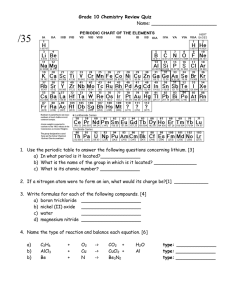
CHEM 1380B Basic Chemistry for Engineers Assignment 3 Due date: 21 April 2022 (The assignments should be submitted on Blackboard by 6:30 pm) Late assignments within 24 hours will have 50% score deduction. Late for more than 24 hours will have no marks. Section A Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following reaction(s) have/has positive ΔS value? (i) C3H8 (g) + 5 O2 (g) → 3CO2 (g) + 4 H2O (g) (ii) 2NO (g) + O2 (g) → 2NO2 (g) (iii) Mg (s) + Cl2 (g) → MgCl2 (s) A. (i) only B. (ii) only C. (iii) only D. (i) and (ii) E. (ii) and (iii) F. All of the above E. (ii) and (iii) F. All of the above 2. Which of the following is/are BrØnsted-Lowry acid? (i) CH3COOH (ii) HNO2 (iii) (CH3)3NH+ A. (i) only B. (ii) only C. (iii) only D. (i) and (ii) 3. Which of the following is the correction description of steel? A. Steel consists of pure iron. B. Steel is an alloy of iron. C. Steel is a mixture of iron and silver. D. Steel is an oxidized iron. 4. CsCl crystallizes in a unit cell that contains the Cs+ ion at the center of a cube that has a Cl- at each corner. How many Cs+ ion(s) and Cl- ion(s) occur in each unit cell respectively? A. 1 Cs+ and 8 ClB. 1 Cs+ and 4 ClC. 1 Cs+ and 2 ClD. 1 Cs+ and 1 Cl5. What is the oxidation number of bromine in the BrO3- ion? A. +1 B. +3 C. +5 D. +7 Section B Short and Long Questions 1. What is the pH of a 0.15M solution of NH3? (Given: Kb of NH3 is 1.8 x 10-5) 2. Compound A is one of the effective liquid crystalline substances employed in liquid crystal displays (LCDs). Its structure is shown below: Compound A (a) Describe three features of this molecule that make it prone to show liquid crystalline behavior. (b) A national explorer wears a smart watch with LCD. He found that the watch did not function well during his trip to North Pole. Explain why the LCD might not function properly at North Pole. 3. Determine Ho for the following reaction: 1 CH 4 ( g ) O2 ( g ) CO ( g ) 2 H 2 ( g ) 2 Given: CH 4 ( g ) 2O2 ( g ) CO2 ( g ) 2 H 2O( g ) H o 802kJ CH 4 ( g ) CO2 ( g ) 2CO ( g ) 2 H 2 ( g ) H o 247 kJ CH 4 ( g ) H 2O( g ) CO ( g ) 3H 2 ( g ) H o 206kJ 4. Consider the following exothermic equilibrium reaction: 2CO ( g ) C ( s ) CO2 ( g ) How will each of the following changes affect an equilibrium mixture? (a) A catalyst is added to the mixture. (b) CO2(g) is added to the system. (c) CO(g) is removed from the system. (d) The reaction mixture is heated. (e) The volume of the reaction vessel is doubled. (f) The total pressure of the system is increased by adding a noble gas. 5. Complete and balance the following equations, and identify the oxidizing and reducing agents. (a) Cr2O72 (aq) I (aq) Cr 3 (aq ) IO3 (aq ) (acidic solution) (b) MnO4 (aq ) Br (aq ) MnO2 ( s) BrO3 (aq ) (basic solution) 6. A certain reaction has Ho = +43.7 kJ and So = +72.4 J/K. (a) (b) (c) (d) Is the reaction exothermic or endothermic? Does the reaction lead to an increase in the randomness of the system? Calculate Go for the reaction at 298 K. At what temperature does this reaction become spontaneous? 7. An electrochemical cell was made up of solid silver metal and liquid mercury electrodes, with electrolyte solutions of 0.075 M AgNO3 and 0.85 M HgCl2 solution, and a salt bridge. (a) Write down the cell diagram. (b) Write down the half equations for oxidation and reduction respectively. [End of Assignment 3]