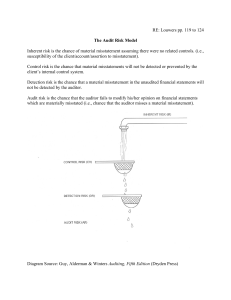
Understanding and assessing internal control Learning objectives i. ii. iii. iv. v. vi. vii. Definition of terms Process for Understanding Internal Control and Assessing Control Risk Understanding Internal Control Documenting of Internal Control Assessment of Control Risk Tests of Controls Test your knowledge 1.0 Definition of terms i. Compliance tests are those designed to provide evidence as to whether the internal control procedures are being operated as planned. …….Definition of terms ii. Substantive tests are those designed to substantiate the validity, accuracy and completeness of amounts appearing in the financial statements and related notes. ……Definition of terms iii. Audit risk means the risk that the auditor gives an inappropriate audit opinion when the financial statements are materially misstated. Audit risks has three components: inherent risk, control risk and detection risk. ….Definition of terms iv. Inherent risk is the susceptibility of an account balance or class of transactions to material misstatement that could be material, assuming that there were no related internal controls. ….Definition of terms v. Control risk: This is the risk that the internal control system may not prevent or detect and correct material misstatements or errors in account balances or class of transactions. ….Definition of terms Detection risk is the risk that an auditors substantive procedures will not detect a material misstatement that exists in an account balance or class of transactions. vi. 2.0 Process for Understanding Internal Control and Assessing Control Risk The four phases performed by the auditor are: Phase 1 Obtain an understanding of internal control: design and operation. Phase 2 Assess control risk …..Process for Understanding Internal Control and Assessing Control Risk Phase 3 Design, perform, evaluate tests of controls. Phase 4 Decide planned detection risk substantive tests. 3.0 Understanding internal control For every audit, irrespective of intended reliance on internal control, an auditor must obtain sufficient understanding of internal control to plan the audit and determine tests to be performed. ……Obtain an Understanding of Internal Control The auditor should obtain an understanding of each of the five components of internal control in order to plan the audit. This knowledge is used to: i. Identify types of potential misstatements ……Obtain an Understanding of Internal Control ii. Pinpoint the factors that affect the risk of material misstatement iii. Design tests of controls substantive procedures and Steps in the auditor’s consideration of internal control structure Steps in the auditor’s consideration of internal control structure (cont.) ………Understanding internal control The auditor obtains an understanding of ICs to assess control risk and: Identify the types of potential misstatements that could occur and the factors that contribute to the risk that they will occur ………Understanding internal control Understand the accounting system sufficiently to identify the client documents, etc., that may be available and ascertain what data will be used in audit tests Determine an efficient and effective approach to the audit. 3.1 Understanding the control environment An auditor gains an understanding of the control environment by: Making inquiries of key management personnel Inspecting documented policies and procedures ........Understanding environment Observing the activities control and operations Considering past experience with the client. 3.2 Understanding the risk assessment process Auditor needs to determine how management identifies business risks, estimates their significance, assesses their likelihood of occurrence, and decides upon actions to manage them. ….Understanding the risk assessment Auditor inquires of management about business risks that management have identified and considers whether they may result in a material misstatement. If auditor identifies a risk of material misstatements that management failed to identify, they need to consider whether management should have identified it and, if so, why the process failed. 3.3 Understanding the information system Auditor is required to obtain sufficient knowledge of the information system to understand: Significant classes of transactions Initiation of transactions Records, documents and accounts ….. Understanding the information Accounting processing Financial reporting processes Controls surrounding journal entries. Being able to follow transaction flows (the audit trail) is an important technique in understanding the information system. 3.4 Understanding the control activities Procedures include: Making inquiries of appropriate client personnel Inspection of documentation Observation of activities, and procedures the entity’s operations …. Understanding the control activities — tracing a few transactions through the accounting system. When the transactions selected are typical of those transactions that pass through the system, this procedure may be treated as part of the tests of control. Walkthrough 3.5 Understanding monitoring of controls Auditor is required to obtain an understanding of how the entity monitors internal control over financial reporting and initiates corrective actions. In many entities, internal auditors contribute to the monitoring of an entity’s activities. ……Understanding monitoring of controls The auditor needs to obtain an understanding of the sources of the information related to the entity’s monitoring activities and the basis upon which management considers the information to be sufficiently reliable. 4.0 Documenting the understanding of internal control Different techniques may be used to document information relating to accounting and internal control systems. Selection of a particular technique is a matter of the auditor’s judgment. Common techniques used alone or in combination are; …Documenting the understanding of internal control Internal control questionnaires. Narrative descriptions — written description of internal control policies and procedures. Flowcharts. 5.0 Assessment of control risk After obtaining an understanding of the five components of internal control, the auditor assesses control risk, at the assertion level, for each material account balance or class of transactions. The auditor must decide whether to assess control risk for a particular assertion as high or as less than high. …. Assessment of control risk The assessment of control risk is the process of evaluating the likely effectiveness of an entity’s accounting and internal control systems in preventing or detecting and correcting material misstatements. ….Assessment of control risk There will always be some control risk because of inherent limitations in any internal control system. 5.1 Assessing control risk at a high level The auditor assesses control risk at a high level for some or all assertions. Here lower level of reliance placed on the internal control and the more assurance the auditor must obtain from substantive tests. ……Assessing control risk at a high level If control risk is high, then There is great risk of material misstatement in the financial statements, implying that; Internal controls are NOT effective Lower level of reliance placed on internal control …….Assessing control risk at a high level Therefore, the auditor would perform more substantive tests to gather evidence. ie. Skip tests of controls and go directly to substantive tests – teats of details on transactions and account balances. 5.2 Assessing control risk at less than high The auditor assesses control risk as less than high, the auditor must obtain sufficient evidence to support that level. In other words,…… …….Assessing control risk at less than high If control risk less than high, then There is low risk of material misstatement in the financial statements, implying that; Internal controls are Effective More reliance placed on internal control …….Assessing control risk at less than high Therefore, the auditor would perform tests of controls ie. If controls are good, they are tested for operating effectiveness. Summary In summary, steps related to risk assessment are: i.Obtain an understanding of the entity and its environment, including internal control ii. Assess the risk of material misstatement iii. Respond to the assessed level of risk by designing further audit procedures based on this assessment …….Assessing control risk at less than high iv. v. vi. Test internal controls to evaluate their operating effectiveness. Perform substantive tests. Evaluate the sufficiency and appropriateness of audit evidence obtained. 4.3 Benefits of Audit Risk Assessment The benefits of audit risk assessment are: (a) It saves audit cost and fees; (b) It ensures that the audit work is completed expeditiously and economically (c) It removes all avoidable pitfalls in the audit procedure; (d) It reduces the possibility of under or over auditing; ……Benefits of Audit Risk Assessment (e) It results in a more effective and efficient audit work; (f) It focuses the auditors attention on factors which are more likely to result in misstatement; and (g) It facilitates the use of sampling and the attendant benefits derived there from. 5.0 Tests of controls Tests of controls are performed to obtain audit evidence about the effectiveness of the: a) Design of the accounting and internal control systems, ie. whether they are suitably designed to prevent or detect and correct misstatements. b) Operation of internal throughout the period. controls ……Tests of controls Tests of controls may include: i. Inspection of documents eg. verifying that a transaction has been authorized. ii. Observation of control related activities ……Tests of controls ii. Inquiries of client personnel iii. Re-performance of internal controls eg. reconciliation of bank accounts to ensure they were correctly performed by the entity. Test your knowledge 1. What is the auditors principal purpose for obtaining understanding of internal control and assessing control risk? a) To comply with generally accepted accounting principles. b) To obtain measure of assurance of Mgt efficiency c) To maintain state of independence in mental attitude during the audit d) To determine the nature, timing, and extent of subsequent audit work. …..Test your knowledge 2. a) b) c) d) The auditor uses assessed control risk to; Evaluate the effectiveness of the entity's internal controls. Identify transactions and account balances where inherent risk is at the maximum. Indicate whether materiality thresholds for planning and evaluation purposes are sufficiently high. Determine the acceptable level of detection risk for financial statement assertions …..Test your knowledge 3. To obtain evidential matter about control risk, the auditor ordinarily selects tests from a variety of techniques including; a) Analysis b) Confirmation c) Re-performance d) Comparison …..Test your knowledge 4. The objective of tests of details of transactions performed as tests of controls is to; a) Detect material misstatement in the account balances of financial statements. b) Evaluate whether internal control structure policy of procedure operated effectively. c) Determine the nature, timing and extent of substantive tests for financial statements assertions. d) Reduce control risk, inherent risk and detection risk to an acceptably low level. …..Test your knowledge 5. Describe four phases performed by the auditor when obtaining an understanding of internal control and 6. What are the benefits of audit risk assessment? 7. Differentiate between compliance tests and substantive tests. END