________________________ 6.________________________________________ Used Pesticide Containers 7.________________________________________ 8.________________________________________ 9.________________________________________ 10._______________________________________ 9 Activity 3 ( Performance Task) Directions: Collage Making, Collect pictures related to the different general farm waste, You may print it or cut it out from the unused magazines or books then paste it on the garbage bin below. Show your understanding, appreciation and creativity through collage making. 10 RUBRIC Point Creativity Content Visual Impact Total Student’s Point 15 10 5 30 General Farm Waste Farm Waste Medical Waste Used Pesticide Containers Post Assessment I. Direction: Match column A with column B about the 12 forms to be use in reporting depending the kind of problem arises in working areas. Write your answer, letters only on the space provided. A B 11 _____1. Work Request a. used when there is a facility that needs repair replacement b. this is prepared if there is machine needs replacement due to damage c. in this form, damage certain was tag for a certain to keep safe d. is to be filled out if something happens in the working area. e. This is the form use if there are different waste material _____2. Tag-out Bill _____3. Waste Segregation Plan _____4. Inspection Report _____5. Repair Report II. Direction: Analyze and compete the table below with the information needed about 5s 5S in Japanese In English Sort 6. Seiton Definition segregation of the workplace contents and removing unnecessary items. 7. Seiso is putting the necessary items in their place and providing easy access. In other words, these is orderliness. Shine 9 8 Standardize Shitsuke always follow and observe the standard. 10 workers should always set the workplace clean and orderly III. Direction: In two sentences, Make a brief and simple instruction of the following scenario (11-15 items) A. Proper disposal of farm waste _________________________________________________________________ 12 _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ B. Proper storage of farm waste _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ Rubrics Content and Clearly express ideas Neatness Total Student’s Points Points 3 2 5 Key to Correction (for teachers) Review: 1 BOLO 2 AXE 3 RAKE 4 SPADE 5 ROTAVATOR 13 Activity 1 1. cross 2. farm 3. storage 4. lids 5. empty 6. recapping 7. sprayer 8. two 9. non 10 hazardous Activity 3 Collage will be based on the rubric which is 30 point RUBRIC Point Creativity Content Visual Impact Total Student’s Point 15 10 5 30 Activity 2 (in any order) Disposal of Farm Waste 1. Remove farm waste often enough and in a manner to prevent cross-contamination 2. Dispose of all materials according to municipal laws and provincial regulations. 3. store and ship them so as not to pose a food safety hazard. Medical Waste 4. Follow suppliers’ or manufacturers’ instructions for disposal 5. Contact local Environmentalist. 6. Make sure medicated feed and water are disposed in a manner that does not contaminate the environment. Used Pesticide Containers 7. Return unopened pesticide container to the dealer before winter. 8. Apply pesticide to another crop specified on the label. 9.. Pay a Hazardous Waste Disposal Company to dispose of the pesticide. 10. Participate in the local government programs on waste management. Post test I. 1B 2C 3E 4D 5A II. 6 Seiri 7 Systematize 8 workplace is orderly 9 Seiketsu 10 Sustain III. Rubrics Points Content and Clearly express ideas Neatness Total Table of Specification (for teachers) 14 3 2 5 Student’s Points Learning Competency/Code: Store waste material and debris in the designated area according to workplace procedure TLE_AFA-ACP10IW-IIi-l-33 Remembering 1,2,3 Understanding 4,5 Analyzing 8,10 15 Applying 6,7,9 Evaluating Creating 11,12,13, 14,15