Uploaded by
Syed Mohammad Fariduzzaman Wasim
Trigonometric Functions: Formulas, Identities, Graphs
advertisement

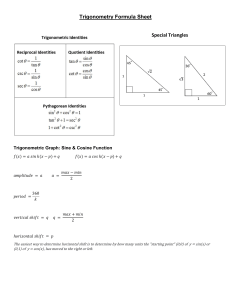
Made by: Wasim Trigonometric Functions Table of Contents • About • Formulas • Identities • Values • Quadrants • Graphs • Domain & Range • Key Terms Trigonometric Functions • Trigonometric functions are the functions of an angle of a triangle. Ergo, the relationship between the angles and sides of a triangle are given by these functions. • The six basic trigonometric functions: • Sine • Cosine • Tangent • Cosecant • Secant • Cotangent Formulas Trigonometric Functions • The basic formulas to find the trigonometric functions are as follows: • sin 𝜃 = 𝑂𝑝𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑒 𝐻𝑦𝑝𝑜𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑢𝑠𝑒 • cos 𝜃 = 𝐴𝑑𝑗𝑎𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝐻𝑦𝑝𝑜𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑢𝑠𝑒 • tan 𝜃 = 𝑂𝑝𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑒 𝐴𝑑𝑗𝑎𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡 • cosec 𝜃 = 𝐻𝑦𝑝𝑜𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑢𝑠𝑒 𝑂𝑝𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑒 • sec 𝜃 = 𝐻𝑦𝑝𝑜𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑢𝑠𝑒 𝐴𝑑𝑗𝑎𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡 • cot 𝜃 = 𝐴𝑑𝑗𝑎𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝑂𝑝𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑒 Identities Trigonometric Functions Reciprocal Identities • cosec θ = • sec θ = • cot θ = 1 sin θ 1 cos θ 1 tan θ Quotient Identities • tan θ = • cot θ sin θ cos θ cos θ = sin θ Pythagorean Identities Sum & Difference Identities • cos 2 x + sin2 x = 1 • 𝑠𝑖𝑛 (𝐴 + 𝐵) = 𝑠𝑖𝑛 𝐴 𝑐𝑜𝑠 𝐵 + 𝑐𝑜𝑠 𝐴 𝑠𝑖𝑛 𝐵 • 1 + tan2 x = sec 2 x • 𝑐𝑜𝑠 (𝐴 + 𝐵) = 𝑐𝑜𝑠 𝐴 𝑐𝑜𝑠 𝐵 − 𝑠𝑖𝑛 𝐴 𝑠𝑖𝑛 𝐵 • cot 2 x + 1 = csc 2 x • 𝑡𝑎𝑛 (𝐴 + 𝐵) = 𝑡𝑎𝑛 𝐴 + 𝑡𝑎𝑛 𝐵 1 − 𝑡𝑎𝑛𝐴𝑡𝑎𝑛𝐵 • 𝑠𝑖𝑛 (𝐴 − 𝐵) = 𝑠𝑖𝑛 𝐴 𝑐𝑜𝑠 𝐵 − 𝑐𝑜𝑠 𝐴 𝑠𝑖𝑛 𝐵 Double-Angle Identities • sin2A = 2sinAcosA • cos2A = cos 2 A − sin2 A • tan2A = 2tanA 1−tan2 A • 𝑐𝑜𝑠 (𝐴 − 𝐵) = 𝑐𝑜𝑠 𝐴 𝑐𝑜𝑠 𝐵 + 𝑠𝑖𝑛 𝐴 𝑠𝑖𝑛 𝐵 • 𝑡𝑎𝑛 (𝐴 − 𝐵) = 𝑡𝑎𝑛 𝐴 − 𝑡𝑎𝑛 𝐵 1 + 𝑡𝑎𝑛𝐴𝑡𝑎𝑛𝐵 Quadrants Graphs Domain & Range Key Terms Trigonometric Functions • 𝑦 = 𝑎𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑏 𝑥 − 𝑐 + 𝑑 • Amplitude – a – the maximum vertical distance the graph of a sinusoidal function varies above and below the horizontal central axis of the curve, or else, the y-axis. • 𝑀𝑎𝑥 −𝑀𝑖𝑛 2 • Period – T – the length of the interval of the domain over which a graph repeats itself, or in other words, the horizontal length of one cycle on a periodic graph. • 360 |𝑏| • Vertical Displacement – d – the vertical translation of the graph of a periodic function. • Phase Shift – c – the horizontal translation of the graph of a periodic function. To conclude The trigonometric functions and identities are the ratio of sides of a rightangled triangle. The sides of a right triangle are the perpendicular side, hypotenuse, and base, which are used to calculate the sine, cosine, tangent, secant, cosecant, and cotangent values using trigonometric formulas. Thank you for paying attention!