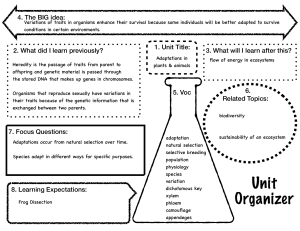
Sophia Nichole C. Bazar BIJI 2 Summary of Natural Selection: Natural selection is a process of evolution and diversification of species. It is a gradual and natural event that has shaped the vast diversity of life on Earth. Charles Darwin played a significant role in developing the concept of natural selection. He embarked on a five-year voyage, collected species, and conducted extensive observations and studies. His findings and knowledge about the mechanism of gradual change in life on Earth are documented in his notebooks. It's important to note that Darwin's idea of natural selection was not solely based on his voyage but also influenced by the theories and observations of other great minds like Thomas Malthus and Jean-Baptiste Lamarck. Natural Selection is driven by the concept of "survival of the fittest," where individuals with advantageous traits are more likely to survive and reproduce, passing those traits on to future generations. One of the key components of natural selection is genetic variation. Within a population, individuals have different genetic traits due to mutations, genetic recombination, and other processes. These variations can lead to differences in physical characteristics, behaviors, and abilities. In a changing environment, certain traits may provide a survival advantage. For example, imagine a population of birds with different beak sizes. If the environment has a limited food supply, birds with larger beaks may be better equipped to crack open tough seeds and survive. Over time, the individuals with larger beaks will have a higher chance of reproducing and passing on their genes for larger beaks to the next generation. This process, known as "natural selection," results in the gradual adaptation of the population to its environment. It's important to note that natural selection does not involve a conscious or intentional decision-making process. Instead, it is a consequence of the interaction between organisms and their environment. Individuals with traits that are well-suited to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce, while those with less advantageous traits are less likely to pass on their genes. Natural selection operates on various levels, from small-scale changes within a population to largescale patterns of speciation and extinction. It is a continuous and ongoing process that has shaped the incredible diversity of life on Earth. There are several lines of evidence that support the concept of natural selection and evolution. Here are some key pieces of evidence: 1. Fossils: The fossil record provides a wealth of evidence for the existence of extinct species and the gradual changes in species over time. Fossil evidence shows the transitional forms between different species, demonstrating the gradual nature of evolutionary changes. 2. Comparative Anatomy: Similarities in the anatomical structures of different species provide evidence for common ancestry. These similarities can be seen in homologous structures, which are structures that have the same origin but may have different functions in different species. 3. Molecular Biology: DNA and genetic analysis reveal similarities and differences between species. By comparing the genetic sequences of different organisms, scientists can determine the degree of relatedness and trace evolutionary relationships. 4. Biogeography: The distribution of species around the world provides evidence for evolution. Similar species are often found in the same geographic regions, indicating a common ancestry and the influence of environmental factors on species diversification. 5. Direct Observation: In some cases, scientists have been able to directly observe natural selection in action. For example, the famous study of Galápagos finches by Peter and Rosemary Grant demonstrated how changes in beak size and shape occurred in response to changes in food availability during a drought.