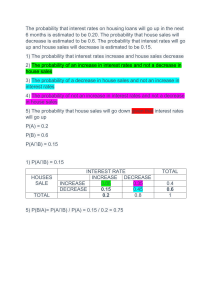
Topic 5: Microfinance and Financial Inclusion Introduction Poverty is a multifaceted concept. The elemental definition of poverty has perennially been rooted in monetary dimension, with income or consumption serving as symbolic standards. When individual’s earnings dip below the established poverty line, they find themselves ensnared in poverty’s grasp. Conversely, the multidimensional perspective of poverty encompass the deprivation of fundamental human necessities – ranging from sustenance, shelter, education, clean water, sanitation and health and participation in societal realms. Poverty, a pervasive and consequential global issue, has gained significant attention within the framework of sustainable development goals (SDGs) due to its wide – reaching prevalence and profound implications. Various strategies, including microfinance, have been implemented to tackle this pressing concern. Microfinance is often seen as a poverty alleviating tool, specifically, to smoothen the consumption stream of low income households. Apart from the credit that microfinance provides for the poor, it also gives them access to other financial services such as savings, financial education and insurance among others. Microfinance has enabled the poor to climb up the financial ladder. As such , microfinance has been likewise seen as one of the tools to combat financial exclusion. The World Bank Group considers financial inclusion a key enabler to reduce extreme poverty and boost shared prosperity. DEFINITIONS Microfinance can be defined as provision of both financial and non – financial services to marginalized individuals - services such as deposits, loans, payment services, money transfers and insurance to poor and low – income households. It is an attempt to improve access to small loans for poor individuals who are neglected by formal commercial banks. Financial Inclusion means that individuals and low income groups have access to useful and affordable financial products and services that meet their needs–transactions, payments, savings, credit and insurance delivered in a responsible and sustainable way. The World Bank Group considers financial inclusion a key enabler to reduce extreme poverty and boost shared prosperity. Being able to have access to a transaction account is a first step toward broader financial inclusion since a transaction account allows people to store money, send and receive payments. It serves as a get pass to other financial services. Financial access facilitates day – to – day living, and helps families and businesses plan for long term goals and unexpected emergencies. As account holders, people are more likely to use other financial services such as credit and insurance, digital financial services, to start and expand business, invest in education or health, manage risk and withstand financial shocks, which can improve the overall quality of their lives. Close to one – third of adults’ world population are still unbankable and about half of unbankable people include women households in rural areas. Gender gap in account ownership (in developing countries) hinder women from being able to effectively control their financial lives. Countries which have made commitments to financial inclusion, have either launched or developed a national strategy. Characteristics of Microfinance Microfinance services are aimed at the poor clients, who do not have access to formal financial sources. Microfinance has its unique characteristics which are as follows: Mostly is collateral free MFIs go to clients rather than clients going to MFIs Simplified savings and loan procedures Small size of loans and savings Free use of loans no restrictions on specified purpose) Repayment considers incomes from business as well as other sources. Objectives of Microfinance The organizations working to promote microfinance institutions in different parts of the world determine various objectives to microfinance. The important among them are listed as follows: i) Promote socio – economic development at the grass root level through community – based approach. ii) Develop and strengthen people’s groups called Self – Help Groups and facilitate sustainable development through them. iii)Provide livelihood training to disadvantaged population iv) Promote programs for the disabled v) Empower and mainstream women The essential features of credit for microfinance i) The borrower are low – income groups ii) The loans are for small amounts iii) The loans are without collateral iv)The loans are generally taken for income – generating activities, although loans are also provided for consumption, housing and other purposes v) The tenure of the loan is short vi) The frequency of repayments is greater than for traditional commercial loans Credit Delivery Methods used by Microfinance Institutions MFIs use two basic methods in delivering financial services to their clients These are: i) Group Method ii) Individual Method Group Method: This is one of the most common method for providing micro–finance. Group method primarily involve a group of individuals, which become the basic unit of operation for the MFIs. Since MFIs have to provide collateral free loans, group method help in creating social collateral (peer pressure) that can effectively, substitute physical collateral. Group becomes a basic unit with which MFIs deal. The advantage of group method is that: i) Groups ensure repayments from all individuals in that group and incase of a default. ii) Groups are trained to own joint responsibility for loans that are taken by individuals in the group. iii) Groups function as the forum where the credit discipline and other related issues are discussed. iv) Groups may have to jointly own the responsibility of defaults and pay on behalf of defaulting client. v) Group also help credit appraisal and provide opinion on creditworthiness of each individual in the group. vi) Groups method also help in controlling costs. Having a group helps the MFIs in getting all clients at one spot rather than visiting each individual’s house. Increases the efficiency of staff and controlling costs. Creates a forum where individuals come and discuss, provide opinions and exert social pressure. vii)The clients that the MFIs are dealing with are generally poor and may face genuine problems at times. Rather than taking an aggressive/legal approach with such vulnerable clients, it is always better to have more constructive and collective approach, which is provided by the groups. Individual Method MFIs are also increasingly providing loans to individuals. In individual lending method, MFIs provide loans to an individual based on his/her personal credit worthiness. Individual lending is more prevalent with clients who generally need bigger size loans and have the capacity to produce guarantee and generate enough comfort to the MFI. MFIs generally base their decision on personal knowledge of the client, his/her reputation among peers and society, clients income sources and business position. MFIs also ask for individual guarantors from clients. Individual guarantors come from friends or relatives well known to the borrower and who are ready to take liability of repaying the loan, should the borrower fail to do so. If the loan is significantly larger, the MFIs may also take some collateral security. Microfinance’s contribution to poverty reduction and its challenges Despite the inadequacies of microfinance as a sole tool for poverty reduction, studies have reported significant contributions of MFIs towards poverty reduction. Based on the study by Sulemana et.al. (2023): “Effects of Microfinance and Small loans centre (MASLOC) on poverty reduction in Wa West District in Ghana”, we can identify several contributions and challenges as follows; Contributions 1. Increased consumption Many respondents, indicated that before they benefited from the MASLOC loans, they could not eat a balanced diet daily or provide some other basic necessities such as clothing and paying for healthcare because of lower incomes. Others used the loan to buy food. 2. Acquiring assets Assets acquired after benefiting from the MASLOC loan included land, sheep, goat, cattle, farm tools and house hold chattels. Some of the assets acquired were crucial in poverty reduction because can be sold directly to obtain income to meet their basic needs in times of hardship, while others can be used to generate income for them. Constraints/Challenges 1. Repayment problems It was indicated that, some beneficiaries did not invest the monies they took while others just spent the money to satisfy other requirements such as food, clothing, medical expenditures, household utensils and children’s learning materials, so repayment became a problem. Loans used for consumption and not for productive purpose, does not serve the real purpose of micro– credit. Loan repayment problem default was because of the short period allocated. They claimed, the repayment duration of one month was too short since most of the business could not have started to make a profit. Invested the money in retail business but it was not profitable, could not make adequate revenue to repay the loan because of wrong investment decision. The rural poor have irregularity/volatility in income streams and expenditure patterns, and there is possibility of systemic risks such as crop failures or fall in commodity prices and therefore, may face real difficulties in servicing loans. Banks have genuine concerns while dealing with the rural poor, and tend to identify such loans as risk. Female clients repay their loans more than their male counterparts. 2. Hidden information An official of MASLOC remarked: The beneficiaries do not provide all the information needed by the field officers and programme officers to better judge their situation before approving the loan, thus making loan recovery an issue. Besides this, the beneficiaries' attitudes towards loan repayment are very harmful. Most of them will not even explain why they are not paying back the loans. 3. Staffing related issue Some staff needed to be more competent. There was limited in-service training programmes for staff . These situations make it difficult for them to discharge their responsibilities effectively and efficiently. It might have contributed to their inability to retrieve loans from clients. Political interference in the recruitment process, hijack it and recruit their friends who sometimes lack the necessary competencies for the job. When these people can not discharge their duties, they can not be taken accountable because of the politicians that brought them. 4. Inadequate credit to clients Inability to generate funds. MFIs have inability to raise sufficient fund in microfinance sector which is again an important concerning challenge. 5.Lack of education Financial illiteracy. One of the major challenges towards the growth of the microfinance sector was illiteracy of the people. This makes it difficult in creating awareness of microfinance and even more difficult to serve them as microfinance clients. 6.Interest rates. MFIs are charging very high interest rates, which the poor find difficult to pay. MFIs are private institutions and therefore require being economically sustainable. They do not get any subsidized credit for their lending activities and that is why they need to recover their operational costs from borrowers. 7. Weak regulatory framework. Government has not been able to develop and enforce a legal and regulatory framework conducive to rural finance. Government should strengthen, policies and programmes that create environment for growth and development of strong microfinance institutions. Lack of conducive regulatory framework, makes it even difficult for financiers to provide borrowers with the right incentives for repayment. 8.Language difficulty. Language barrier makes communication with the clients (verbal and written) difficulty. As the education level of clients is low so it is difficult to communicate with them. For this reason, it is also difficult for the MFIs employees to make the clients to understand the policy and related details.