Uploaded by
Roland G. Sayago
Human Transport System: Circulatory & Respiratory Systems
advertisement

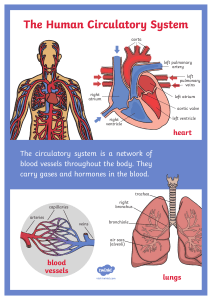
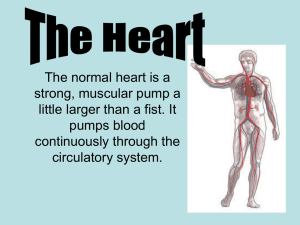
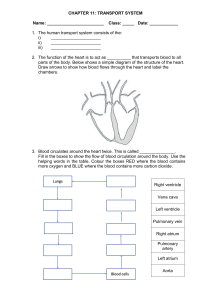
Who are they? 𝐎 𝟐 𝐍𝐮𝐭𝐫𝐢𝐞𝐧𝐭𝐬 𝑯𝟐 𝑶 𝑪𝑶𝟐 LESSON 1: TRANSPORT SYSTEM BY ROLAND SAYAGO LESSON OBJECTIVES 01 Explain the relationship between circulatory and respiratory system; 02 Identify the parts and functions of human circulatoy system; 03 Trace how blood circulates in the body. THE HUMAN TRANSPORT SYSTEM THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM HEART BLOOD VESSELS BLOOD VALVES BLOOD VESSELS BLOOD VESSELS Artery The arteries are the blood vessels that deliver oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the tissues of the body. Vein The veins are the blood vessels that deliver nonoxygenated blood towards the heart. BLOOD VESSELS Arterioles & Venules Arterioles and venules are small diameter blood vessels that allow blood flow to and from capillary beds, respectively. BLOOD VESSELS Capillaries Capillaries are delicate blood vessels that deliver blood, nutrients and oxygen to cells throughout the body. BLOOD BLOOD The red liquid that circulates in the arteries and veins of humans and other vertebrate animals, carrying oxygen to and carbon dioxide from the tissues of the body. PLASMA Makes up about 55% of the body's total blood volume. Helps with immunity, blood clotting, maintaining blood pressure, blood volume, and pH balance in the body RED BLOOD CELLS Red blood cells are the most common type of blood cell and the vertebrate's principal means of delivering oxygen to the body tissues—via blood flow through the circulatory system. WHITE BLOOD CELLS White blood cells are part of the body's immune system. They help the body fight infection and other diseases. PLATELETS Platelets are tiny blood cells that help your body form clots to stop bleeding. BLOOD TYPES a ab b o BLOOD TYPES Antigen Blood type: A BLOOD TYPES BLOOD TYPES BLOOD TYPES BLOOD TYPES ab BLOOD TYPES O HEART HEART Your heart is the primary organ of your circulatory system. It pumps blood throughout your body, controls your heart rate and maintains blood pressure. VALVES The valves are made of strong, thin flaps of tissue called leaflets or cusps. The leaflets open to let blood move forward through the heart during half of the heartbeat. They close to keep blood from flowing backward during the other half of the heartbeat.. PARTS OF THE HEART The right side of the heart receives deoxygenated blood collected from different parts of the body The left side of the heart receives oxygenated blood from the lungs PARTS OF THE HEART The two atria are thinwalled chambers that receive blood from the veins. The two ventricles are thick-walled chambers that forcefully pump blood out of the heart. PARTS OF THE HEART The Vena Cava is a large vein that carries blood to the heart from other areas of the body. The Pulmonary Vein collects the oxygenated blood and carry it from the lungs back to the heart. The Pulmonary Arteries carry blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs. The Aorta is the main artery that carries blood away from your heart to the rest of your body. Blood Flow Sequence Right Atrium Vena Cava Aorta valve Left Ventricle valve valve Right Ventricle Left Atrium valve Pulmonar y Artery Pulmonar y Veins Organs of Respirati on Nose Air enters the nostrils, which are lined with tiny hair, called cilia, and mucus membranes all of which filter dust particles from the air we breathe. Pharyn x The pharynx is the common opening for food that we swallow and air that we inhale. A flap muscle called epiglottis guards the path of the pharynx to ensure that food and air will enter their respective destinations. Larynx The hollow muscular organ forming an air passage to the lungs and holding the vocal cords in humans and other mammals - the voice box. Trachea Bronchi Bronchiole s Air Sac Each air sac consists of many tiny out-pocketing called alveoli. It is within the alveoli that the gas exchange occurs The Breathing Process Breathing is the process of drawing air into the lungs (inhalation) and its corresponding (exhalation). Blood Flow Sequence Right Atrium Vena Cava Aorta valve Left Ventricle valve valve Right Ventricle Left Atrium valve Pulmonar y Artery Pulmonar y Veins THANKS! Do you have any questions? roland.sayago@pcu.edu.ph Philippine Christian University CREDITS: This presentation template was created by Slidesgo, including icons by Flaticon, and infographics & images by Freepik