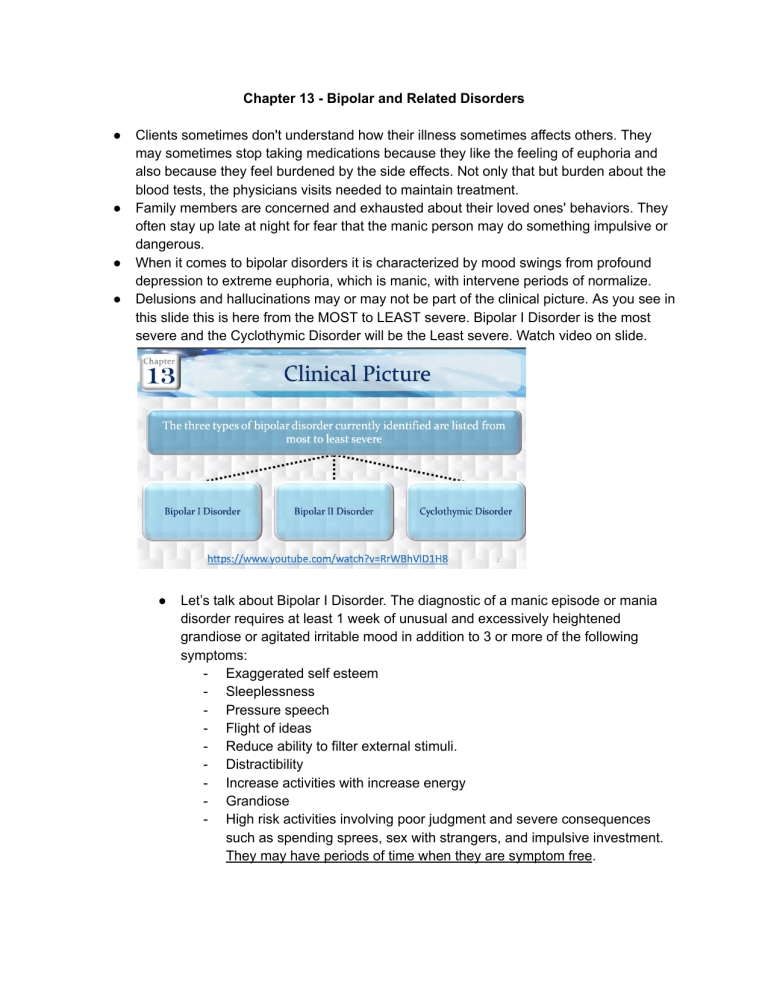
Chapter 13 - Bipolar and Related Disorders ● ● ● ● Clients sometimes don't understand how their illness sometimes affects others. They may sometimes stop taking medications because they like the feeling of euphoria and also because they feel burdened by the side effects. Not only that but burden about the blood tests, the physicians visits needed to maintain treatment. Family members are concerned and exhausted about their loved ones' behaviors. They often stay up late at night for fear that the manic person may do something impulsive or dangerous. When it comes to bipolar disorders it is characterized by mood swings from profound depression to extreme euphoria, which is manic, with intervene periods of normalize. Delusions and hallucinations may or may not be part of the clinical picture. As you see in this slide this is here from the MOST to LEAST severe. Bipolar I Disorder is the most severe and the Cyclothymic Disorder will be the Least severe. Watch video on slide. ● Let’s talk about Bipolar I Disorder. The diagnostic of a manic episode or mania disorder requires at least 1 week of unusual and excessively heightened grandiose or agitated irritable mood in addition to 3 or more of the following symptoms: - Exaggerated self esteem - Sleeplessness - Pressure speech - Flight of ideas - Reduce ability to filter external stimuli. - Distractibility - Increase activities with increase energy - Grandiose - High risk activities involving poor judgment and severe consequences such as spending sprees, sex with strangers, and impulsive investment. They may have periods of time when they are symptom free. ● ● And there is the type of bipolar disorder and when it comes to Rapid Cycling Bipolar Disorder. And there is some people with Bipolar I and Bipolar II disorder WILL experience rapid cycling and may have at least 4 mood episodes in a 12 month period. These moods episodes can be: - Mood episodes - Major depressive - Manic - Hypomanic Cycling can also occur within the course of 1 month or even 24 hour period and rapid cycling is associated with more severe symptoms such as: - Poor global functioning: this is like global assessment on how well the individual is functioning in their daily lives. Global assessment is also a way to measure the impact of psychiatric illness on a person’s life and daily functional skills and abilities. - High recurrence risk - Resistance to conventional somatic treatments ● Let’s talk about the stages here. - Stage 1: Hypomania - this is only going to happen in the Bipolar II Disorder in Cyclothymic Disorder. Disturbances here is not sufficiently severe to cause impairment in social or occupational functioning or to require hospitalization. Their mood is going to be hypomanic which is: - Cheerful - Expansive but underlying they have irritability that surfaces rapidly when the person's wishes and desires go unfulfilled. The nature of the hypomanic person is dovetail and fluctuating. Their cognition and perception is that their self are exalted meaning that the individual has ideas of great worth and ability. - Thinking is flighty with - Rapid flow of ideas - Perception of the environment is heightened but the individual is so easily distracted by irrelevant stimuli that goal directed activities are difficult. - Their activity and behavior hypomanic individual’s exhibit: Increase motor activity - they are perceived as being extraverted and socially and does attract numerous acquaintances. However, they lack the depth of personality and warmth to formulate close friendships. - They talk and laugh a great deal, usually very loudly and often inappropriately. - They have increased libido is very common! - Some individuals experience anorexia and weight loss - Their exalted self perception that leads some hypomanic individuals to engage in inappropriate behaviors such as running down a debt on credit card without having the resources to pay. ● Then, they get into Stage 2: Mania - Stage 2 will ONLY happen in Bipolar I Disorder. - Symptoms of acute mania may progress in intensification from those experience in hypomania or they may be manifested directly - Most individuals experience more impairment and functioning and REQUIRE hospitalization. - Their mood is euphoria and elation - the person appears to be on a continuous high. However the mood is always subjective, frequent variation, easily changed to irritability and anger or even to sadness and crying. - Their cognition and perception becomes fragmented and often psychotic in acute mania. - They have accelerated thinking, perceive to racing thoughts, over connection of ideas, and rapid abrupt movement from one thought to another, which is called flight of ideas - This is a continuous flow of accelerated pressured speech with abrupt changes from topic to topic - They also can manifest a continuous flow of accelerated pressure speech, which we call it loquaciousness to the point that conversing with this individual may be extremely difficult. If normal speech is analogous to the flow of a garden hose, then loquacious speech is like the stream of the fire hose. - When flight of ideas is severe, speech may be disorganized and incoherent. They are distractible and become all pervasive. Attention can be diverted by even the smallest of stimuli. - Hallucinations and delusions usually paranoid and grandiose are quite common. - Loose associations represent the disorganized way the person is processing information. Thoughts are only loosely connected to each other in the person’s conversation. For example, they would say in loose association, “The sky's the limit now that I have money I took a flight a you know from Kennedy drinking beer is a belly full of bags ” - They will also exhibit clang associations, which are string together words that rhythm without regard to their meaning. For example: “Cinnamon 1, 2 last row row row row your boat go get your throat cut your throat get out on boat and so i wrote” - Then we get conventional speech and it’s similar to circumstantial speech with one KEY DIFFERENCE. When people think conventionally they lose the point that they were trying to make and never find it again. Awareness of losing the point indicates less thought disturbance. For example: “Sorry I’m so scattered I got a lot on my mind” indicates insight. The degree of tangentially also helps identify how serious a thought disturbance is. Often a common word connects sentences. For instance, “I have to do my laundry that day because it was Saturday. On Saturday I also watch ninja turtles on television. Have you seen those 16 inch televisions? Giants. I used to think of Giants as I fell asleep and I thought that sleep activated them. - - - - ● Circumstantial speech is adding unnecessary details when communicating with others unlike the other verbal derailments the person eventually gets the point. “I plan to have my old chain today when I got in my car I noticed the letter on the seat was dirty. The dog we got a white and brown eagle because Jim insisted upon it he’s a blacker that’s how things have gone since we’ve been married in 1986 at a lovely church I’ll never forget the minister wore a green suit and shoes”. As you see this is your circumstantial speech. Their activity and behavior is excessive Sexual interest is increased There is poor impulse control and low frustration tolerance. The individual that is normally discrete may become socially and sexually uninhibited. Excessive spending is common. In acute mania the individual typically has little insight into his or her behavior and communication. The lack of insight manifests at times as unreliable reporting of events and denial of problems when comforted by friends or family, which may be interpreted as lying. Energy seems inexhaustible and the need for sleep is diminished An individual experiencing acute mania may go from many days without sleep and still not feel tired. Hygiene and grooming may be neglected. Dress may be disorganized, flamboyant, bizarre, or the use of excessive make up or jewelry is quite common. Then we get into Stage 3: Delirius Mania - This is a serious form of a disorder characterized by severe clouding of consciousness and an intesification of the symptoms associated with acute mania. This stage only will happen in Bipolar I disorder. The condition has become relatively rare since the availability of antipsychotic medication. - The mood of a delius person is very labile. - ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● He or she may display feelings of despair quickly converting into unrestrained merriment and ecstacy or becoming irritable or indifferent to the environment. Panic level anxiety may be evident. - Their cognition and perception are characterized by a clouding consciousness with accompanying confusion, disorientation, and stupor. - Other common manifestations include DELUSION of: - Religiosity - Grandeur - Persecution - Hallucinations - Auditory or visual - The individual is extremely distractible and incoherent - Psychomotor activity frenzied, agitated and purposeless movements AS YOU CAN SEE IN THE BOLDED RED LETTERS, WITHOUT INTERVENTION AT THIS STAGE IT WILL WILL LEAD TO EXHAUSTION, INJURY TO SELF OR OTHERS, AND EVENTUALLY DEATH. The best way to remember your manifestations to remember your bipolar manifestations is to remember DIG FAST. Primary symptoms of a manic attack. D - istractibility I - ndiscretion G - randiosity F - light of Ideas A - ctivity Increase S - leep Deficit T - alkativeness ● Then we get into Depressive Characteristics. As we already talked about this depression in the depressive disorder but they also will alternate with depression and these are some of the symptoms of what’s happening with them when they’re at this depressive state and of course it's going to be more intense and hospitalization is definitely required when they’re manifesting suicidal ideation, psychosis, or catatonia is present. ● Bipolar II as we mentioned this is a low level type of mania which is a hypomania. The episode is not severe enough to cause impairment in social or occupational functioning or to necessitate hospitalization. A full hypomanic episode that emerges during antidepressive treatment, which is medication or electrocompulsive therapy but persists at a fully syndromal level beyond the physiological effect of that treatment is sufficient evidence for hypomanic episode diagnosis. However, we need to CAUTION this because it is indicated that one or two symptoms, particularly increased irritability, aginess or agitation, following antidepressant use are not taking as sufficient for diagnosis of hypomanic episode. NOT NECESSARILY INDICATIVE of bipolar diathesis. ● Last Bipolar Disorder: Cyclothymic Disorder - To be diagnosed with this disorder is that it has to be at least 2 years. At least 1 year in children and less than 2 years in adults. There’s been numerous periods of hypomanic symptoms that do not meet criteria for hypomanic episode and numerous periods with depressive symptoms that do not meet the criteria for major depressive episode that is cyclothymic. - During the 2 year period and 1 year in children and adolescents, the hypomanic and depressive periods have been present for at least half of the time and the individual has not been without the symptoms for more than 2 months at a time. - Criteria for a major depressive manic or hypomanic episodes have never been met. The symptoms cause clinical significance stress or impairment in social occupational or other important areas of functioning. ● What is etiology? - Biological Factors - Genetics. Research shows that bipolar disorders strongly reflect an underlying genetic vulnerability. - Then we have the biogenic amines - which is the neurotransmitters of norepinephrine and dopamine that are excessive in bipolar disorder. And when they are in depression and mania, their serotonin remains low. Acetylcholine is another neurotransmitter believed to be related to bipolar disorder. - - Neuroanatomical factors and this is correlated with dysfunction in the prefrontal cortex, also in the frontal lobes as well. There is that medication side effects also, certain medication used to treat somatic illnesses have been known to trigger manic responses and the most common of these are the steroids, frequently used to treat chronic illnesses such as multiple sclerosis and systemic lupus erythematosus. So some clients whose first episode of mania occurred during steroid therapy have reported spontaneous recurrence of maniac symptoms years later. THAT’S interesting information. Lastly, psychosocial theories - there are interest in psychosocial theories has declined in the recent years with the focus of research in genetics and biochemical predisposing factors. However, there are several studies have confirmed a link between childhood trauma with the development of bipolar disorder. That the experience of a child's trauma insight changes in genes along several different pathways. These genetic changes may be linked not only to an increase risk for bipolar disorder but also earlier onset, more severe symptoms like substance abuse and suicidal risk. Let’s talk about your favorite topic, which is the medications. ● Mood Stabilizing Medications: 1) Lithium Carbonate, Lithium: for many years the drug of choice is for treatment and management of bipolar mania. In recent years several other medications have demonstrated the effectiveness either alone or in combination with lithium. Most notable are many drugs in the class of anticonvulsant medications, which are now FDA approved for mood stabilization. - Some second generation, atypical antipsychotic drugs have also demonstrated benefits from management of this disorder. - When it comes to Lithium Carbonate they're going to be used for bipolar disorder with agitation. If they have SEVERE AGITATION Lithium is going to work very well. - The onset of action of lithium is within 10-21 days, because the onset of action is so slow, it is usually supplemented in the early phases of treatment by second generation antipsychotics OR anticonvulsants or even anti anxiety meds. - Lithium is particularly effective in reading the following: - Elation - Grandiosity - Inexpensiveness - Flight of ideas - Irritability - Manipulation - Anxiety - Self injurious behaviors - Some clients complain that they miss the high feeling of being in a manic or hypomanic state. Once beginning mood stabilizer medication like lithium so they may be at risk for self adjustment medication or discontinuation of treatment. - There is a small window between therapeutic and toxic levels of lithium. And lithium must reach therapeutic levels to be effective. Therapeutic level will usually take 7-14 days or longer for patients. In the acute manic phase the lithium is usually started at 600-1200 mg a day in 2 to 3 divided doses. It is then increased every few days by 300mg a day with a maximum of 1800 mg per day. - The target serum lithium level for maintenance is 0.6 - 0.8, BUT we want to have the lithium level as 0.8 - 1.2 mEq/L. The first lithium level should be drawn every 2-3 days, after beginning lithium therapy and after every dosage change until the therapeutic level has been reached. Blood levels are then checked every 3-6 months. - Before administering lithium we need to complete a baseline assessment of renal function and thyroid status. Including levels of thyroxine and thyroid stimulating hormone. Perform other clinical and laboratory assessments like ECG, depending on the individual's condition. - Why are we doing all these baseline? Because of the adverse effects. They can get renal toxic, goiter, and hypothyroidism may occur with long term use. - So you have to teach the patient and family multiple information. Lithium is a mood stabilizer, it helps prevent relapse, it is important to continue taking the drug even after a current episode subsize. It is also important to monitor lithium blood levels closely until therapeutic levels are reached, and after it is reached, we need to continue monitoring to prevent toxicity. It is important to maintain consistent fluid intake, at least 1500- 3000 mL a day or 6 to 12 oz glass of fluid. Sodium intake can affect lithium levels. High sodium intake levels lead to low levels of lithium and less therapeutic effect. Low sodium intake level leads to higher lithium levels which could produce toxicity. So we need to aim for consistency in sodium intake. We need to tell the patient to stop taking lithium if they have excessive diarrhea, vomiting or sweating. ALL of the symptoms could lead to dehydration, which will increase blood lithium to toxic levels. Let your prescriber know if you are taking diuretics and also talk to the prescriber about having thyroid, parathyroid, and renal function checked periodically because they are at risk for high hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, and decrease kidney function. Make sure to tell them not to take OTC meds without checking with your prescriber. Even nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs like ibuprofen, Naproxen, why? BECAUSE IT WILL influence lithium levels. Take lithium with meals to avoid stomach irritation. And the first week you need to let them know that they will gain up to 5 lbs of water weight. Additionally weight gain may reoccur particularly in females. Other mood stabilizing: Antiepileptic or Anticonvulsant Medications. These meds were developed to treat seizures associated with epilepsy. The FDA approved them for use in acute mania, bipolar depression, and or bipolar maintenance. They are generally superior for continuous cycling patients. They are more effective when there is no family history of bipolar disorder and they are effective in diminishing impulsive and aggressive behavior in some non psychotic patients. Beneficial in controlling mania. It can control mania in 2 weeks and depression within 3 weeks or longer. 1) Valproate, divalproex (Depakote), Valproic Acid: Valproate available as divalproex or Valproic Acid and this is for treating acute mania. The common SE include: - Nausea, weakness, somnolence, indigestion, diarrhea, dizziness, and vomiting. - FDA has a black box warning for several adverse effects: hepatotoxicity (why we need to monitor liver function), thrombocytopenia (means low platelet so platelet count or coagulation studies should also be done), blood dyscrasias (e.g. leukopenia, neutropenia which will affect the bone marrow production), pancreatitis (A lot of time this condition could be dose related so the lowest beneficial dosage should be used), fatal hemorrhagic, teratogenicity (Also the FDA has a black box warning against pregnant women because of its teratogenicity). - The therapeutic level for Valproic Acid is going to be established as 50 125 micrograms/milliliter 2) Carbamazepine (Equetro, Tegretol): This is a second line for bipolar disorder. It reduces the firing weight of over excited neurons by reducing the activity of sodium channels. We need to monitor the LFTs, CBCs, ECG, and sodium levels at baseline and periodically thereafter. Blood levels are monitored to avoid toxicity and to establish therapeutic range for bipolar disorder will be 4-12 micrograms/milliliter. So you have three of the specific therapeutic levels that you need to know! - Pregnancy test is necessary before starting treatment due to the risk of birth defects. - Common SE are: dizziness, somnolence, nausea, vomiting, ataxia, blurred vision, hyponatremia or leukopenia (may occur) - Adverse effects: potentially life threatening condition: Stevens Johnson syndrome (SEVERE rash and happens in asia descent). Why is it required before starting this medication to do genetic testing for patients of asia descent. If the test reveals a patient is positive, the doctor will not prescribe Carbamazepine. Another AE: blood dyscrasias 3) Lamotrigine (Lamictal): Last one! This one is mainly approved for maintenance therapy in bipolar disorder. This one will inhibit sodium channels and modulates the release of excitatory neurotransmitters, which is glutamate and aspartate. - This med has a gradual dose titration because of rapid dose escalation will increase the risk for rash. So it is important to educate the patient to promptly report any rashes which could be a sign of Stevens Johnson syndrome. In about 10% of people taking this med, a rash appears within 8 weeks of starting treatment. The U.S. food and drug administration requires that all Antiepileptic/Anticonvulsant, which is all these 3 medications carry a warning label indicating the use of a drug that can increase the risk or suicidal thoughts of behaviors. The patient being treated with these medications should be monitored for the emergency or worsening of depression, suicidal thoughts or behavior or any unusual changes in mood or behavior. ● ● Also there are other medications. These are your anticonvulsants. - Clonazepam - Gabapenitn - Oxcabazepine - Topiramate And we have the 2nd generation antipsychotic medications as well: - Olanzapine ○ ● Quetiapine Aripiprazole (blue) Cariprazine Risperidone (red) Ziprasidone (red) Asenapine (red) These medications are going to prevent a switch to mania, which person’s are treated for depressed episodes and manage psychotic symptoms that are associated with mania in some people. There are mood stabilizing properties of the second generation antipsychotics. Because a lot of times when other mood stabilizers alone are inadequate in controlling symptoms, the addition of these medications is effective in BOTH acute and maintenance phases of treatment. You already know the SE and AE of the second generation antipsychotics (Review those). What are we going to do with our patients that are in our locked unit? - It is important to reduce environmental stimuli. You are going to provide a quiet environment without noise, television or other distraction. Please assign a private room with simple decor and quiet unit as possible. Keep lighting and noise level low. - Patient are extremely distractible and respond even to the lightest things that are exaggerated. So if a milieu unit may be too stimulating that is why we are reducing the environment to stimuli. Anxiety level increases as well, and suspicious and agitated patients may perceive others and the environment as threatening. - Stay with the patient who is hyperactive and agitated because your presence as a nurse may offer support and provide a feeling of security towards the patient. - Provide a structured schedule of activities that includes established rest periods throughout the day. Limit group activities. A structured schedule and a one to one activities provides a feeling of security for the patient. - - - - - - Why do we need to provide physical activities? Because this helps relieve tension and excessive energy. Avoid highly competitive activities, because competitive situations can exacerbate hostile feelings or reinforce low self esteem. It’s so important to intervene at the first signs of increased anxiety or agitation or any kind of verbal aggression by saying “you seem anxious” or “how can i help you?” This is a validation of the patient’s feelings, which will convey an attitude of caring and collaboration and facilitating establishing trust. Because the patient is highly distractible, providing a distraction can also aid in diffusing anxiety and agitation. It's all about maintaining and conveying a calm attitude by responding to them matter of factly to verbal hostility. With having a calm attitude it will facilitate the escalation of the patient’s anxiety and agitation. So if anxiety is increasing, we need to offer some alternatives, like maybe walking or other physical exercise, talking about the situation, and taking some anti anxiety medication. Because when we offer alternatives to our patients it will empower the patient to have a self sense of control over the situation. Nutrition is another area of concern. Maniac clients may be too busy to sit down and eat or they might have such poor concentration that they feel unable to stay interested in food for long. It is important to provide high protein, high calorie, nutritious finger foods and drinks that can be consumed “on the run”. Finger foods are foods that clients can consume while moving around and are the best option to improve nutrition. Also, foods should be as high in protein and high calorie as possible, for example, celery and carrots are finger foods, but they supply little nutrition. The best one would be sandwiches, protein bars, and 45 shakes. Clients with mania also benefit from food that is easy to eat, meals that must be cut into bite sizes or plates of spaghetti are likely to be successful options. The patient will have difficulty sitting or concentrating long enough to complete a sit down meal. Have juice and snacks available on the unit at all times. - - - - - - Nutritious intake must compensate for increased caloric requirement due to high hyperactivity, so we also need to provide a supplement diet with vitamins and minerals. Walk or sit with the patient while he eats. Your presence offers support and encouragement for the patient to eat food that will maintain physical wellness. We need to set limits on manipulative behaviors, because when you limit it must be established by you when your client is unable to use internal controls effectively. Explain to the patient what is expected and what the consequences are if the limits are violated. Terms of limitations must be agreed on all the staff who will be working with the patient. When the patient is unable to establish its own limits, this must be done for the patient, unless administration of consequences for violation of limits is consistent, manipulative behavior will not be eliminated. These clients physically and psychologically will invade your boundaries. That is why setting limits on their manipulative behaviors is important. E.g. “John, you are too close to my face. Please stand back 2 feet” Do not ever argue, bargain, or try to reason with your patient. Clearly set the limits and expectations, confront the patient as soon as possible when the interactions with others are manipulative or exploitative. Because the patient may be vulnerable to impulsive, reckless, or pleasuring behaviors without considering the consequences. Patients should receive immediate feedback when behavior inacceptable. Consistency in reinforcing consequences is essential. Positive outcomes are to be achieved, because when you are inconsistent and others are inconsistent it will create confusion and it encourages testing their limits. We must use a firm yet calm, relaxed approach. Your presence and your manner will communicate your interest, expectations, and limits as well as your self control. When the patient is unable to establish their own limits, you must do this for them. For instance “ John, come with me. Eat this sandwich”. Unless administration of consequences for violation is consistent, manipulative behavior will not be eliminated. This is why it is important to treat them with dignity and respect, despite their inappropriate behavior. It is not helpful to scold them, they are not children engaging in wrongful behavior. In the manic phase clients do not understand personal boundaries, so it is our role to keep clients in view for intervention as necessary. E.g. you see the client invading the space of others, you can see “It is unacceptable to hug other clients. You may talk to them but do not touch them”. I don't like unacceptable but rather he will say “Please do not hug other clients. You may talk to them but do not touch them”. “ John please do not yell at Peter, if you cannot control yourself, we will help you”. Or “The seclusion room will feel less out of control and prevent harm to yourself and others”. It is about using short and concise explanations or statements. The speech of manic clients may be pressured, rapid or circumstantial or rhyming or noisy. With flight of ideas, with these types of speech will indicate thought processes that are flooded with thoughts, ideas and impulses. You must keep the channels of communication open with clients regardless of speech patterns. E.g. John, please speak more slowly I’m having difficulty following you” In acute manic episodes clients may lose sexual inevitions resulting in provocative and risky behaviors. Clothing may be flashy or reveling or clients may undress in public areas. They may engage in unprotected sex with strangers. Clients may ask staff - members or other clients of the same or opposite sex for sex. They may even graphically describe sexual acts or display their genitals. You will handle this behavior in a matter of fact not judgmental matter. E.g. “Mary, let's go to your room and grab a sweater” or “John, please put away your genitalia. It is not good to show your genitals to others” You will be assigned to the same clients as possible. But I want you to keep in mind the stress of working with a client with manic behavior for extended periods of time. Consistency can reassure the client. Working with this client could be difficult and tiring when going through his agitation and hyperactivity. That's why sometimes we need to give these types of patients to other staff members.



